Risk Management & Internal Audit Department Structure
The Risk Management & Internal Audit (RMIA) Department plays a critical role in providing independent, objective assurance and consulting activities to improve an organization's operations. It aims to enhance the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes. The department's structure includes a RMIA Board, Audit Committee, Director General, Directors, Secretaries, and various Officers. Additionally, it follows specific objectives in internal auditing and an established audit process to ensure compliance, reliability, and integrity. The mandate of RMIA encompasses risk management and internal audit practices to safeguard assets and enhance organizational performance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Risk Management & Internal Audit (RMIA) Department
STRUCTURE OF RMIA BOARD, AUDIT COMMITTEE (BAC) DIRECTOR GENERAL DIRECTOR GENERAL Director/RMIA (1) Director/RMIA (1) Secretary (1) Secretary (1) AD/RMIA (1) AD/RMIA (1) A AM/RMIA M/RMIA (1) (1) Audit Officer (1 Audit Officer (1) ) Audit Officer (1 Audit Officer (1) )
MANDATE OF RMIA INTERNAL AUDITING Overall objective and the purpose; anindependent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations. It helps an its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes. Source: International Professional Practices Framework (IPPF) Guided by: Internal Audit Charter Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing (of The Institute of Internal Auditing
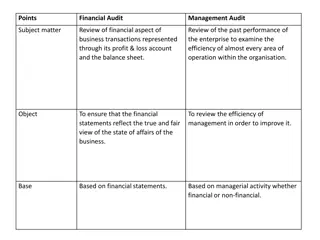
INTERNAL AUDITING -Specific objectives Review operations or programs; Provide reasonable assurance: reliability and integrity (financial and operational information); Check compliance to policies, procedures, laws and regulations; Assess if assets safeguarded; Effectiveness of the system of internal controls: Appraise economy /efficiency of resource utilization; Assist in effective and successful performance of responsibilities by providing analysis, appraisals and value adding recommendations and other pertinent information concerning the activities being reviewed
AUDIT PROCESS Approved Annual Audit Plan after Risk Assessment Audit Notification letter Preliminary survey Kick off meeting Carrying out audit Fieldwork Formal DRAFT audit report; Closing meeting: - issues & recommendations; - factual accuracy Management comments, implementation responsibilities and timelines; FINAL audit report, Presentation to BAC. Follow up
MANDATE OF RMIA RISK MANAGEMENT Definition of ERM a process, effected by an entity's board of directors, management and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risks to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives. Source: COSO Enterprise Risk Management Integrated Framework. 2004. The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) Definition of Risk Risk; The effect of uncertainty on objectives ISO 31000 Risk Management principles and guidelines Guided by: Treasury circular No.3/2009: Development & Implementation of Institutional Risk Management Policy Framework (IRMPF) in the Public Sector
Risk Management Basics Risk (uncertainty) may affect the achievement of objectives. Effective mitigation strategies/controls can reduce negative risks or increase opportunities. Residual risk is the level of risk after evaluating the effectiveness of controls. Acceptance and action should be based on residual risk levels.
Benefits of Risk Management Increase risk awareness What could affect the achievement of objectives? What could change? What could go wrong? What could go right? Increase understanding of risk sensitivities. What makes my risks increase/decrease/disappear? Promote a healthy risk culture It s safe to talk about risk. Open and transparent. Develop a common and consistent approach to risk across the organization. Not intuition-based. Allows intelligent informed risk-taking. Focuses efforts helps prioritize. Top 10 list. Or top 3. Or Is proactive . not reactive Prepare for risks before they happen. Identify risks and develop appropriate risk mitigating strategies. Improve outcomes achievement of objectives Really comes to down to simple good management Enables accountability, transparency and responsibility And maybe even mean survival
Institutional Risk Management Framework 5. Governance Board, Audit & Risk committee, Exec Risk Committee(s), Risk appetite 4. Organisation Structure Roles and responsibilities, Risk domains, Risk Mgr, HODs, Departmental risk champions Internal/ External audit ref 5.2/8.0 Management reporting Risk Risks / Opportunities identification 6. Lines of Assurance 2. Risk assessment / measurement 1. Risk Universe (All Risk Types) Risk monitoring & reporting Risk mitigation & Treatment Risk Register Risk Matrix 3. Tools, resources, policies & procedures, training, risk culture, systems ref 5.4
Conclusions I thank you I thank you