Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Biomarkers in Heart Failure Patients
Explore the distribution of pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) and associated biomarkers in heart failure patients undergoing right heart catheterization. Discover the correlation between various cytokines and proteins in relation to PVR levels, aiding in understanding the pathophysiology of heart failure with high PVR. Uncover putative protein-protein interaction networks across the pulmonary circulation in patients with heart failure and high PVR, providing insights into potential regulatory mechanisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
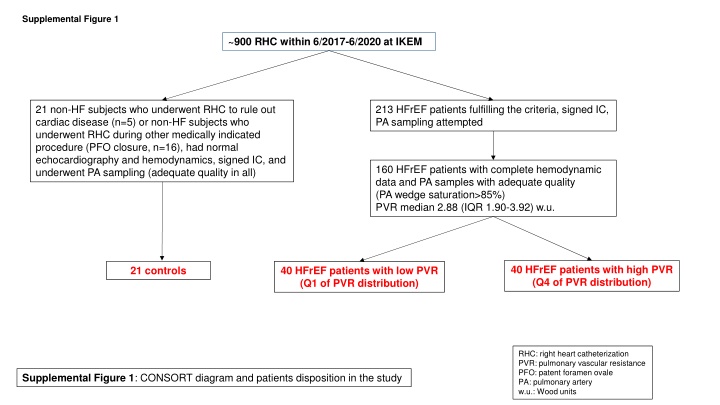
Supplemental Figure 1 ~900 RHC within 6/2017-6/2020 at IKEM 21 non-HF subjects who underwent RHC to rule out cardiac disease (n=5) or non-HF subjects who underwent RHC during other medically indicated procedure (PFO closure, n=16), had normal echocardiography and hemodynamics, signed IC, and underwent PA sampling (adequate quality in all) 213 HFrEF patients fulfilling the criteria, signed IC, PA sampling attempted 160 HFrEF patients with complete hemodynamic data and PA samples with adequate quality (PA wedge saturation>85%) PVR median 2.88 (IQR 1.90-3.92) w.u. 40 HFrEF patients with high PVR (Q4 of PVR distribution) 21 controls 40 HFrEF patients with low PVR (Q1 of PVR distribution) RHC: right heart catheterization PVR: pulmonary vascular resistance PFO: patent foramen ovale PA: pulmonary artery w.u.: Wood units Supplemental Figure 1: CONSORT diagram and patients disposition in the study
Supplemental Figure 2 Suppl. Figure 2: A) Histogram showing distribution of pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) in Wood s units and cutoffs for top and bottom quartiles. B) The correlation between BNP (ln, pg/ml) measured by immunoassay from peripheral vein and by PEA from mixed venous blood from PA artery. C) The correlation between Interleukin 6 measured by PEA and by IL-6 by ELISA (both from mixed venous blood from PA artery). D) The correlation between IL-6 measured by different PEA Olink panels (CVII or Inflammation).
Supplemental Figure 3 A B C 25 1.8 up (33) down (5) CCL3 PSP-D NT-proBNP 1.6 TNFRSF13B 20 1.4 BNP GDF-15 FGF-23 -log10 FDR adj. P value 1.2 -log10 FDR adj. P value IL8 15 1 ACE2 PON3 0.8 10 0.6 TWEAK 0.4 5 0.2 0 0 -3 -1 log2 fold change (HF vs CTRL) 1 3 5 -0.4 0.1 0.6 1.1 log2 fold change (HF high PVR vs HF low PVR) higher concentration in controls higher concentration in HF higher concentration in HF low PVR higher concentration in HF high PVR Suppl. Figure 3: A) heat map and hierarchical tree clustering of PA (mixed venous) concentrations of proteins in controls, HF patients with low PVR (Q1) and high PVR (Q4) B) Biomarkers of Heart Failure state identified by comparisons of proteins in PA (mixed venous blood) in controls (n=21) and in all HF subjects (n=80,Q1+Q4). C) Biomarkers of High pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) identified by comparing HF patients with low PVR (Q1, n=40) and high PVR (Q4. n=40). For abbreviations see Text and Suppl. Table 1.
Supplemental Figure 4 Suppl. Figure 4: Putative protein-protein interaction network for proteins differentially regulated (uptake or release) across pulmonary circulation in patients with heart failure and high pulmonary vascular resistance (STRING, v 12, https://string-db.org/). For abbreviations, see suppl table 1.






















