Power Control and EVM Trade-off in Wireless Communication
Explore the trade-off between maximizing transmission power and maintaining signal quality in wireless communication, particularly in OFDM WiFi environments. Learn about the impact of Error Vector Magnitude (EVM), pathloss estimation, and the role of feedback mechanisms like Null Data Packets (NDP) in optimizing Tx power and EVM levels.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
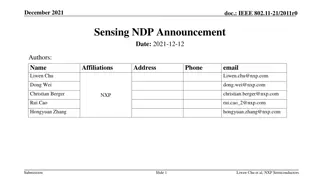
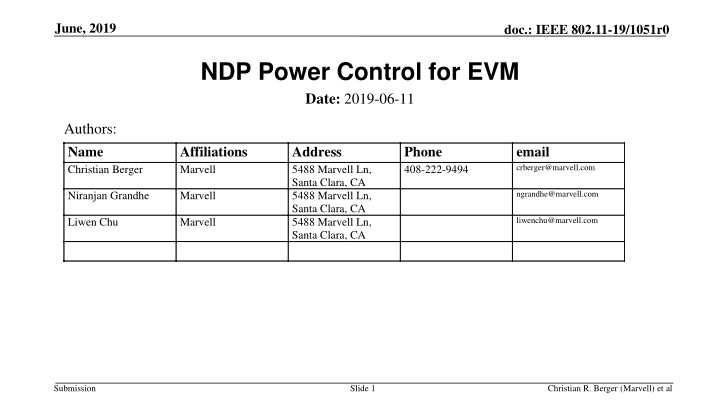
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 NDP Power Control for EVM Date: 2019-06-11 Authors: Name Christian Berger Affiliations Marvell Address 5488 Marvell Ln, Santa Clara, CA 5488 Marvell Ln, Santa Clara, CA 5488 Marvell Ln, Santa Clara, CA Phone 408-222-9494 email crberger@marvell.com ngrandhe@marvell.com Niranjan Grandhe Marvell liwenchu@marvell.com Liwen Chu Marvell Submission Slide 1 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Need for Power Control Trade-off between Tx power and Tx EVM In any wireless communication Especially OFDM in WiFi, has large peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) Needs power amplifier to back off more (so peaks avoid non-linear region) Maximizing Tx power usually reduces signal quality Typically sacrifice back-off Power amplifier will go (more often) into non-linear region Tx signal distortion is measured as Error Vector Magnitude (EVM) Typical range -10 to -30 dB WiFi s 11ax has increased EVM range (1024 QAM, MU-MIMO, etc) Submission Slide 2 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Typical Approach Based on ACK Most WiFi Packets are acknowledged If no ACK is received, packet was most likely lost Typically due to insufficient SINR at receiver to decode packet Required SINR to decode a packet depends on the Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) used Definition of receiver sensitivity maps required SINR for each MCS Given required SINR Maximize Tx power Keeping EVM below required SINR (reduces SINR by at most 3 dB) If packet is lost, drop MCS (assumes SINR is fixed) and adjust Tx power Submission Slide 3 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 EVM on Channel Sounding Packets Channel Sounding In WiFi uses Null Data Packets (NDP) No data in packet, no frame check sequence (FCS) There is no correct reception of NDP SNR will gradually change quality of channel estimates (no cut-off) To set Tx power and EVM correctly, transmitter needs to know the pathloss or get some other feedback (to replace the ACK) Estimate pathloss Receiver can measure RSSI, but needs to know Tx power Submission Slide 4 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Effect of EVM on SINR Effective Signal-to-Interference+Noise Ratio (SINR) Received power (Tx power minus path loss ?PL) EVM is part of the interference (?EVM) Other interference and receiver thermal noise ?Tx?PL SNR = ?0+?EVM?PL?Tx For example at ?Tx= 0 dBm ?PL= 60 dB ?0= 90 dBm ?EVM= 20 dB SNR = 19.6 dB (dominated by Tx EVM) Submission Slide 5 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Optimize EVM in Non-TB Ranging Each STA transmits one data packet and one NDP Best to measure RSSI of NDP packets Pathloss is symmetric (assume tx/rx antenna gain symmetric) Data packets could either include RSSI (of some previous NDP) Tx power level of NDP Measurement Sounding part Measurement Reporting part NDP-A UL NDP Initiator SIFS SIFS SIFS DL NDP LMR Responder Submission Slide 6 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Proposal Add Tx power in NDP-A Reuse format of trigger frame AP Tx Power subfield is 6 bit, mapping values of 0:60 to - 20:40 dBm; would have to add an extra STA Info 32 bit, similar to SAC B0 B10 B11 B16 B27 B28 B31 B17 B26 AP Tx Power RSVD AID11 Disambiguation RSVD RSVD Bits: 11 6 1 4 10 Alternatively only use 4 MSB of AP Tx Power subfield, mapping 0:4:60 to -20:4:40 dBm, can fit into 4 reserved bits in STA Info SAC , which would then be always present B0 B10 B11 B26 B27 B28 B31 AP Tx Power (4) RSVD AID11 SAC Disambiguation Bits: 11 16 1 4 Submission Slide 7 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Proposal (cont.) Add RSSI in LMR 7 bits (0:127) Map to 0:-1:-127 dBm RSSI Public Action Dialog Token ToD Error ToA Error Category ToD ToA RSSI Octets: 1 1 1 6 6 1 1 1 Secure LTF Parameter (optional) AoA CFO Alternatives Add Tx Power Add pathloss (Tx Power RSSI) Feedback (optional) Parameter Octets: 2 13 9 Submission Slide 8 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 How to Set EVM at Tx Side Tx side can control EVM Maps Tx Power to EVM Some dependence on modulation used How to optimize SINR? Tx side does not know receiver noise figure Related to receiver sensitivity Options Receiver shares N0 in negotiation Submission Slide 9 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Strawpoll I Do you support to add subfields in Ranging NPD-A and LMR to facilitate tx- power and EVM optimization in Non-TB Ranging? Yes: No: Abstain: Submission Slide 10 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Strawpoll II Do you support to add the AP Tx Power subfield in the Ranging NPD-A as presented in Option Option I (6 bits) Option II (4 MSBs) B0 B10 B11 B16 B27 B28 B31 B17 B26 B0 B10 B11 B26 B27 B28 B31 AP Tx Power AP Tx Power (4) RSVD AID11 Disambiguation RSVD RSVD RSVD AID11 SAC Disambiguation Bits: 11 6 1 4 10 Bits: 11 16 1 4 Option III (Appendix) I: II : III: Abstain: Submission Slide 11 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Strawpoll III Do you support to add the following field in the LMR frame from non-TB Ranging Option I: AP Tx Power Option II: RSSI Option III: Pathloss I: II : III: Abstain: Submission Slide 12 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al
June, 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1051r0 Appendix Alternatively place Tx Power on top of Offset Only used in TB Ranging STA Info Field B0 B10 B11 B16 B17 B19 B20 B22 B23 B25 B26 B27 B28 B30 B31 AID11/ RID11 Tx Power / Offset Disambiguati on DL N_STS DL Rep UL N_STS Reserved UL Rep Reserved Bits: 11 6 3 3 3 1 1 3 1 Submission Slide 13 Christian R. Berger (Marvell) et al