Public Finance and Agricultural Finance
Explore the roles of government in the economy through public finance and delve into the study of financing services in agriculture. Discover the importance and impact of public expenditure and revenue on national income, employment, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
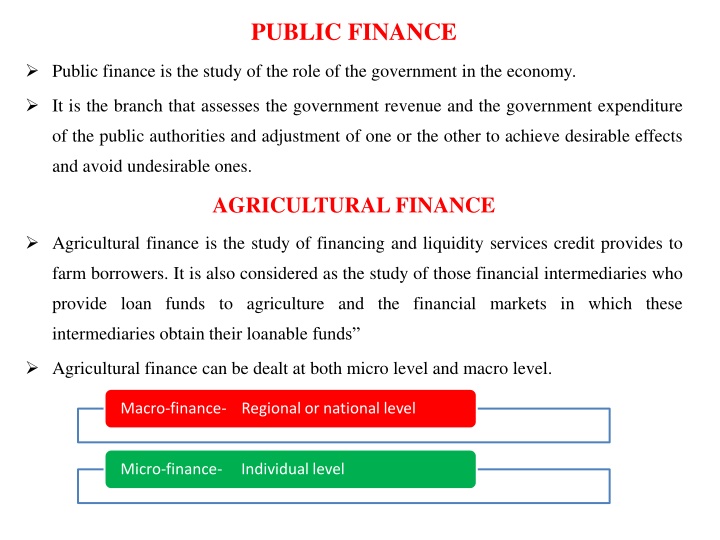
PUBLIC FINANCE Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch that assesses the government revenue and the government expenditure of the public authorities and adjustment of one or the other to achieve desirable effects and avoid undesirable ones. AGRICULTURAL FINANCE Agricultural finance is the study of financing and liquidity services credit provides to farm borrowers. It is also considered as the study of those financial intermediaries who provide loan funds to agriculture and the financial markets in which these intermediaries obtain their loanable funds Agricultural finance can be dealt at both micro level and macro level. Macro-finance- Regional or national level Micro-finance- Individual level
Macro Finance : Macro finance deals with different sources of raising funds for agriculture as a whole in the economy. It is also concerned with the lending procedure, rules, regulations, monitoring and controlling of different agricultural credit institutions. Hence macro- finance is related to financing of agriculture at aggregate level. Micro-finance: It refers to financial management of the individual farm business units. And it is concerned with the study as to how the individual farmer considers various sources of credit, quantum of credit to be borrowed from each source and how he allocates the same among the alternative uses with in the farm. It is also concerned with the future use of funds.
Need forAgricultural Finance Agricultural influence on national income Agriculture plays vital role in generating employment Agriculture makes provision for food for the ever increasing population Contribution to capital formation Supply of raw material to agro-based industries Market for industrial products Influence on internal and external trade and commerce Contribution in government budget
PUBLIC EXPENDITURE Public government in the various sectors of economy viz., agricultural sector, industrial sector, infrastructural sector, export-import sector etc. expenditure is the expenditure incurred by the Need for Public Expenditure: In order to bring about desired and balanced growth between backward and developed regions in the country, we require huge amounts of public expenditure. Development ofAgriculture Provision of Public Utilities Technological Changes Requirements of Employment
PUBLIC REVENUE This is the revenue accrued to the government from different sources viz., direct taxes, indirect taxes, and non- tax revenue such as prices and other miscellaneous receipts. Thus the government would have two major sources of revenue i.e. taxes and prices. The minor sources are fee, special assessment, rates, fines, tributes and indemnities, grants, gifts and donations.
TAX A tax is a mandatory fee or financial charge by any government on an individual or an organization to collect revenue for public works providing the best facilities and infrastructure The collected fund is then used to fund different public expenditure programs. Taxes are classified as Proportional, Progressive, Regressive and Degressive.
A Proportional tax is one in which same percentage is levied as tax irrespective of tax base or the size of the income. Eg: Sales tax, tithe A Progressive tax means the rate of tax increases as taxable income increases. Higher the income, greater would be tax amount. Eg: Income tax A tax is said to be Regressive, when it is affecting the poor rather the rich i.e., the burden of payment of tax would be more on the poor. It is just opposite to progressive tax. Eg:All commodity taxes.
A tax is called Degressive, when the higher income groups do not make due sacrifice. This happens when a tax is mildly progressive, but not steep. A tax is progressive up to certain limit, after which a uniform tax is levied. This tax also affects the poor than the rich. Taxes are also classified in to Direct and Indirect taxes. Direct taxes are the taxes directly paid by the persons. In other words, the person who pays the tax is also intended to bear it. Eg: Income Tax Indirect taxes are the commodity taxes. They are indirectly paid by the consumer through the dealers. Eg: Sales Tax






















