Pushing Past ‘I Don’t Know”
Gabriela Taylor, based in Portland, Oregon, provides insights on effective communication strategies. Discover how to push past communication barriers for enhanced relationships and personal growth at Dirkse Counseling & Consulting.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pushing Past I Dont Know Effective Communication Strategies Gabriela Taylor DirkseCounseling & Consulting William Ramis-Portland Oregon DIRKSE Counseling and Consulting, Inc.
Introduction Communication - the human connection - is the key to personal and career success. Paul J. Meyer
The Basics of Communication No matter how experienced we are, we should always review the basics, to continually strengthen our own foundation, to be the most effective to those we support.
Four Basic Communication Skills Thinking Listening Speaking Non-Verbal By understanding the basics of each component, we are better able to find the source of breakdowns in communication
Communication Skills # 1: Thinking -Most people do not consider thinking a communication skill! If a person doesn t have an opinion to make- how can we expect it to be communicated? What do you want to do for work? -Having a strong understanding of the ideas in your head, or the concepts that you wish to illustrate is the starting point to effective communication. -If a person does not have an idea straight in their own mind, it makes expressing it to others , almost impossible. Example: If you are asked to describe an animal to a friend , but you do not have an animal in mind, it would be nearly impossible to clearly communicate this information.
Communication Skills # 2: Listening -An ability to use active listening and to be able to understand the purpose or intent of what the others are saying is key in communication It is important to understand the environment, and take the time to understand distractions to listening ! -Only when information is heard and understood is response communication effective -You cannot truly communicate with someone if you do not understand the purpose of the communication It goes both ways-both parties need to understand the intent by truly listening !
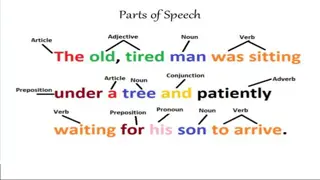
Communication Skills # 3: Expressing/Speaking -Actually choosing the words, pictures, or symbols is the next step in communication Be Careful! Just because someone speaks with clarity and confidence, or uses assistive technology or pictures with ease, does not always mean they are confident or sure in the content of what they are expressing! -Although this is the piece that most people focus on when talking about communication , research has shown that the nonverbal portions of communication can actually change the meaning of what is expressed -Although this piece is important, we must remember that this is not the step where communication is successful or not successful
Communication Skills # 4: Non-Verbal - Non verbal communication is the bulk of our communication (93% of it, to be exact!) - Our bodies speak volumes everyone is constantly sending signals, whether they are intending to or not - Body language (in conjunction with tone) can easily cancel out the things being expressed !
Putting the 4 Steps Together -Understanding the role of each will help you map out where the break down is occurring If we become complacent, and do not take the time to assess , all communication with the customer moving forward will not be as successful as it could be. -It is our job as providers to identify these basic communication skills for both the people we serve and ourselves so that communication is effective Listening -Once we identify which skill is compromised, we can than develop a plan to work around it Thinking Success Expressing Non-Verbal
Where's The Holdup? -Did they understand? -Do they know what I asked? -How do I know -Can they express? -How do they express? -Any go to answers -Do they have the means to express? Thinking Expressing Tone? Face? Body ? What am I doing? What are they doing? Distractions? Noise? Lights? People?Smells? Traffic?Lighting? Non- Verbal Listening
Barriers to Communication To effectively communicate, we must realize that we are all different in the way we perceive the world and use this understanding as a guide to our communication with others. -Tony Robbins Although there are countless barriers to communications in our day to day interactions, for the purposes of this presentation we are going to focus on the barriers that fall under the following definition : The things stopping us from getting the bulk of our information from the perspective of the client themselves. https://encrypted-tbn1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRDIvehMJ9rw_D0dOQ1CkVhgbFDMWncQF4qCIhpGpMDvSujvJHC Stereotypes Attitudinal Barriers Learned Helplessness Support Team Professional Complacency
Stereotypes Stereotyping is an attitude that alters communication because of a general, non specific opinion applied to a particular group. 1. Individuals who experience ID/DD struggle with open ended questions What information could be lost when we assume and only ask yes or no questions? 2. Individuals on the spectrum struggle with communication, keep questions direct, focused, and literal. This stereotype takes away the ability to work within creative ideas, which is where most job carves develop from 3. Individuals with limited ability to use expressive communication get overwhelmed by too many questions Expressive communication and thoughts are two separate things, questions evoke thoughts and ideas, doing this limits the persons ability to be supported towards their goals
Attitudinal Barriers Attitudinal barriers are behaviors or perceptions that prevent providers from communicating properly. IGNORANCE SPREAD EFFECT Attitudes are commonly formed by an individual's opinions or personal feelings on a subject or person and can be difficult to alter. When attitudinal barriers override the client perspective, communication will not be effective, and services will no longer be client centered. FEAR It is imperative to understand both your own personal attitudinal barriers, as well as being mindful of your clients potential attitudinal barriers EMOTIONAL EDITING
Attitudinal Barriers Ignorance: People with disabilities are often dismissed as incapable of communicating clearly without the opportunity to try The Spread Effect: People assume that an individual's disability negatively affects all of their abilities, including communication . Emotional Editing: Using past experiences as the soul source of information in the current situation. Fear: The fear of offending, challenging or pushing too hard
Learned Helplessness Decide what I am good at Choose for Me Learning to tolerate the reality of the environment and those in it, due to the information received on a regular basis. Speak for me Tell people what is important to me in a job Identify my interests for me Act for me
You are the professional , what are you afraid of? We often find ourselves scared to: We often let ourselves: Speak up against a support team member Get lazy To push our clients , to challenge them Be hurried To offend them Ignore the client Take risks Take the easy route Push boundaries Become complement Change our own professional routine Be afraid of prolonged silence Get bullied away from effective practices
Developing a Communication Plan Step 1: Identify Key Members of the support team Step 2: Use the communication interview support tool Step 3: Develop a communication plan Step 4: Implement communication plan & assess
Communication Interview Support Tool Go to the source! Do the ground work ! It s not about what works for you, or about what past experience you have, it s about what works for them! -Who does that person communicate the best with ? -Where do they communicate the best ? Professional Experience -In what situations are the individuals barriers to communication least impactful ? Support Team -What are the unique and specific aspects of this persons communication patterns?