Scaling Latency in Bitcoin: Improving Performance and Security
This content delves into the optimization of latency in Bitcoin transactions, focusing on reducing processing time while preserving security measures. It discusses the challenges associated with latency, strategies to enhance Bitcoin performance, and the trade-offs between latency reduction and security. Additionally, it explores methods to separate security concerns from latency considerations in the context of blockchain technology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lecture 9: Scaling Latency Lecture 9: Scaling Latency
Four modules Four modules Bitcoin (lecture 2-7) Scaling Bitcoin (lecture 8-12) Improve Bitcoin performance while still retain basic structure of the longest chain protocol Throughput (#8) Latency (#9) Storage & compute (#10) Trust taken out externally (#11) Energy (#12) Beyond Bitcoin Applications
Bitcoin latency Bitcoin latency Time from when a transaction was broadcast until the transaction is confirmed in the ledger ?1: Time from when a transaction was broadcast until the transaction is put into a mined block B ?2: Time from when the transaction was put into a mined block B until block B is ?-deep in the longest chain ? = ?1+ ?2 ?2 is the real bottleneck, depends on how large ? is.
Bitcoin latency Bitcoin latency Assume low forking (? 1), ? ? = 1 ? ? From Lecture 6, error probability ? = ? ?? 1 ?log(1 1 ? ?= ?(1 ?) ?log(1 ? = ?))
Bitcoin latency Bitcoin latency ? = ?(1 ?log(1 ?)) Bitcoin: 1 ? = 10 minutes
Improve Bitcoin latency Improve Bitcoin latency Only way to improve latency is to reduce ?; but this reduces security Increase ?; but this also reduces security Ethereum: 1 latency = 25 minutes Way better than Bitcoin performance; improvement simply by picking better parameters. ? = 15s; ? = 100
Improve Bitcoin latency Improve Bitcoin latency Question: can we make relatively small changes to the longest chain protocol and PoW mining while scaling latency? Do not want latency to depend on security level Decouple security from latency
Prism Prism Prism achieves optimal latency Prism 1.0 achieves optimal throughput; last lecture Decoupling principle
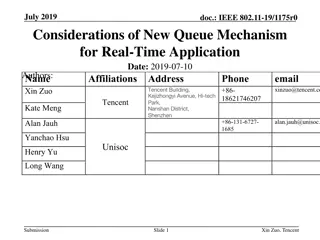
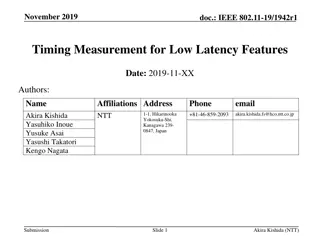
Decoupling voting Decoupling voting K-deep confirmation rule is a form of voting G Satoshi s Table Can think of one block = one vote underneath B K votes in sequence ?-deep Really need k large for sampling the miners 1 deep => .45 25 deep => 0.0006
Bitcoin Bitcoin Bitcoin Deconstruct Voting Proposing Ledger construction 1. Select votes along longest voter chain vote 2. Order the proposer blocks by votes
Bitcoin Bitcoin Bitcoin Bitcoin Deconstruct Deconstruct Deconstruct Deconstruct Prism Prism Fast Confirmation Fast Confirmation Voting Proposing . . . . votes s vote . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Many voter chains Ledger Construction: For each level choose the proposer block with maximum maximum votes
Prism Prism Proposal rule: longest chain Voting rule: a) each voter chain votes for one and only one proposer block at each level b) each voter block votes for all the proposer levels that have not been voted by its parent. Mining rule: honest miner picks to be proposer/voter/transaction block at random
Cryptographic sortition Cryptographic sortition How do you prevent adversary from m focusing its mining power on a specific type of blocks or on a specific voter chain?
Fast confirmation Fast confirmation Bitcoin Bitcoin 1000 Voter Trees G 1000 votes A 1 deep => .45 1-deep 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 Pr(>500 votes reverted) < 0.0006 25 deep => 0.0006 bag of weak classifiers => strong classifier Ledger Construction: For each level choose the proposer block with maximum maximum votes