Scaling Up Communication Strategies for Effective Documentation
Delve into the art of effective communication and documentation processes for scaling up community health initiatives. Explore methods for capturing, organizing, and distributing information, alongside guidelines for team collaboration and best practices in documentation. Learn the importance of clear purpose, avoiding errors, and documenting innovations to report key events successfully.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Communications & Documentation Workshop Community Action for Health Deliberating Pathways to Scaling Up Guwahati January 25, 2017 PREETI SINGH preeti193@gmail.com
GETTING STARTED So, what do you struggle with? How can I help?
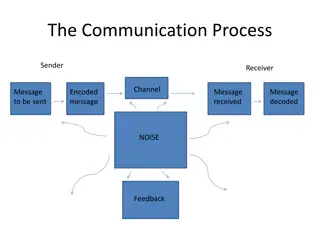
General: EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION ABCs & The Complicated Art of Simplicity Writers versus COMMUNICATORS The ABCs of Effective Communication A = Accuracy B = Brevity C = Clarity Positive Reinforcement Planting Magic Beans & Dealing with Blindspots Ensuring Responsiveness Knowing what you want & how to get it Identifying Essential Ingredients of Communications (e.g.: Dinner for X ) Intra-organisational + Public Communications DOCUMENTATING IT ALL TAKING NOTES; Emails; MoMs; Briefs; Concept Notes; Discussions; Presentations; PPTs; Reports/ Case Stories / all other Documentation DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS Checklists & Etiquette
PROCESS DOCUMENTATION, REPORTS & CASE STORIES UNDERSTANDING TOOLS/CHECKLISTS FOR: CAPTURING THE PROCESS: Interviews; GDs; Videos; Photos; Users observations; Field diaries ORGANISING INFORMATION: Summarising Secondary Resources - knowledge in articles case studies, video bytes VISUALISING PROCESSES: E.g. process documentation software DISTRIBUTING INFO: Email; Pamphlets/Charts; Newspapers; Digital internet MUST : Have clear purpose; Explain motivation; Be kept up-to-date AVOID: Poor writing; Info/ data gaps; Misleading/ unnecessary/ distracting info. Templatise to Standardise, but Adapt Save Time; Effort; Energy + Avoid Errors; Duplication FEATURING: Documentation of Innovations Writing Case Stories Reporting Key Events
DOCUMENTATION Processes, Innovations & More
The PROCESS of DOCUMENTATION How to get there? Team Documentation who does what & dividing core competencies LAYING BREADCRUMBS & GUIDING THE WAY + Emails; Notes; Tracking; MoMs Process Documentation why do it & what does it feed into END GAME? PLANNING: Notes Organising Coordinating/Comparing Assimilating Compiling; Start with Listing (Pre-writing strategy); TARGETING: Audience (What do they know?); How will it be used & by whom; Why do they need it?; Make it person neutral use job titles; DESIGNING: Create small & separate process docs; Identify boundaries (starts & ends); Determine Outputs/ Outcomes; Inputs (Resources); Split into Sequential Steps (Club similar ones); Expand, where reqd. List Pitfalls, Troubleshooting advice etc.; Create Process; Supplement w/- Flowchart/ Graphics/ Screenshots FORMATTING: Easy to scan/read/understand Use layers/ subheadings; Tables; Bullets; Show connections/links to other processes, where reqd. TEST; Review; Feedback; Revise; Update STORE & STANDARDISE: Keep backup in local drives/ cloud; Create a style guide STEPS: Outline Process Name; Boundaries; Outputs; Inputs; Activities; Organization; Review; Roles; Transcribe Process; Final Review; Secure Approval; Put It All Together
Process Documents: A Checklist Make them easy so they are difficult to ignore! How (implementation) > What (Impact) / Who (People neutral?) Goal = Replicability = Roadmap PROVIDE: Consistency; Monitoring; Responsibility; Checklists; Security; Standards True? No process is set in stone Ongoing = EVOLUTION = flexibility. AIMED AT: Transparency; Efficiency (time; resources; costs); Outlining & Allocation; Tracking; Productivity; Performance & Output Quality SHOULD BE: Concise; As Open as possible allowing more people to use them + for easily bringing new people on board a project & as Teaching Tools; Reviewed, at least annually EASY TO : Access, Search & Edit esp. internally/ for multiple stakeholders/ both should allow for New Inputs & Feedback + Facilitate Outsourcing IMPORTANT TO: Break down info into Clear & Concise steps = focus attention IDENTIFY: Gaps & Friction Points & re-build around solutions = Imp. Interventions to eliminate flaws RECORD: (Changing) Perceptions of Stakeholders + Context (the big picture, for individual projects) & Impact + Preserve Knowledge (people neutral) ADDRESS: Bottlenecks; INFORM: Debates/ Discussions; Troubleshooting (Who to call?/ Revisions/ Additions or Deletions; Course Correction) PROBLEMS: Do creators understand it? Special Interest Groups? Honesty? Slower projects?
Quickly ANY QUESTIONS?
CASE STUDIES/ STORIES Why we need them, who are they for, planning one & how it can help
CASE STORIES: Why & what? Can be Celebratory but always with a specific Objective End-Goal/Audience ORIENTED Biases; Subjectivity; Opinion VERSUS Individuality/ Innovation + Inserting your organisation/ entity as an Integral Part of the solution/ success Purpose (examples): documenting a report; doing a research; developing a proposal; documenting an interesting incident Help In Evidence-based Decision Making Definition: Analysis of problem/ success story featuring a unique incident wrt an individual/ group / community/ events/ projects/ government policies/ institutions etc. Problem/ success can be small/ area specific or can prevail in the entire country/ continent Reasons to write case stories: A case study gives an interesting overview of an existing problem or success story It attracts the attention of non-experts to understand the problem or success in a story format It could be an important document for raising funds or mobilizing resources for NGOs It shares evidence for the problem you are trying to explain or a success you want to publicise Steps to Writing: Identify the 'Protagonist / hero ; Research & Collection of Info; Prepare Questions; Catchy Title & Introduction; Background - locate your 'hero'; Body text = the unique story itself; Conclusion + Check: DOES IT CONNECT WITH YOUR TARGET READER??
Quick Checklist: CASE STORIES (contd.) Be VERY clear on: CONTEXT; Your Reader/ TG s needs; Objective Facts Involve the subject from the get-go Write about someone/ something your TG can actually relate to Tell it like any other Story with A BEGINNING, A MIDDLE & AN END = catchy Use numbers effectively + Avoid jargon Use good imagery + easy formatting to help locate key information/ messages Use good visuals/video + Re-purpose content for different user types; Go digital! Don t be shy to get professional help, where possible/ required Basic STRUCTURE: Title Page; Abstract; Introduction; Case presentation; Management & Outcome (Links to the bigger picture why it is important for the reader?); Discussion; Acknowledgements; References; Legends (tables, graphs, figures, charts, pictures); Annexures; Permissions [always a good idea to include specific permission from subject / hero(es) ] - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2597880/ Include: Quotes; Testimonials; A results summary (benefit/ advantage statements that help showcase YOU too); A challenge/ problem summary (should show empathy with your TG); A compelling keyword-friendly title (can align with readers needs); A call to arms/ action; An About Us section
Quicklyonce more ANY QUESTIONS?
REPORTING EVENTS and getting more out of each one!
Reporting Key Events/ Rapporteuring What; When; Where; Who was there? What was discussed; Who said what (careful: Chatham House Rules)? Summarise key discussion points (brief outline of issues/ challenges) What was decided/ how did it conclude/ key messages/outcomes/ recommendations/ follow-up any information on the next one? Make notes that can be USED to feed into other reports/ plans/ docs GO THE EXTRA MILE: Provide an audience profile (+ list speakers/ participants/organisations; curate presentations; Background notes/docs) Provide quotes/ testimonials OWN IT: Give your/ your organisation details for follow-up/ more business
Communications Checklist Make good writing a Habit treat every communication as the real one Always keep it Simple, especially when in doubt Keep the End Game in Mind = You are ONLY the conduit = Win-Win Start NOT from the beginning but from the point of action get right to it! Positive begets positive = you can catch more flies w/- honey than vinegar! Remember the ABCs Never Forget the Audience/ Users Complications = Lost message/ No Use use most effective platform; medium; language Plan Work Backwards from the Goal FINALLY, All communication is about TRUST mistakes versus a pattern (you & others) SIMPLE will always have a larger audience (simple words, short sentences) SHARP will help attract & retain attention SMALL is always bigger (short attention spans we re all human!) MIX IT UP: Don t be Afraid to be Different No one likes to be Bored but Hub & Wheels Approach focus versus embellishing
Once again ANY QUESTIONS?
MORE ON WRITING (FORMAL) REPORTS (?) Basics: What you need to know about reports
Why Report Writing? Opportunity to assimilate reading; research; experience & chance to leverage all this Helps in assessment of integrated learning outcomes Opportunity to locate & use the right info Exercise: to structure material in a logical & cohesive manner Learning to reach well-supported conclusions Making recommendations Helps you master A KEY WORKPLACE SKILL
It must have A Clear Purpose A Specific Audience Choice Information & Select Evidence Toward Analysis of/ Application to a Specific Problem A Clear, Structured format to present Info Easy-to-locate information
It needsTo shoot straight! Direct, PROFESSIONAL approach Economy of words/ economic use of language clear sentences; plain language Planning & Preparation Clarity of Thought/ Evidence/ Inferences/ Conclusion Judicious use of white spaces The correct font Relevant footnotes, supporting tables, figures etc.
Basic Structure Title Page {Purpose (if not clear in title); name; date; author(s)} Terms of Reference, as subtitle/single para {audience; purpose; message(s); methodology} Executive Summary (Abstract) {brief description of content aims; what was found; action points} very precise & concise outline Table of Contents
Basic Structure (contd.) 1 Introduction Can include section each on Methods & Results Findings/ Discussion main body of the report Discuss your material Analyse & present facts & data collected, with specific reference to the problem Clear referencing & citations Clearly-defined segments / sub sections/ bullet points etc. to guide readers
Basic Structure (contd.) 2 Conclusion/ Recommendations Overall significance of report Recap for readers Highlights NO NEW MATERIAL SHOULD BE ADDED HERE! Appendices Charts Questionnaires / Surveys Tables Graphs Transcripts
Basic Structure (contd.) 3 Bibliography/ References Style Guide Acknowledgements Glossary (of technical terms/ abbreviations/ acronyms etc.) NOTE: Structure can vary slightly (esp. order of Biblio. & Glossary & Appendices etc.)
The Process Understanding the Brief (For whom? Why?) Gathering & Selecting Information (expand reading to narrow it down) Organising Material (grouping; sequencing; pruning) Analysing Material (360-ing the evidence) Writing (explained in the next slide) Reviewing & Redrafting (let it breathe!) Presentation (check for corrections, consistency & adherence to basics) Fact-checking & Proof-reading
Writing the Report Introduce main idea of each chapter/ section/ paragraph Explain & expand the idea, defining key terms Present relevant evidence to support point(s) Explain evidence - show how it relates to them Conclude your chapter/ section/ para by either showing its significance to the report as a whole or making a link to the next chapter/section/para
Essential Ingredients A general checklist for writing reports Purpose Backdrop Facts; Numbers & Statistics - evidence Ecosystem what else is out there? Trend Analysis? Conclusion/ Forecast References RE-CHECK: Headlines/ Sub-heads for Sections/ Sub-sections (e.g. the 1.1.1 format explained) References & Citations acknowledgements
Respecting the Format What it isn t What it is Opinion Summary of research & findings geared toward a specific issue/ problem A first-person account Conjecture A chance to write simply strip your analytical & writing skills down to their very basic elements A chance to vent, circle aimlessly or waffle
References/ Sample Readings: All About Process Documentation , Lucidchart (https://www.lucidchart.com/pages/process- documentation); Last accessed on 22-01-2017 'How To Document Your Current Processes In 10 Easy Steps , QuickBase, February 4, 2015; ; Last accessed on 22-01-2017 (http://www.quickbase.com/blog/how-to-document-your-current- processes-in-10-easy-steps) 'How to write a business report', Victoria Business School, University of Wellington; March 2016; Last accessed on 23-01-2017 (http://www.victoria.ac.nz/vbs/teaching/resources/VBS-Report-Writing- Guide-2016.pdf) Writing reports , University of Leicester; Last accessed on 23-01-2017 http://www2.le.ac.uk/offices/ld/resources/writing/writing-resources/reports Sample READINGS: John A. Joseph, 'Process Documentation', UNESCO link; Last accessed on 23-01-2017 (http://www.unesco.org/education/aladin/paldin/pdf/course02/unit_02.pdf) Process Documentation, Sustainable Sanitation and Waste Management (SSWM) link; Last accessed on 23-01-2017 (http://www.sswm.info/content/process-documentation)