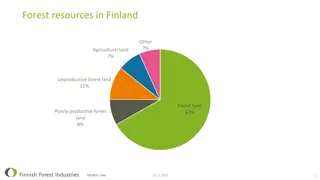
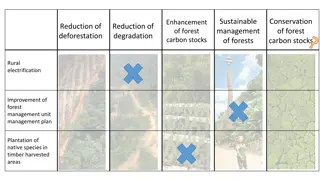
Silviculture and Sustainable Forest Management
Silviculture is the art and science of controlling the establishment, growth, composition, health, and quality of forests to meet specific objectives. It involves applying treatments and practices to influence forest ecosystems towards desired outcomes. Sustainable timber production, biodiversity conservation, forest regeneration, forest health management, and carbon sequestration are key objectives of silviculture. Different silvicultural systems guide forest management activities over time, including clear-cutting, shelterwood, selection, and coppice systems. Silvicultural practices like site preparation, tree planting, thinning, pruning, stand tending, and rehabilitation play essential roles in maintaining forest health and productivity. Forest certification programs such as FSC and PEFC promote sustainable forest management practices.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Forest managment Forth Stage Lecture 3 Salahaddin University -Erbil College of Agricultural Engineering Sciences Forest Department 2023_2024 Ekhlass.hamad@su.edu.krd
Silviculture and Sustainable Forest Management Silviculture is the art and science of controlling the establishment, growth, composition, health, and quality of forests to meet specific objectives. It involves applying various treatments and practices to influence forest ecosystems towards desired outcomes.
Objectives of Silviculture Sustainable timber production: Silviculture aims to maximize timber yields while ensuring the long-term health and productivity of forest stands. Biodiversity conservation: Silvicultural practices can enhance habitat diversity, promote the growth of desirable species, and maintain ecological balance. Forest regeneration: Silviculture includes techniques to regenerate forests after disturbances like harvesting or natural disasters, ensuring the continuity of forest resources. Forest health management: Silviculture helps prevent and mitigate forest health issues, such as insect outbreaks or disease infestations. Carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation: Silviculture practices can optimize carbon storage in forests, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Silvicultural Systems Silvicultural systems are approaches that guide forest management activities over time. Different systems include clear-cutting, shelterwood, selection, and coppice systems, among others. The choice of silvicultural system depends on forest characteristics, management objectives, and ecological considerations.
Silvicultural Practices Site preparation: Before planting or regeneration, site preparation involves removing competing vegetation, reducing fuel loads, and improving soil conditions to promote successful establishment. Tree planting: Planting seedlings or establishing new trees helps regenerate forests and maintain desired species composition. Thinning: Thinning involves selectively removing trees to enhance growth and vigor of the remaining trees, improve stand structure, and promote species diversity. Pruning: Pruning is the removal of lower branches from trees to improve timber quality, reduce fire risk, and increase light penetration to the forest floor. Stand tending: Stand tending activities, such as fertilization, weeding, and pest control, aim to promote healthy growth and improve overall forest condition. Rehabilitation: After disturbances, rehabilitation practices restore forests by controlling erosion, planting new seedlings, and managing invasive species.
Sustainable Forest Certification and Silviculture Forest certification programs, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC), promote sustainable forest management. Silviculture practices play a vital role in meeting certification standards by ensuring responsible harvesting, biodiversity conservation, and the protection of ecological processes.
Challenges in Silviculture Climate change: Changing climatic conditions affect forest growth, species composition, and the spread of pests and diseases. Invasive species: Invasive plant species can disrupt forest ecosystems and hinder the growth of desired tree species. Changing market demands: Shifts in consumer preferences and market demands for forest products require adaptive management and the cultivation of new species. Socio-economic factors: Balancing economic objectives with ecological and social considerations is often complex, particularly in communities dependent on forest resources.