Proposed New Method for Displaying Quality Information by International Hydrographic Organization
A proposal for a new method to display quality information presented by the International Hydrographic Organization during the Data Quality Working Group Meeting 14 in Monaco. The proposal includes end-user requirements for mariners planning routes near navigational objects or dangers, development constraints of Conditional Symbology Procedure, and the importance of Under Keel Clearance for vessel navigation safety.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
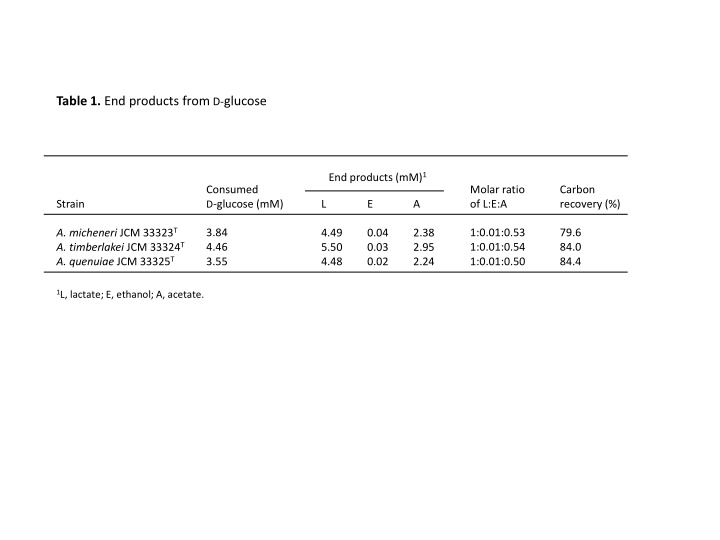
Table 1. End products from D-glucose End products (mM)1 Consumed D-glucose (mM) Molar ratio of L:E:A Carbon recovery (%) Strain L E A A. micheneri JCM 33323T A. timberlakei JCM 33324T A. quenuiae JCM 33325T 3.84 4.46 3.55 1:0.01:0.53 1:0.01:0.54 1:0.01:0.50 79.6 84.0 84.4 4.49 5.50 4.48 0.04 0.03 0.02 2.38 2.95 2.24 1L, lactate; E, ethanol; A, acetate.
Table 2. Species possessing small genomes (<1.69 Mbp) included in the present study ID /Accession No. Genome size (Mbp) No. of CDSs No. of genes in class G Mode of D-glucose fermentation3 Species Amylolactobacillus amylophilus DSM 20533T Amylolactobacillus amylotrophicus DSM 20534T Apilactobacillus apinorum Fhon13T Apilactobacillus kunkeei YH-15T Apilactobacillus micheneri Hlig3T Apilactobacillus ozensis DSM 23829T Apilactobacillus quenuiae HV_6T Apilactobacillus timberlakei HV_12T Dellaglioa algidus DSM 15638T Fructilactobacillus florum DSM 22689T Fructilactobacillus fructivorans DSM 20203T Fructilactobacillus lindneri JCM 11027T Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis TMW 1.1304 Fructobacillus durionis DSM 19113T Fructobacillus ficulneus JCM12225T Fructobacillus fructosus NRIC 1058T Fructobacillus pseudoficulneus DSM15468T Fructobacillus tropaeoli F214-1T Holzapfelia floricola DSM23037T Lactobacillus acetotolerans DSM20749T Lactobacillus amylolyticus DSM11664T Lactobacillus iners DSM13335T Lactobacillus jensenii DSM20557T Lactobacillus psittaci DSM15354T Lentilactobacillus senioris DSM24302 Leuconostoc fallax KCTC3537T Ligilactobacillus aviarius ssp. araffinosus DSM 20653T Ligilactobacillus aviarius ssp. aviarius DSM 20655T Ligilactobacillus hayakitensis DSM 18933T Limosilactobacillus equigenerosi DSM 18793T Limosilactobacillus gorillae KZ01T Limosilactobacillus pontis DSM 8475T Limosilactobacillus secaliphilus DSM 17896T GCA_001436185.11 ERR3874861 GCA_001281175.11 GCA_001281265.11 NZ_POSO000000002 ERR4334791 NZ_POSN000000002 NZ_POST000000002 GCA_001434695.11 GCA_001436645.11 SRR11511901 GCA_001311115.11 GCA_000225325.11 GCA_900112405.12 GCA_001047075.22 GCA_001047095.22 GCA_001047115.22 GCA_001047135.22 GCA_001436605.11 ERR3875271 GCA_000178475.11 GCA_000160875.11 SRR11511621 GCA_000425905.11 GCA_001436555.11 AEIZ010000002 GCA_001435375.11 ERR3875301 ERR3874611 SRR11511381 GCA_001293735.11 SRR11512521 GCA_001437055.11 1.55 1.60 1.46 1.58 1.46 1.48 1.58 1.54 1.59 1.35 1.37 1.44 1.38 1.33 1.55 1.49 1.41 1.69 1.29 1.57 1.54 1.28 1.62 1.54 1.57 1.64 1.48 1.67 1.64 1.60 1.64 1.66 1.65 1,561 1,602 1,315 1,353 1,485 1,439 1,553 1,570 1,531 1,302 1,336 1,632 1,402 1,221 1,397 1,437 1,312 1,572 1,252 1,518 1,567 1,191 1,478 1,340 1,568 1,882 1,414 1,585 1,543 1,545 1,568 1,614 1,503 96 89 65 71 54 62 53 55 99 61 73 81 72 61 69 61 63 74 46 150 108 100 152 111 75 107 84 102 79 89 85 107 156 Homo Homo Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Homo Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero Homo Homo Homo Homo Homo Hetero Hetero Homo Homo Homo Hetero Hetero Hetero Hetero FLAB are written in bold. 1Data from DAGA 2Data from NCBI Database 3Mode of D- glucose fermentation (Homo; homofermentative, Hetero; heterofermentative) CDS
Table 3. Gene content profiles obtained for Apilactobacillus spp. and Fructobacillus spp. A. micheneri Hilg3T A. quenuiae HV_6T A. timberlakei HV_12T A. apinorum Fhon13T A. kunkeei YH-15T A. ozensis DSM 23829T Fructobacillus spp. (n =5)3 401 26 78 63 54 36 37 175 83 88 73 (2.7)2 (1.8) (5.3) (4.2) (3.6) (2.4) (2.5) (11.8) (5.6) (5.9) (4.9) (0.3) (3.8) (3.0) (0.5) (5.8) (6.3) (1.9) (0.9) (1.4) (1.2) [C] Energy production and conversion [D] Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning [E] Amino acid transport and metabolism [F] Nucleotide transport and metabolism [G] Carbohydrate transport and metabolism [H] Coenzyme transport and metabolism [I] Lipid transport and metabolism [J] Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis [K] Transcription [L] Replication, recombination and repair [M] Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis [N] Cell motility [O] Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones [P] Inorganic ion transport and metabolism [Q] Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism [R] General function prediction only [S] Function unknown [T] Signal transduction mechanisms [U] Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport [V] Defense mechanisms [X] Mobilome: prophages, transposons 41 25 88 63 53 39 39 169 93 89 82 (2.6) (1.6) (5.7) (4.1) (3.4) (2.5) (2.5) (10.9) (6.0) (5.7) (5.3) (0.5) (3.1) (2.5) (1.0) (5.8) (6.5) (1.7) (1.2) (1.9) (0.9) 38 26 84 63 55 38 37 172 84 94 87 (2.4) (1.7) (5.4) (4.0) (3.5) (2.4) (2.4) (11.0) (5.4) (6.0) (5.5) (0.4) (3.3) (2.7) (0.6) (5.2) (6.4) (1.9) (1.0) (2.1) (1.3) 33 35 93 73 65 43 44 183 81 81 77 11 46 47 (2.5) (2.7) (7.1) (5.6) (4.9) (3.3) (3.3) (13.9) (6.2) (6.2) (5.9) (0.8) (3.5) (3.6) (0.6) (5.6) (6.9) (2.4) (0.9) (2.0) (0.9) 37 33 113 72 71 45 46 186 88 91 88 15 60 46 11 83 103 33 13 26 13 (2.7) (2.4) (8.4) (5.3) (5.2) (3.3) (3.4) (13.7) (6.5) (6.7) (6.5) (1.1) (4.4) (3.4) (0.8) (6.1) (7.6) (2.4) (1.0) (1.9) (1.0) 42 33 109 75 62 40 44 184 96 91 77 15 55 52 (2.9) (2.3) (7.6) (5.2) (4.3) (2.8) (3.1) (12.8) (6.7) (6.3) (5.4) (1.0) (3.8) (3.6) (0.6) (6.3) (6.8) (2.6) (0.8) (2.1) (2.0) 31 31 109 60 56 43 35 173 79 87 70 (2.2) (2.2) (7.8) (4.3) (4.1) (3.1) (2.5) (12.6) (5.7) (6.3) (5.1) (0.3) (2.9) (3.4) (0.7) (5.1) (7.1) (1.7) (1.0) (2.2) (1.3) 4 7 6 4 56 44 8 86 94 28 14 21 18 48 39 15 90 101 27 18 29 14 52 43 10 82 101 30 16 33 20 41 47 9 71 98 24 14 30 19 8 9 74 91 32 12 26 12 90 98 37 12 30 29 1Number of genes in each COG class 2Ratio of genes against the total number of genes in all COGs 3The values for Fructobacillus spp. indicate means (standard deviation) of the number of genes used for the pathways in all five species.
Table 4. Number of genes in each metabolic pathway found in Apilactobacillus spp. and Fructobacillus spp. pathway ID1 A. micheneri Hlig3T A. quenuiae HV_6T A. timberlakei HV_12T A. apinorum Fhon13T1 A. kunkeei YH-15T1 A. ozensis DSM 23839T Fructobacillus spp.(n = 5)1,2 Pathway definition 00020 00130 00190 02010 02060 2 3 12 30 1 2 3 14 30 1 2 2 14 29 1 1 2 10 30 0 2 1 11 26 0 1 1 11 31 0 0 (0) 1.0 (0) 9.2 (0.4) 33.8 (3.1) 0.4 (0.5) Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) Ubiquinone and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis Oxidative phosphorylation ABC transporters Phosphotransferase system (PTS) 1Data for A. apinorum, A. kunkeei, and Fructobacillus spp. were obtain from elsewhere (12). 2The values for Fructobacillus spp. indicate means (standard deviation) of the number of genes used for the pathways in all five species.
Table 5. Specific and missing genes found in FLAB Conservation (%) KEGG orthology Enzyme commission numbers FLAB (n=10) Other Lactobacillaceae species (n=164) Proteins (gene) Class K06872 - 90.0 15.3 Uncharacterized protein - Specific genes (81.8)2 (16.0)2 (diamine N-acetyltransferase (speG))1 K00657 EC 2.3.1.57 Amino acid metabolism K00691 K00849 K00965 K01443 K01534 K01785 K01838 K02564 K02794 K02795 K02796 K03799 K05808 K05847 K06958 K10254 EC 2.4.1.8 EC 2.7.1.6 EC 2.7.7.12 EC 3.5.1.25 EC 3.6.3.3, 3.6.3.5 EC 5.1.3.3 EC 5.4.2.6 EC 3.5.99.6 EC 2.7.1.69 - - EC 3.4.34.- - - - - 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 10.0 81.1 82.9 83.5 87.8 81.7 82.3 85.4 84.1 90.9 89.6 89.6 82.3 82.3 81.1 95.1 80.0 maltose phosphorylase (mapA) galactokinase (galK) UDP glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (galT) N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate deacetylase (nagA) Cd2+/Zn2+-exporting ATPase (zntA) aldose 1-epimerase (galM) -phosphoglucomutase (pgmB) glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase (nagB) PTS system, mannose-specific IIB component (manX) PTS system, mannose-specific IIC component (manY) PTS system, mannose-specific IID component (manZ) heat shock protein HtpX (htpX) putative sigma-54 modulation protein (yhbH) osmoprotectant transport system ATP-binding protein (opuA) UPF0042 nucleotide-binding protein Myosin cross-reactive antigen (mycA) Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism - Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism - - Membrane transport - - Missing genes (18.2)2 (9.1)2 (0.0)2 (0.0)2 (81.6)2 (80.4)2 (80.4)2 (80.4)2 (succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (NADP+) (gabD))1 (mannose-6-phosphate isomerase (manA))1 (monovalent cation:H+ antiporter-2, CPA2 family (TC.KEF))1 (GntR family transcriptional regulator (ytrA))1 K00135 K01809 K03455 K07979 EC 1.2.1.16 EC 5.3.1.8 - - Amino acid metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism - - Specific genes and missing genes in FLAB were defined as genes conserved in greater than 80% of FLAB species and less than 20% of other species in Lactobacillaceae, and genes conserved in less than 20% of FLAB species and greater than 80% of other species in Lactobacillaceae, respectively. 1Protein names shown in parenthesis were further added as specific or missing proteins in Fructobacillus-Apilactobacillus group (n=11) to the single specific and 16 missing genes found in FLAB, when A. ozensis was included in this group. 2Conservation ratio was calculated for Fructobacillus-Apilactobacillus group and other Lactobacillaceae species, when A. ozensis was included in the former group.
Table 6. Enzyme activities of Adh, Aldh, and NADH oxidase NADH oxidase Strain Adh Aldh 2915 1270 720 A. micheneri JCM 33323T A. timberlakei JCM 33324T A. quenuiae JCM 33325T 0 0 0 >1 0 118 (mU/mg protein)