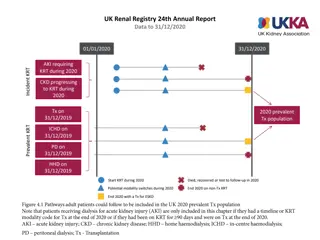
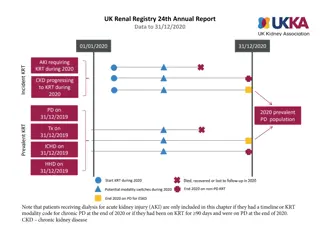
Renal failure
Renal failure results from a significant loss of kidney function, leading to acute or chronic kidney damage. Learn about the causes, pathophysiology, and treatment options for renal failure, including acute renal failure and its reversible nature, as well as the different types of failure such as pre-renal, intra-renal, and post-renal. Discover the importance of diagnosing renal failure through history, physical examination, and laboratory investigations like blood urea and serum creatinine levels, as well as imaging techniques such as renal biopsy and CT scans. Explore the treatment strategies for acute renal failure, including correcting underlying causes, managing fluid and electrolyte imbalances, and potential dialysis intervention for recovery.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Renal failure DR.HUSSEIN LAFTA
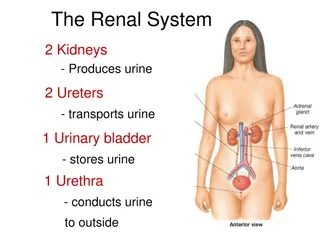
Renal failure Renal failure is defined as a significant loss of renal function in both kid. to the point of about 10-20% of the GFR. Renal failure may occure as an acute and rapidly progressing process or may present as chronic form in which there is a progressive loss of renal function over a many yrs. Acute renal failure has an abrupt onset and it is potentially reversible. Chronic renal failure progresses slowly over at least three months and can lead to permanent renal failure. HUSSEIN LAFTA
Pathophysiology of renal failure In renal failure there is either glomerular or tubular dysfunction . Glomerular dysfunction : as main function of glomeruli is filrtration,glomerular dysfunction lead to fall in GFR with retention of those substances usually cleared by filteration,including water. Tubular dysfunction: as the main function of tubules is reabsorption, tubular failure result in the voiding large volume of dilute urine {polyuria} of low specific gravity ,along with electrolytes and nutrients. HUSSEIN LAFTA
Acute renal failure Sudden decrease in renal function. ARF may be pre-renal ,intra-renal or post-renal in nature . ARF is often reversible so long as permanent injury to the kid. has not occurred. Clincal features -oliguria{ reduced urine output}. -possilble odema and fluid retention. -elevated blood urea and serum creatinine. -alteration in serum eletrolytes. -poor appetite. -heamaturea HUSSEIN LAFTA
Causes of ARF. Pre-renal failure -result from impaired or reduced blood flow to the kidney. e.g. shock ,sever hypotention,anaphylaxis ,sever heart ischemia (extensive MI). Intra-renal failure -result from acute damage to renal structures. -possible causes: Acute GN,PN.,acute tubular necrosis{ATN},or damage of the kid. From exposure to toxins,solvents,drugs and heavy meatals. ATN is the most common cause of acute renal failure. HUSSEIN LAFTA
Acute renal failure Post renal failure - result from condition block of urine outflow e.g stone, tumours,prostatic hypertrophy. Dx -Hx, -Ex, Lab investigationwhich include : -Blood urea,serum creatinine,Hb. U.Sof the kid.help to determine whether the kid. Problem is acute or chronic. Renal biopsy. C.T scan HUSSEIN LAFTA
Treatment of acute renal failure Try to correct the cause .e.g volume correction,stop nephrotoxic agents or relief the obstruction. Correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Dialysis which may employed while the kid. In recovery phase . Low prottien ,high carbohydrate diet to minimize the formation of nitrogenous wastes products. HUSSEIN LAFTA
Chronic renal failure CRF result of progressive kid. Damage and loss of function. CRF is often classified into four stages according to the degree GFR loss. - diminished renal reserve ( GFR------35-50% OF normal). -renal insufficiency-------GFR -----20-35%. -renal failure -----------GFR less than 20%. -end stage renal disease ---- GFR less than 5%. HUSSEIN LAFTA
Cuases of CRF. Chronic G.N. Chronic P.N. Prolong obstruction. Exposure to toxic chemical,toxins or drugs. D.M Hypertention. Nephrosclerosis. Alport syndrome {inherted disorder include deafness,progressive kid. Damage and eye defect.} HUSSEIN LAFTA
Clinical feature of CRF Aneamia,increase level of phosphate in blood . Malaise . Dry skin. Poor appetite Vomiting. Bone pain Metallic taste in mouth. HUSSEIN LAFTA
Treatment of CRF Correction of fluid and electrolytes. Prodent use diuretics. Careful dietery mangment (restriction of protein intake). Correction of anemia by periodic use of synthetic erythropoitin. Renal dialysis (heamodialysis or peritoneal dialysis). Renal transplant. HUSSEIN LAFTA
heamoldialysis It is medical procedure to remve fluids and waste products from blood and to correct electrolytes imbalance. Done using heamodialysis machineand dialyzer also called artificial kid. Hussein lafta
Indication for HD Acidosis------ PH < 7.1 Electrolytes imbalance -----k>6.5mg/ dl GFR < 10 ml/min. Overload of fluids (pulmonary oedema) uramic symptoms(increase level of nitrogenous waste products) Hussein lafta
Basics for renal transplant kid,. Tranplant is the most effective therapy for end stage renal disease. The transplanted organ can come from either a live donor or deseased donor. Most deseased donor organs come from brain dead donor. Non standard criteria donor: -expanded criteria donors. -donation after cardiac death. Hussein lafta