Second Law of Thermodynamics
Explore the concept of the second law of thermodynamics, focusing on energy dispersion, entropy, and the effects of temperature on spontaneity in chemical reactions. Learn about the balance between energy randomness and positional randomness at different temperatures.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
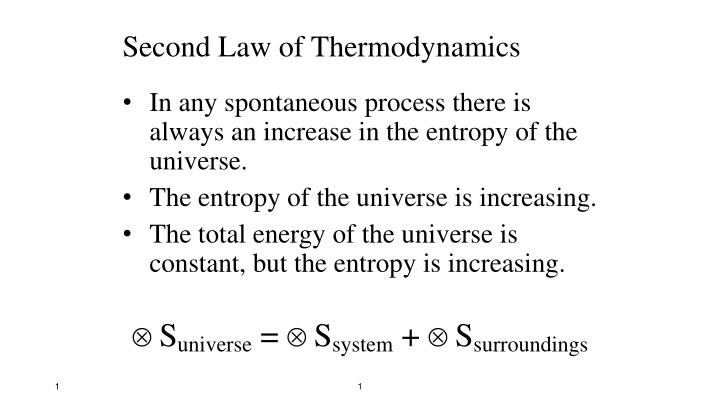
Second Law of Thermodynamics In any spontaneous process there is always an increase in the entropy of the universe. The entropy of the universe is increasing. The total energy of the universe is constant, but the entropy is increasing. Suniverse= Ssystem+ Ssurroundings 1 1
Second Law of Thermodynamics Energy tends to flow from a high energy concentration to a dispersed energy state; Energy dispersion or diffusion is a spontaneous process. Dispersed or diffused energy is called entropy According to S.L.O.T, a process/reaction is spontaneous if the entropy of the universe (system + surrounding) increases. 2 1
Concept Check Effect of Temperature on Spontaneity For the processA(l) involves an increase in energy randomness? Positional randomness? Explain your answer. A(s), which direction As temperature increases/decreases (answer for both), which takes precedence? Why? At what temperature is there a balance between energy randomness and positional randomness? 3 1
Since energy is required to melt a solid, the reaction as written is exothermic. Thus, energy randomness favors the right (product; solid). Since a liquid has less order than a solid, positional randomness favors the left (reactant; liquid). As temperature increases, positional randomness is favored (at higher temperatures the fact that energy is released becomes less important). As temperature decreases, energy randomness is favored. There is a balance at the melting point.
Concept Check Describe the following as spontaneous/non-spontaneous/cannot tell, and explain. A reaction that is: (a) Exothermic and becomes more positionally random Spontaneous (b) Exothermic and becomes less positionally random Cannot tell (c) Endothermic and becomes more positionally random Cannot tell (d) Endothermic and becomes less positionally random Not spontaneous Explain how temperature affects your answers. 5 1
Ssurr The sign of Ssurrdepends on the direction of the heat flow. The magnitude of Ssurrdepends on the temperature. 6 1