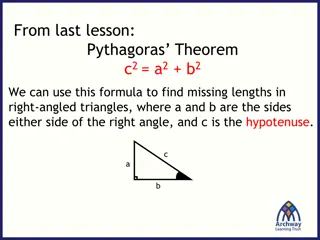
Proving Right-Angled Triangles with Pythagoras' Theorem
In a geometrical problem involving intersecting lines on the x-axis, we demonstrate the formation of right-angled triangles by applying Pythagoras' theorem. Through visual aids and mathematical explanations, the concept of right angles within triangles is illustrated with clarity and precision.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Crossed Lines Don Steward
Crossed Lines Two lines: 2? + 4 = ? and ? + 2? = 8 meet on the x-axis. Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled.
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 2? = 4 2? + 2 = ? ? + 2? = 6 2? + 3 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 2? = 10 ? + 2? = 8 2? + 4 = ? 2? + 5 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 3? = 6 3? + 2 = ? ? + 3? = 9 3? + 3 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 3? = 12 ? + 3? = 15 3? + 4 = ? 3? + 5 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 4? = 12 ? + 4? = 8 4? + 2 = ? 4? + 3 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 4? = 16 ? + 4? = 20 4? + 4 = ? 4? + 5 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 5? = 10 ? + 5? = 15 5? + 2 = ? 5? + 3 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and
Crossed Lines Crossed Lines Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that Show, by using Pythagoras' theorem, that the triangle formed by the lines and the the triangle formed by the lines and the ? ???? is right-angled. ? ???? is right-angled. ? + 5? = 20 ? + 5? = 25 5? + 4 = ? 5? + 5 = ? meet on the x-axis. meet on the x-axis. Two lines: Two lines: SIC_25 SIC_25 and and