Rutherford and Bohr Atomic Model: Discoveries and Implications
Explore the groundbreaking Rutherford and Bohr atomic model as presented by Dr. R. R. Mistry, revealing the small positively charged nucleus, electron orbits, and more. Understand the key findings and implications of these experiments in shaping our understanding of atomic structure.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Topic The Rutherford and Bohr Atomic Model Presented by Dr. R. R. Mistry Asst. Professor Department of Physics Deogiri College, Aurangabad
The Rutherford nuclear atom model:- Rutherford performs experiment on scattering of -particles in 1911.
The -particles are emitted by radioactive material, which are passing through a small hole for fine beam of -particles. This fine beam of -particles is allowed to fall on a thin gold foil F. While passing - particles through the particles are scattered through different angles. A zinc sulphite screen was placed on the otherside of the gold foil. gold foil, the
The following results were noted 1)Most of the -particles passing through the gold foil with small deviation. 2) There were a few particles that were scattered through large angles i.e. greater than 900. A few of them were even scattered directly direction. in the backward
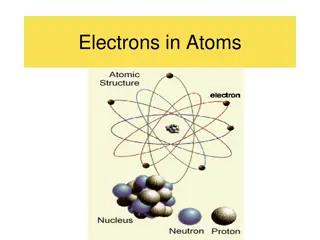
From these results Rutherford Nuclear Atomic model as: 1) The atom has a small positively charged nucleus. All positive charges of an atom and most of the mass of atom are concentrated in the nucleus. The electrons revolve around the nucleus. The dimensions of the nucleus and electrons are very small as compare to the size of atom hence most of the space in a atom is empty. Thus the discovery of the nucleus of the atom is due to Rutherford. explain his
2)The electrons must be revolving around the nucleus in closed orbits due to centrifugal force is balanced by the force of electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. Rutherford proposed a dynamic planetary model in which nucleus plays the role of the sun and electrons correspond to the individual planets of the solar system. The most of the atom is empty because the most of the -particles pass through the foil without appreciable deflection. The particle will be scattered through large angles or turned back when a head on collision occurs with the nucleus.
The positive charge inside an atom is confined within a region having a radius less than 10-14m. Also it was found that almost the entire mass of the atom was concentrated within charged core of the atom which is named as the nucleus of electrostatic attractive force of nucleus on electrons supplies centripetal force for theirorbital rotations. this positively the atom. The the necessary
Drawbacks of the Rutherford Nuclear Atomic Model:- Rutherford atomic model can not explain the stability of the atom. Rutherford suggested that the electrons revolve round the nucleus, like the planets round the sun at such a speed that mechanical centrifugal force just balance the excess of electrostatic attraction and as a result stability could be secured. But such an assumptions brought a serious difficulty because according to electromagnetic electrons should radiate energy continuously. So electrons loss energy continuously and will approach to nucleus by a spiral path. The electrons giving out a radiations of constantly increase frequencies and finally fall into the nucleus. theory revolving
The Bohr atom Model:- The Bohr overcome the drawback of Rutherford atomic model by applying Planck s quantum theory and developed Bohr atomic model. Bohr built his theory of atomic structure on the basis of the following two fundamental postulates. i)The first postulate regarding the electronic structure, states that the electrons cannot revolve in all possible orbits as suggested by the classical theory, but only in certain definite orbits satisfying quantum condition.
ii) The second postulate regarding the origin of spectral lines. The radiation of energy takes place only when an electron jumps from one permitted orbit to another. The radiated energy is equal to the difference in the energies of the twoorbits
Bohr theory explained electronic structure and origin of the spectral hydrogen atom or simplest elements. He could not explain heavy atom and fine structure of spectral lines. Based on these postulates Bohr derived two formulae i) The stationary orbit and ii) The total energy of the electron in the orbit. lines of radius of the