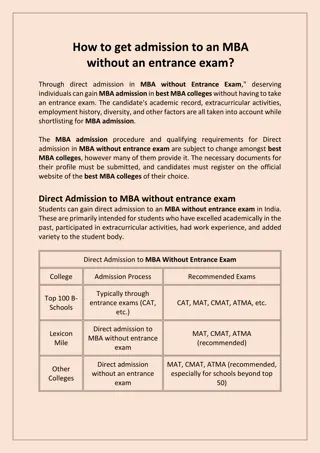
Purpose and Types of HR Audit in Organizations
Learn about the importance of HR audits, their purpose, types, and the need for conducting them in organizations. Explore how HR audits help in identifying gaps, improving HR practices, ensuring compliance, and addressing employee issues effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
HR AUDIT ARMAAN SALIK Assistant Professor Jamal Institute of Management
WHAT IS AN HR AUDIT? An HR audit is a systematic method of investigating the HR department s practices, policies, and procedures. It helps identify gaps in HR practice areas, and HR can prioritize these gaps by identifying ways to improve. Like any other type of business audit, an HR audit also takes place to avoid errors and meet the desired goals.
HR AUDIT An HR audit can be primarily categorized into two areas: 1. Risk mitigation 2. Value creation. Risk mitigation focuses on legal areas and employee-related lawsuits that may get the organization into legal trouble. Value creation, on the other hand, focuses on improving HR policies and processes to maximize the value of the employees.
PURPOSE OF HR AUDIT The main purpose of HR audit is to identify gaps in HR-related areas and improve them. Ensuring compliance and updating regulations to avoid any potential penalties Designing a fair, competitive employee compensation and benefits package Staying relevant with the latest employment laws and trends Identify reasons for employee turnover to improve retention Improve processes, procedures, organizational structures, and job descriptions Identify employee grievances and address issues
NEED FOR HR AUDIT An HR audit is used to review HR activities to identify issues related to policies, practices, regulations, compliance, employee issues, and other HR focus areas. The primary need for an HR audit arises from an organization s interest in connecting HR strategies to employee working lives and business performance. Additionally, HR audit is also needed to ensure that the policies, procedures, documentation, and personal records are regularly maintained and updated.
TYPES OF HR AUDIT 1. Time period 2. Conduct 3. Purpose
TIME PERIOD Time period refers to the frequency of HR audit. Since they are very time- consuming and require review of numerous documents, practices, policies, etc., organizations follow an irregular schedule for HR audit. Some organizations conduct HR audits once a year or once in three years.
CONDUCT In this category, HR audits can be further classified based on how organizations conduct the audits: a) Internal audit As the name itself suggests, internal HR audit takes place within the organization and is conducted by the HR department. This department identifies issues in its performance and efficiency and implements solutions. b) External audit When organizations do not prefer to conduct an HR audit internally, they hire external companies or professionals to do the job. There could be several reasons for external audits lack of resources, time, and unbiased review being a few examples.
PURPOSE While HR audit covers most HR processes, policies, and practices, organizations conduct the audit for different, specific purposes. These purposes are classified into: a) Compliance audit HR compliance audit determines how well a business is complying with all employment laws and regulations. Compliance audit comes under the risk mitigation audit. It helps the organization prevent violations of any laws or being open to liability lawsuits. b) Best practices organization audit Best practices organization audit refers to reviewing the best HR practices of other similar organizations and trying to adopt them. c) Strategic audit A strategic HR audit looks beyond the internal HR operations and tries to align the department s contribution with an organization s strategic goals. d) Job specific audit HR audit is focused on a specific role or job performed by the HR department. It could be related to recruitment,training, performance, etc.
THE HR AUDIT PROCESS 1. Set the HR audit objectives The main objective of an HR audit process is to identify any gaps in HR practices or policies. To do this, objectives must be established by the HR department. Since there are multiple purposes for an HR audit, organizations can list clear objectives based on what they want to achieve. The objective could be anything from ensuring compliance to addressing employee relations issues. 2. Align the HR audit objectives with corporate strategy Once the HR audit objectives are established, make sure that the planning and timing are in line with the business strategy. Misalignment between HR and business goals causes structures and systems to fall apart and create gaps in the expectations of organizations and performance of HR departments. 3. Prepare a rough audit plan Before implementing the HR audit process, prepare a rough plan on what the HR department wants to achieve. To prepare a rough HR audit plan, understand the manpower required, costs to be incurred, and the technology necessary.
THE HR AUDIT PROCESS 4. Collect data through data compilation techniques There are external and internal factors that affect the HR auditing process. Internal factors include company policies, skills, strategies, etc., and external factors include legal environment, competency level, and so on. There are many data compilation techniques like interview methods, task force, questionnaire methods, observation methods, etc. 5. Synthesize the data The data gathered in the above step presents the current situation of the business and HR as a function. This helps HR identify staff patterns and any issues so that they can be prioritized. Specific trends and patterns can be derived from this data by depicting them in the form of trend lines, statistical correlations, and frequency distributions. 6. Develop a detailed audit report This step involves both the improvement of the initial HR audit plan and preparing an audit report. Gather all the HR functioning data consisting of different HR department areas. An HR audit report includes a description of all the HR activities that are effective and ineffective. These reports are brought to the notice of the top management to devise action plans to solve the problems from this audit.
BENEFITS OF HR AUDIT 1. Identify reasons for low productivity By examining HR processes, policies, and employee performance, the audit can identify bottlenecks, gaps in training, or ineffective management practices that may be hindering productivity. This enables organizations to implement targeted improvements, streamlined workflows, and overall organizational efficiency. 2. Gain a competitive advantage HR audit allows organizations to assess their HR practices against benchmarks and best practices. This helps identify areas for improvement, enhancing HR capabilities, attracting top talent, and creating aa positive employer brand. 3. Staying up to date with laws and regulations HR audit helps organizations keep up with changing employment laws and regulations. Non-compliance issues can be identified to take corrective actions. This mitigates legal risks, avoids penalties or lawsuits, and helps maintain a strong reputation for ethical business practices.
BENEFITS OF HR AUDIT 4. Improve talent acquisition strategies An HR audit also assesses recruitment practices, candidate screening, onboarding procedures, and employer branding efforts. By identifying areas for improvement, such as targeting new talent pools, enhancing candidate experience, or optimizing job descriptions, organizations can attract top talent. 5. Low employee turnover Gaps in compensation and benefits, career development, work-life balance, and employee engagement initiatives are identified. This helps address issues and create a more positive workplace. Employee satisfaction is improved by assessing the reasons for turnover. Ultimately, employee retention is increased. 6. Improve safety in the workplace Workplace safety practices, policies, and compliance with health and safety regulations are evaluated. Potential hazards, gaps in safety training, inadequate safety protocols, etc., are identified so that organizations can take corrective action to enhance workplace safety.