Q and A on the details of UV-VIS Instruments
Discussing details of UV-VIS instruments, including the best cell type for UV work, classic double-beam configuration design, the lamp producing UV part of the source, grating types, operational aspects like detector biasing, amplification in PMT, and practical limitations affecting UV-VIS scans.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
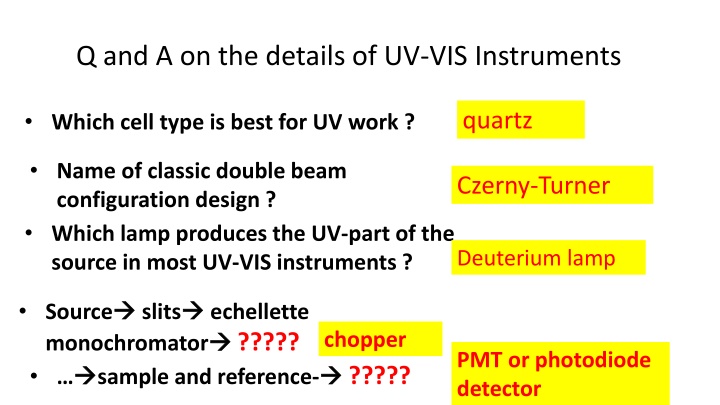
Q and A on the details of UV-VIS Instruments Which cell type is best for UV work ? quartz Name of classic double beam configuration design ? Which lamp produces the UV-part of the source in most UV-VIS instruments ? Czerny-Turner Deuterium lamp Source monochromator sample and reference- slits echellette ????? chopper PMT or photodiode detector ?????
Q and A on the details of UV-VIS Instruments (cont.) Name of old school grating (flat, high scatter) Echellette type grating Name of new school grating (low scatter, focusing) Concave holographic (sinusoidal or focusing) grating What does a UV instrument vary in d(sin in + sin out ) =n to scan ? angle in In the same equation above, what practical reason argues against varying out ? Want detector position to be fixed at out
Q and A on the details of UV-VIS Instruments (cont.) About what amplification (gain) occurs in a typical PMT ? ~100,000-1,000,000 (105 -106) Photodiodes in UV visible instruments are operated under ?????? bias. reverse 1) Linear response to light flux 2) Low capacitance=> fast response For what two reasons is the above biasing done ? Technical term for filtering out all but signals repeating at the chopper motor s turning rate (rpm) Phase locking
Q and A on the details of UV-VIS Instruments (cont.) What practical limitation sets the lower limit of a UV-VIS scan at 180 nm ? Quartz cells start to absorb at 180 nm and down What is the usual line count/mm of a UV-VIS monochromator s grating ? 1000-3000/mm What is the equivalent groove spacing in nm the above range of lines implies? Name two advantages of the holographic focusing grating design. 0.1 mm/(1000-3000) = 1000-330 nm 1) Allows higher intensity of light 2) Corrects spherical aberration issues connected with old style gratings (reduces focus problems)
Q and A on the details of UV-VIS Instruments (cont.) Wavelength range of most double beam instruments ? Gas phase uv-vis spectra are ??????? spectra? solution phase uv-vis spectra are ??????? spectra? If I is the output optical signal and Io is the incident optical signal, what is %T ? 180-1100 nm Line (discrete) spectra Broad band spectra %T= 100*I/Io What atomic level physical event creates UV-VIS absorption ? Electronic transitions between electron orbits