Role of DLPFC in Auditory Hallucinations
Explore the significant connectivity patterns among brain regions in schizophrenia patients with and without auditory hallucinations (AVHs), shedding light on the proposed mechanism responsible for AVHs. Thalamic-auditory cortical-hippocampal dysconnectivity may be key in the pathological perception of internal sounds without external auditory stimuli.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
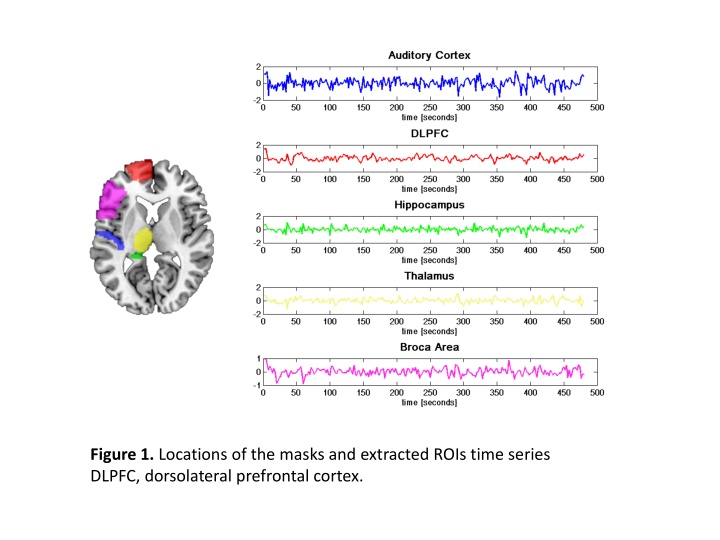
Figure 1. Locations of the masks and extracted ROIs time series DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.
(a) AVHs (b) Non- AVHs (c) HCs Figure 2. Significant effective connectivity (at the group level) among ROIs in the SZ patients and HCs. Significant connectivities in the AVHs group (a), and Non-AVHs group (b), and HCs (c).
(b) (a) (d) (c) Figure 3. Significant effective connectivity (at the between group level) among ROIs between the SZ patients with and without AVHs and correlation analysis. (a) Increased (red) and decreased (green) effective connections in the AVHs group as compared with Non-AVHs group. Correlations between the AHRS score and strength of connection from the thalamus to the auditory cortex (b), from the auditory cortex to the hippocampus (c), and from the Broca area to the auditory cortex (d).
Figure 4. Decreased (green) effective connection in the Non-AVHs group as compared with HCs.
Figure 5. Proposed mechanism responsible for AVHs in SZ. Thalamic-auditory cortical-hippocampal dysconnectivity may lead to increased activity of the auditory cortex and the pathological perception of internal sounds without presenting of auditory stimuli.






















