Potential Difference in Electrical Circuits
Explore the concept of potential difference, also known as voltage, in electrical circuits. Learn about energy transfer, charge, and the role of a voltmeter in measuring potential difference. Practice calculations and circuit diagrams to deepen your understanding.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
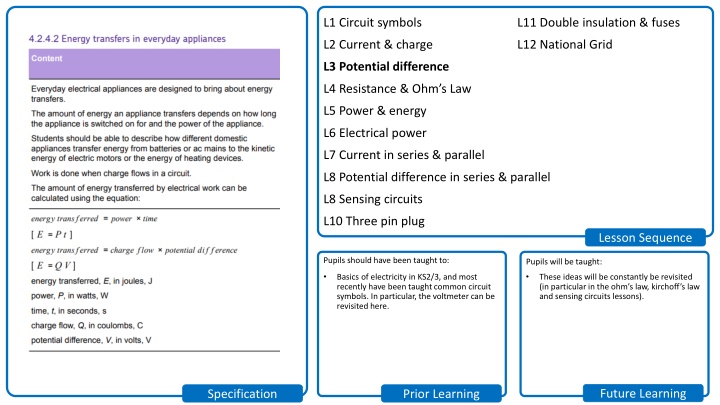
L1 Circuit symbols L11 Double insulation & fuses L2 Current & charge L12 National Grid L3 Potential difference L4 Resistance & Ohm s Law L5 Power & energy L6 Electrical power L7 Current in series & parallel L8 Potential difference in series & parallel L8 Sensing circuits L10 Three pin plug Lesson Sequence Pupils should have been taught to: Pupils will be taught: Basics of electricity in KS2/3, and most recently have been taught common circuit symbols. In particular, the voltmeter can be revisited here. These ideas will be constantly be revisited (in particular in the ohm s law, kirchoff s law and sensing circuits lessons). Future Learning Specification Prior Learning
SciDoc Potential difference Potential difference Last Lesson Last Term Last Year Stretch & Challenge I do We do You do Test I do We do You do Do Now
SciDoc Keywords Learning Objectives Keywords Potential Difference Energy Charge Voltage Voltmeter Recall the definition of potential difference Recall the equation that relates energy transfer, potential difference and charge. Calculate energy transfer, potential difference and charges. I do We do You do Test I do We do You do Do Now
Potential difference (commonly referred to as voltage)is a measure of how much energy is transferred to each coulomb of charge. SciDoc Stretch: A current of 200 mA has been flowing for a time of 5 minutes. How much charge has been transferred? I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
Potential difference has units of Volts (V) and is measured by a voltmeter (in parallel across the component). SciDoc Stretch: A battery is in series with two resistors. Draw a circuit diagram to show how you would measure the potential difference across one of the bulbs. I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
energy transferred = charge voltage E = Q V Where: Energy is measured in Joules (J) Charge is measured in Coulombs (C) Voltage is measured in Volts (V) SciDoc Stretch: Rearrange the equation to give equations for charge and voltage. The unit for voltage is the volt; but what is an alternative unit in terms of joules and coulombs? I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Example question Example question An energy of 20 kJ is transferred is transferred for a charge of 400 C. What is the voltage? I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Worksheet Worksheet Complete the worksheet! I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Basic answers Basic answers 1. How much energy is transferred to each coulomb of charge. 2. A voltmeter which is connected in parallel across the component. 3. E = Q V Units of energy are Joules Units of charge are coulombs Units of potential difference are volts. 4. Joules per coulomb 5. a) 300 J b) 30 J d) 2 J e) 100 J c) 2 J f) 1600 J I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Medium answers Medium answers 6. a) 10 C d) 200 C 7. a) 20 V d) 2,000 V 8. a) 4,000 J 9. a) 460,000 J 10. a) 0.04 C b) 1,000 C e) 666.7 C b) 150 V e) 22.5 V b) 333.3 C b) 2,000 C b) 200,000 V c) 2 C f) 0.25 C c) 1.6 V f) 9 V I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Hard answers Hard answers 11. 2,000 C 12. 4,600,000 J 13. a) 2.4 C b) 21.6 J 14. 3,312,000 J 15. 4,500 J I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Struggle time! Struggle time! Exam question so exam conditions! You have 8 minutes. I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do You do Test I do We do You do LO: