Preemption for Low Latency Applications in IEEE 802.11 Networks
Explore the challenges of enabling low latency applications in heavily loaded IEEE 802.11 networks while minimizing the performance impact on high throughput traffic. This document reviews solutions to reduce latency by addressing conflicting needs and optimizing transmission opportunities for different traffic types.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
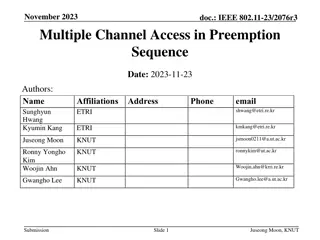
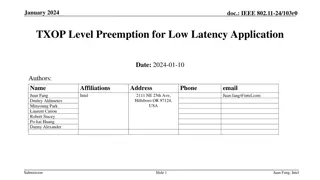
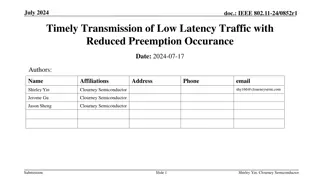
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 Preemption for Low Latency Application Date: 2023-03-13 Authors: Name Juan Fang Dmitry Akhmetov Minyoung Park Laurent Cariou Robert Stacey Affiliations Address Phone email Juan.fang@intel.com 2111 NE 25th Ave, Hillsboro OR 97124, USA Intel Submission Slide 1 Juan Fang, et.al., Intel
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 Introduction Objectives of UHR SG [1]: Improve reliability of WLAN connectivity Reduce latency Increase manageability Increase throughput including at different SNR levels Reduce device level powerconsumption This contribution reviews one of the main challenges to reduce latency and discusses one general solution Submission Slide 2 Juan Fang, et.al., Intel
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 Problem statement How to enable low latency (LL) applications in 802.11 networks that are heavily loaded with other clients high throughput transmissions; while at the same time minimize the performance impact to the high throughput traffic? In other words, how to reconcile the contradicting need: to allow long and efficient TXOPs for high throughput traffic to restrict TXOP limit for latency reduction Submission Slide 3 Juan Fang, et.al., Intel
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 Two main cases with large delay due to large PPDU transmission in TXOP Case A: LL transmitter is the TXOP holder [2-3] Case B: LL transmitter is not the TXOP holder [4]: DL TXOP UL LL data; UL TXOP DL LL data UL TXOP UL LL data Juan Fang, et.al., Intel Submission Slide 4
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 General solution for case A and case B (Event-based or periodic LL traffic with jitters) Divide the large PPDU into small PPDUs with maximum length limitation and xIFS ( ) gaps to provide preemption opportunity for the LL transmitter Case A: TXOP holder can insert DL LL packet within the TXOP Case B: LL transmitter can preempt the on-going transmissions in a TXOP during a xIFS time Further considerations: xIFS length; collisions and hidden node problem between multiple LL STAs Case B: LL transmitter is not the TXOP holder Case A: LL transmitter is the TXOP holder Submission Slide 5 Juan Fang, et.al., Intel
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 Simulation results Traffic information: 4 DL/UL non-LL streams to/from 4 STAs Full buffer traffic Priority : AC_BE LL stream 160 bytes every 12ms to/from 1 LL STA Priority : AC_VO Comparison: Legacy (TXOP=6ms): LL transmitter has to wait until the end of an ongoing TXOP in any direction to do EDCA Proposed solution (TXOP=6ms): Maximum PPDU length = 1ms In the DL, AP can insert the DL LL PPDU within DL TXOP LL transmitter can use xIFS gaps between PPDUs to preempt the next PPDU transmission Aggregated TPT(Mbps) Throughput degradation Legacy 1215 Proposed 1101 -9% The proposed solution can improve the latency performance with low throughput degradation to non-LL traffic while the LL traffic is not frequently generated Submission Slide 6 Juan Fang, et.al., Intel
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 Summary It is challenging to support low latency applications in 802.11 while maintaining good performance for high throughput traffic. In other words, how to reconcile the contradicting need: to allow long and efficient TXOPs for high throughput traffic to restrict TXOP limit for latency reduction We propose a preemption technique to support low latency while there is a long TXOP transmission Submission Slide 7 Juan Fang, et.al., Intel
March 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/0092r0 References [1] 11-22/0708r3, Beyond be Proposed Next Step , Rolf de Vegt [2] 11-22/1393r0, uhr-latency-reduction-scheme-for-uhr [3] 11-22/1880r1, Latency and Reliability enhancements for UHR [4] 11-23/0018r1, uhr-low-latency-support-in-uhr Submission Slide 8 Juan Fang, et.al., Intel