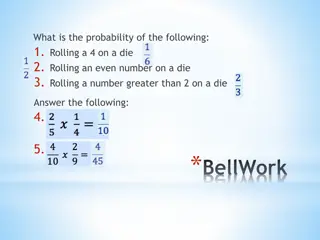Probability
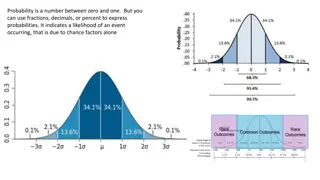
Probability is a measure of the likelihood of an event occurring, with outcomes and events playing key roles. Learn about probability rules, outcomes, events, favorable outcomes, complements, sample spaces, and examples like coin tosses and dice throws. Understand theoretical and experimental probability, sample spaces, and how to calculate probabilities in different scenarios.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Probability VOCAB!
What is probability? The probability of an event is a measure of the likelihood that the event will occur. When all outcomes are equally likely, the probability is found as follows: Number of favorable outcomes Probability of an event = Number of possible outcomes Probability RULE: The SUM of the probability of something happening and its complement (not happening) is always 1. P= P= 0 P= Unlikely P= Likely P= 1 Certain Likely to occur half of the time Impossible
What is an outcome? A possible result of an experiment. What happens. What is an event? A collection of outcomes. What are favorable outcomes? Once you specify an event, the outcomes for that event are called, favorable outcomes. What I want to have happen- the result I prefer. What are total possible different outcomes? The sum of all the different possible things that could happen. What is a complement? How likely it is that what I want will not happen.
There are two types of Probability! Theoretical Probability Experimental Probability The number of possible favorable outcomes compared to the total possible outcomes; Represented as a fraction, decimal or percent. The number of favorable outcomes compared to the number of total outcomes from multiple events.
Sample Space all the possible outcomes of an experiment Example: choosing a card from a deck There are 52 cards in a deck (not including Jokers) So the Sample Space is all 52 possible cards: {Ace of Hearts, 2 of Hearts, etc... }
Tossing a Coin When a coin is tossed, there are two possible outcomes: heads (H) or tails (T) We say that the probability of the coin landing H is . And the probability of the coin landing T is . Mathisfun.com
Throwing Dice When a single die is thrown, there are six possible outcomes: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. The probability of any one of them is 1/6. Mathisfun.com
Example: the chances of rolling a "4" with a die Number of ways it can happen: 1 (there is only 1 face with a "4" on it) Total number of outcomes: 6 (there are 6 faces altogether) 1 So the probability = 6 Mathisfun.com
Example: there are 5 marbles in a bag: 4 are blue, and 1 is red. What is the probability that a blue marble will be picked? Number of ways it can happen: 4 (there are 4 blues) Total number of outcomes: 5 (there are 5 marbles in total) So the probability = 4/5 which is equal to 0.8
STAAR Question #30 Mitsu will be randomly assigned to a seat on an airplane. There are a total of 50 seats on the plane. Of these seats, 16 are aisle seats, and the rest are window seats. What decimal represents the probability that Mitsu will be assigned to a window seat?
Example A die is thrown once. What is the probability that the score is a factor of 6?