Primary and Secondary Storage in Computer Systems
Explore the different types of primary and secondary storage in computer systems, including Registers, RAM, Cache Memory, ROM, Flash Memory, Magnetic Tape, Magnetic Disks, Hard Disks, Optical Storage Devices, Memory Cards, and more. Learn about the features, functions, and significance of each storage medium in computing.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
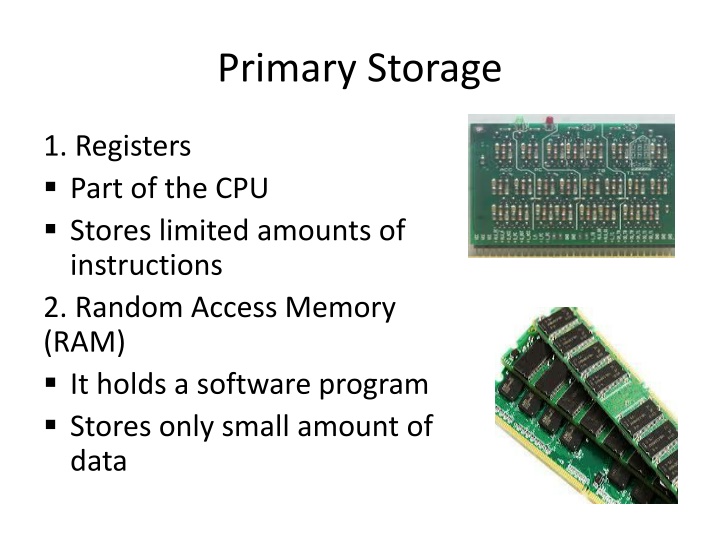
Primary Storage 1. Registers Part of the CPU Stores limited amounts of instructions 2. Random Access Memory (RAM) It holds a software program Stores only small amount of data
3.Cache Memory Temporarily store blocks of data used more often 4. Read-Only Memory (ROM) Critical instructions are safeguarded Storage is non-volatile Retains the instructions when the power is off Flash Memory Rewritable read only memory that is compact, portable and need less power.
Secondary Storage Features It is Non-volatile Takes more time to retrieve data Cheaper than primary storage Take place on variety of media
Various forms of Secondary storages 1. Magnetic Tape Stored on a large open reel or cartridge or cassette. Access the data sequentially. 2. Magnetic Disks Storage on a magnetized disk divided into tracks Sectors that provide addresses for various pieces of data Also called Hard Disks
3. Hard Disks Stores data on platters divided into concentric tracks. Follow direct access mechanism to read data. 4. Magnetic Diskettes Easily portable Stored on Flexible Mylar disks Also called Floppy Disks
5. Optical Storage Devices Laser reads the surface of a reflective plastic platter 6. Compact Disk, Read-only Memory(CD-ROM) Only read and not written on 7. Digital Versatile Disk(DVD) Store digital video or computer data
8. Fluorescent Multilayer Disk(FMD- ROM) Storage capacity is much greater than DVDs 9. Memory Cards Installed in an adapter or in many personal computers. 10. Expandable Storage Devices Removable Disk cartridges used as backup storage for internal hard drives of PCs
11. Enterprise Storage System Includes two or more storage devices 12. Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID) It is an enterprise storage system that links groups of standard hard drives to a specialized microcontroller that coordinates the drives so they appear as a single local drive
13. Storage Area Network(SAN) An enterprise storage system architecture for building special, dedicated networks that allow rapid and reliable access to storage devices by multiple servers 14. Storage over IP Transport stored data between devices within a SAN Also called IP over Small Computer System Interface(SCSI) or Internet Small Computer Systems Interface (ISCSI)






















