Preventing Pressure Injuries in Sitting Positions
Learn about the risk of pressure injuries in sitting positions and guidelines for preventing them, including proper cushion selection, repositioning techniques, and sitting limitations. Find out how to maintain proper alignment and support to reduce the risk of sacral or ischial pressure injuries.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
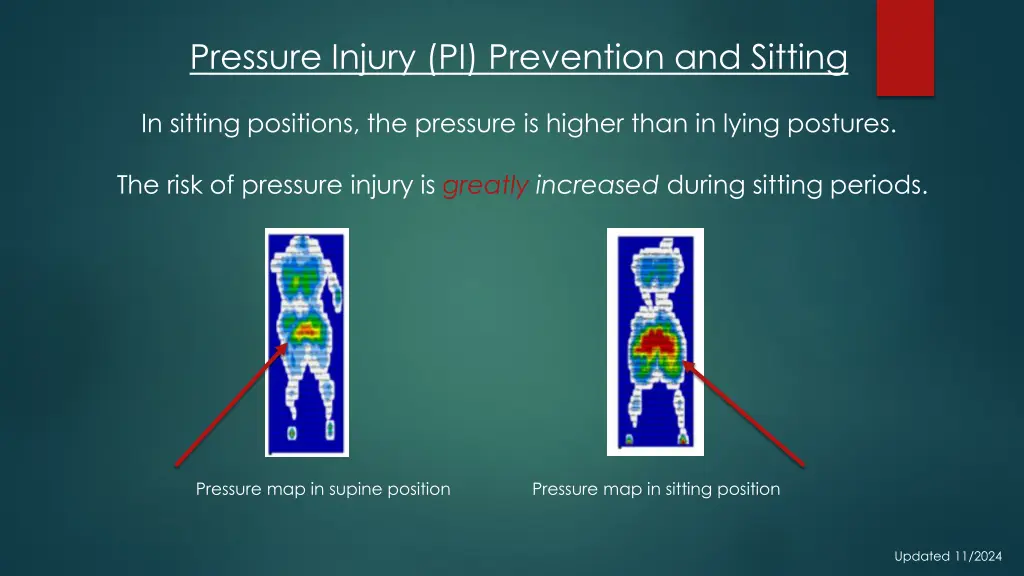
Pressure Injury (PI) Prevention and Sitting In sitting positions, the pressure is higher than in lying postures. The risk of pressure injury is greatly increased during sitting periods. Pressure map in supine position Pressure map in sitting position Updated 11/2024
All patients with chair orders AND Have a sacral or ischial pressure injury OR Are at risk for a pressure injury GENERAL GUIDELINES: Apply Mepilex foam Use chair air cushion under patient. Do not use donuts. Maintain proper alignment; recline with legs elevated if possible or ensure feet are well supported on the floor. Assess skin after each period of sitting to evaluate. For a patient with an ischial pressure injury, avoid seating in a fully erect posture in chair. REPOSITIONING: If patient is unable to reposition themself or can reposition but won t because of pain, dementia, etc: assist with repositioning at least q1h. If patient is able to reposition themselves: encourage q15 minute pressure shifts. CONSIDER SITTING LIMITATIONS: 2 hours for at risk patient 1hour TID for patient with ischial or sacral pressure injury. Sitting time can be increased or decreased based on improvement or deterioration of the pressure injury.
YES NO If chair does not recline, sit patient upright with feet on the ground. Maintain proper position and alignment in chair. Slouched or slid-down postures create significant increases in pressure. YES NO If chair reclines, lean patient back and elevate legs on a rest. Preferred chair position if patient has an ischial pi. Do not sit patient upright with feet elevated
Chair Cushion Selection Criteria Medline Standard Cushion EHOB Extra Large Waffle Chair Cushion For patients 250 pounds or less For patients between 250-700 pounds PMM 1782 PMM 89576