Radiology Anatomy of the Pituitary Gland
Learn about the normal structure and size of the pituitary gland, indications for imaging, and the best modalities to image it. Explore images depicting the anatomy, including the anterior and posterior lobes. Discover common pathologies like pituitary adenomas and understand the role of different imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays in evaluating pituitary disorders.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
RADIOLOGY ANATOMY OF THE PITUITARY GLAND
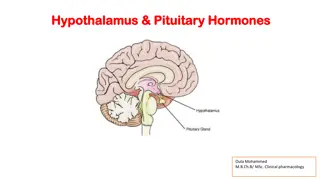
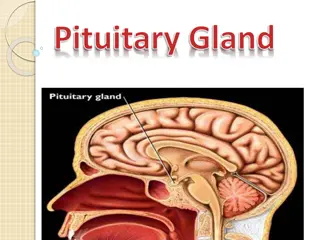
NORMAL PITUITARY GLAND The gland is composed of two parts: Anterior lobe (adeno hypophysis) Posterior lobe (neuro hypophysis) Normal size: Weight: 0.5g Height: 4-16 mm Anterior posterior: 5-16 mm
INDICATIONS FOR IMAGING THE PITUITARY GLAND Hormonal dysfunction Cushing syndrome Growth abnormalities e.g. Growth hormone deficiency, acromegaly Visual abnormalities headache
What is best modality to image the pituitary gland ? A. X ray B. CT scan C. MRI D. US E. Nuclear medicine
What is best modality to image the pituitary gland ? A. X ray B. CT scan C. MRI D. US E. Nuclear medicine
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 1-Optic sulcus 2- Anterior clinoid process 3-Floor of sella turcia (Pituitary fossa) 4- Posterior clinoid process 5- Dorsum sella 6- Sphenoid sinus 3 4 5 6
4 3 5 2 6 1
4 3 1- pituitary gland 2- sphenoid sinus 3- optic chiasm 4- hypothalamus 5- pituitary stalk 6- claivus 5 2 6 1
NORMAL PITUITARY ADENOMA
2 3 1 4 5 6
2 3 1 4 5 6
Optic chiasm Pituitary stalk Pituitary gland Carotid artery Cavernou s sinus Sphenoid sinus