RNA Purification: Key Tweaks and Differences
Explore the nuances of isolating RNA from DNA, highlighting essential steps to prevent degradation by RNases. Learn about key differences between RNA and DNA, including stability and structural variances. Understand the importance of using denaturants and following proper extraction techniques to ensure successful RNA purification.
Uploaded on | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
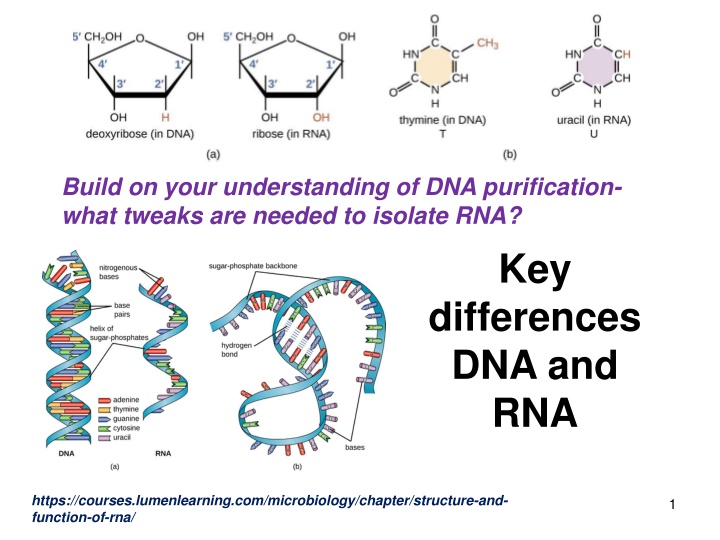
Build on your understanding of DNA purification- what tweaks are needed to isolate RNA? Key differences DNA and RNA https://courses.lumenlearning.com/microbiology/chapter/structure-and- function-of-rna/ 1
Some differences: RNA: Is single stranded *Has 2 OH group Has uracil in place of thymine *Is more stable at pH 4-5 than physiological pH Is less stable than DNA! 2
IMPORTANT!! Essential to inactivate endogenous RNA nucleases (RNases) as soon as possible. Otherwise the RNA will be degraded and useless. 1. RNAse can be boiled, or autoclaved, chemically denatured, and once cooled or allowed to renature WILL STILL DEGRADE RNA 2. RNA is much less stable than DNA - more vulnerable to nuclease degradation 3
Therefore These steps are needed to prevent RNases from degrading your RNA during preparation 1. Keep material frozen at all times before extraction 2. Use strong protein denaturants or other compounds that inhibit RNase activity (Denatured enzymes cannot degrade RNA) 3. Remove proteins (including RNase) ASAP (i.e. organic extraction) 4
Guanidinium and other denaturants are used in extraction buffer or other reagents to quickly denature RNases NH2 Guanidine hydrochloride . HCl HN C NH2 NH2 Guanidinium isothiocyanate . HSCN HN C NH2 Guanidinium is one of the most powerful protein denaturants Keeps RNases denatured until removed with phenol/chloroform extraction Strong irritant use gloves! 5
The purification of RNA and DNA is much the same. The trick is to separate RNA from DNA We can either selectively precipitate out the DNA or selectively precipitate out the RNA, depending on which method we choose 6