Sampling Techniques in Research: Overview and Methods
Sampling is a crucial aspect of research methodology, allowing researchers to draw conclusions about a larger population by observing a subset. This overview covers the definition, rationale, objectives, characteristics, steps, types, and methods of sampling in research. From probability sampling to the lottery method, each technique serves a specific purpose in ensuring the reliability and validity of research findings.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SAMPLING J.RAJEES Assistant Professor Department Of Commerce Computer Application St.Joseph s College (Autonomous) Tiruchirappalli
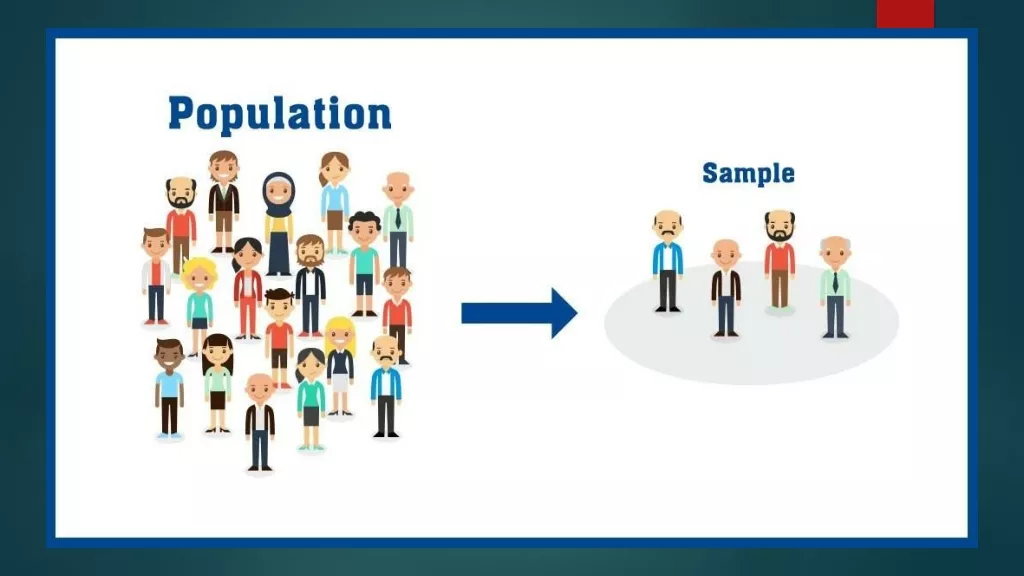
SAMPLING Definition : a sample is a smaller representation of a larger whole samples are devices for learning about large masses by observing a few individuals Snedecor -Goode and Hatt
Why sampling is used Economical Less time consuming Reliability Detailed study Sampling is a scientific technique Greater suitability
Objectives of sampling To make an inference about an unknown parameter from a measurable sample To test the hypotheses relating to population To avoid the vast study about the entire population To obtain quick result
Characteristics of a good sampling Representativeness Independence Adequacy Homogeneity
Steps taken to make the sample useful and reliable Defining the population Specifying the sampling frame Specifying the sampling unit Specifying the method of sampling Determining the size of sample Specifying the sampling plan Selection of sample
Types of sampling methods Probability sampling (or)random sampling Non probability sapling (or ) non random sampling
Probability sampling Random Unrestricted random sampling (or) simple random sampling Lottery method Random number method Restricted random sampling Stratified random sampling Systematic sampling Cluster and area sampling Multi stage sampling Sequential sampling
Lottery method Lottery method of sampling refers to the process of drawing a lot among the population or universe. Under this method the required number of samples are selected from the total population by blindfold from the drum or urn.
Random number method This method is an alternative to lottery method. Samples are drawn by using the table of random numbers. The random numbers are generally obtained by some mechanism that could be expected in a random sequence of the digits 0 to 9
Standard tables of random sample Tippett s (1927) random number tables consisting of 41,600 random digits. Fisher and Yates (1938) table of random numbers with 15,000 random digits. Kendal and Babington Smith (1939) table of random numbers consisting of 1,00,000 random digits. C.R.Rao, Mitra and Mathai(1966) table of random numbers.
Restricted sampling method Under this method the size of the population is restricted to normal size on the basis of certain characteristics.
Methods of obtaining restricted random sample Stratified random sampling Systematic sampling Cluster and area sampling Multi stage sampling Sequential sampling
Stratified random sampling Under this method the population is divided in to some groups or classes(stratum) based on their homogeneity and samples are drawn from each stratum at random .
Systematic sampling Under this method the universe is arranged on the basis of some systems. (alphabetical , numerical , geographical etc.,) Sampling internal (or) K size of population = ---------------------------- size of sample
Cluster and area sampling Cluster sampling refers to the procedure of dividing population into groups called clusters and samples are drawn from these clusters.
Multistage sampling Multi stage sampling is a type of sample design in which some information is collected from the whole sample and additional information is also collected from sub sample of the full sample.
Sequential sampling Under this method , the size of the sample units is not determined in advance , but fixed according to mathematical decision rules based on the survey. This is usually adopted in case of acceptance sampling plan in context of statistical quality control.
NON PRABABILITY SAMPLING NON PRABABILITY SAMPLING Convenience sampling Judgment (or) purposive sampling Quota sampling
Convenience sampling This method also called as chunk method which means to the fraction of population to be invested Eg. Sample obtained from readily available list such as car booking , telephone directories , etc.,
Purposive sampling Under samples are drawn on the basis of personal judgment of a person. this method the
Quota sampling This method is adopted in the market survey