Precision Estimation Technique Using Randomly Dropped Sticks
Create a series of parallel lines on a surface and randomly drop sticks, estimating precision based on the number of crossings. Explore the effects of dropping area, error sources, and the importance of angle. Improve accuracy by refining dropping techniques. Evaluate a method's pros and cons through charts and testing efforts.
Uploaded on Sep 15, 2024 | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
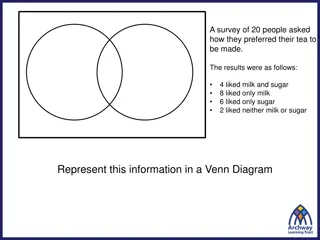
Problem no. 1 ROSE SADEGHI IRAN A TEAM
Draw a series of parallel equally spaced lines on a horizontal surface. Pick a bunch of sticks (e.g.matches or needles) slightly shorter or longer than the separation between the lines, and randomly drop them on the surface. It is claimed that the number of times the sticks cross the lines allows estimating the constant to a high precision. What accuracy can you achieve?
What is the effects of the area that we drop the needles on it on our experiments? What should we do to make the accurate of? higher?
How did you drop the needles ? How did you get errors ? Was your distance between lines the same ? (slide 8) why Angle is effective ? Why it is not in your formula ? Is it happened two needle fall on each other? Is it happened one needle cut two line? Did you measure the height of throw needles?
Cons Her method was not correct It was better for her to drop the sticks with each other She did not explain her formula
Pros She had chart She tried her test a lot