Quality System Maturity Model Update by MDIC
MDIC Open Forum Quality System Maturity Model Update featuring George Serafin from Deloitte & Touche LLP. Learn about the project team members, background, objectives, key milestones, overall timeline, and the approach for adapting CMMI process framework for medical devices.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MDIC Open Forum Quality System Maturity Model Update George Serafin Deloitte & Touche LLP 1 MDIC
Quality System Maturity Model Project Team Team Members Company Pat Baird Baxter Jodie Bastian Stryker Sarah Deegan Johnson & Johnson Jeff Fecho (AdvaMed Rep) St. Jude Medical Bob Kenney Veeva Bill Murray (Co-Lead) Nick Premnath MDIC Deloitte Tim Rew Terumo Nicole Schumacher Deloitte George Serafin (Co-Lead) Deloitte Jason Spiegler (ASQ Rep) Camstar Dan Torrens CMMI Francisco Vicenty FDA Rusty Young CMMI 2 MDIC
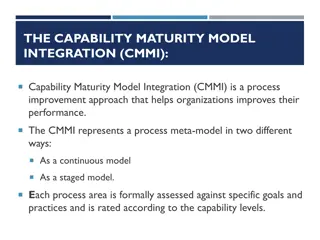
Background / Objective: Quality System Maturity Model Background In May 2015, MDIC presented research on current Maturity Models established across various industries and provided recommendations regarding how specific options can be adopted by MDIC stakeholders including, but not limited to, industry members and the Food & Drug Administration. Objective As a result of this research, a quality maturity model work stream was formed to develop and implement a Quality System Maturity Model based on the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) for the medical device industry that is focused on promoting product quality and patient safety. 3 MDIC
Key milestones and overall project timeline July 2015 August 2015 September 2015 October 2015 November 2015 December 2015 January 2016 February 2016 March 2016 Maturity Model Development Develop Pilot Strategy and Approach Connect with Measures Team Define Maturity levels CMMI alignment and identify gaps/enhancements Adapt CMMI process framework Present adapted CMMI Model at CfQ Forum Timeline CMMI Pilot Development Selection of process areas Selected pilot process areas built out Identify pilot participants Present pilot plan at CfQ Forum Develop plans and on-board pilot participants Conduct Pilot Kick-off pilot Complete pilot 4 MDIC
Approach for adapting CMMI process framework for Medical Devices Our approach focuses on adapting the CMMI process framework to medical devices then developing content for the selected process areas. Fill in Gaps / Enhance Address identified gaps and enhance process framework; define maturity levels Identify Gaps Conduct gap analysis and identify any missing elements in the process framework Alignment to QSR / ISO Align combined CMMI process framework to QSR and ISO 13485 CMMI Process Framework Leverage and combine CMMI process frameworks for Development, Acquisition, and Service constellations to create a process framework for medical devices 6 MDIC
Mapping of CMMI Process Framework The CMMI Framework approximately maps to 80% of Quality System Regulations and ISO 13485 requirements All three standards align to the following: Management oversight 100% Percent Alignment to QSR and ISO 13485 Quality Policy & Practice Medical Device Profile Establishment of organizational standards & practices 90% Monitoring & control 80% Training 70% 60% Both FDA & ISO incorporate requirements specific to Medical Devices which CMMI does not 50% Medical Device Requirements 40% CMMI Model 30% 20% FDA and ISO are aligned, but address risk management in separate standards focused on patient impact 10% Risk Management CMMI focuses only on project risk 7 MDIC
Risk Management CMMI, ISO and the QSR all incorporate risk differently, with different emphasis. Risk Management is an area where further alignment will be needed. CMMI Risk management framework is project-centric Project Risk CMMI Risk Management ISO addresses risk for medical devices in a separate standard ISO 14971 ISO 14971 Medical Device Risk FDA Guidance ICH Q9 FDA addresses risk for medical devices mainly through guidance documents. It also references ISO 14971 Medical Devices 8 MDIC
Level Definitions and Process Area Selection
Maturity Indicator Level Definitions Maturity indicator levels (MILs) for the Quality System Maturity model are aligned to the CMMI MILs Maturity Indicator Levels: Level 4 Quantitatively Managing Level 1 Initial Level 2 Managed Level 3 Defined Level 5 Optimizing Maturity Indicator Levels were defined based on the following areas: Monitoring and Auditing Reporting Communications and Training Risk Management Processes and Procedures IT Systems & Information Management Organization Governance Culture 10 MDIC
Maturity Indicator Levels - Characterizations Maturity Indicator Levels (MILs) Level 4 Quantitatively Managing Level 1 Initial Level 2 Managed Level 3 Defined Level 5 Optimizing Defined locally Defined & consistent for regulated activities Processes defined & institutionalized Integrated Automation Inconsistent application & results Governance structure Improved application & results Fully life cycle management framework Consistent inputs/outputs Consistently applied with consistent results Project or unit specific Quality by Design Change management Execution dependent on individuals Enforcement inconsistent Automation Formal training program by roles & responsibilities Centers of excellence No formal training program Developed of SMEs or project teams Formal training syllabi by roles & responsibilities Fully trained, highly skilled Beginning RM framework Sporadic or non-existent Focus on professional & personal development Selective training Active tracking & reporting Risk integrated into processes Qualitative Formal risk methodologies applied RM framework institutionalized Predictive risk used strategically No RM framework Quantitative/semi- quantitative Sporadic or non-existent Project/unit specific Risk fully integrated & specialized to processes Drives business opportunities Qualitative No RM Framework Well-defined toolbox & procedures Quantitative/predictive/proa ctive No RM framework Often pro-forma Patient focus Analytics Focus on testing & meeting specs Lagging metrics Analytics driven, predictive Complete toolbox Two-way communication with management Internally focused Incorporate business metrics Implementation of methodologies (e.g. Lean/Six-Sigma) Lagging metrics QA/compliance driven Improved problem resolution Ad hoc reporting Cost of Quality Reporting internal to local units No management review Proactive Analytics Continuous Improvement Inconsistent problem resolution Analytics-based quantitative reporting Limited or ad hoc Management Review Proactive management involvement Inconsistent problem resolution Strategic preventative action 11 MDIC
Process Area Selection for Pilot Study Selection of focused process area for the pilot study will be based on the following criteria Impact on Product Quality Process area should have a significant impact on patient safety and product quality. Value to Business Well Defined Process area should be of value from a business perspective Process area should be holistic in terms of people, process, and technology. Size Agnostic Ease of Implementation Process area should be relevant to small, medium, and large organizations Process area should be narrow in scope and could easily be implemented in a pilot study Alignment to Metrics Team Process area should align with the Metrics and Measures work stream. 12 MDIC
Next Steps Pilot Study In addition to building out the selected process areas for the pilot, planning for the pilot study will the focus for the next quarter. Pilot Study Develop 1-2 process areas (process areas will be determined based off of selection criteria) Identify at least 3 companies that will participate in pilot study FDA will shadow pilot assessment to gain an understanding of how maturity is assessed Next Steps Process Area Model Development Company Identification Execution Incorporate measures work stream output into maturity model Reach out to companies to determine interest in pilot study Develop execution plan / schedule for assessors and FDA members Identification of potential process areas Determine resources required Analysis and selection of 1-2 process area Selection of at least 3 companies Perform maturity model assessment Frame out incentives 14 MDIC