Single-Core Lock Implementation
This technical content discusses lock implementation for single-core and multi-core systems, covering various versions and scenarios. It includes code snippets, struct definitions, and methods for acquiring and releasing locks in a synchronized manner. The slides illustrate different approaches to ensure data integrity and prevent race conditions in concurrent programming.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
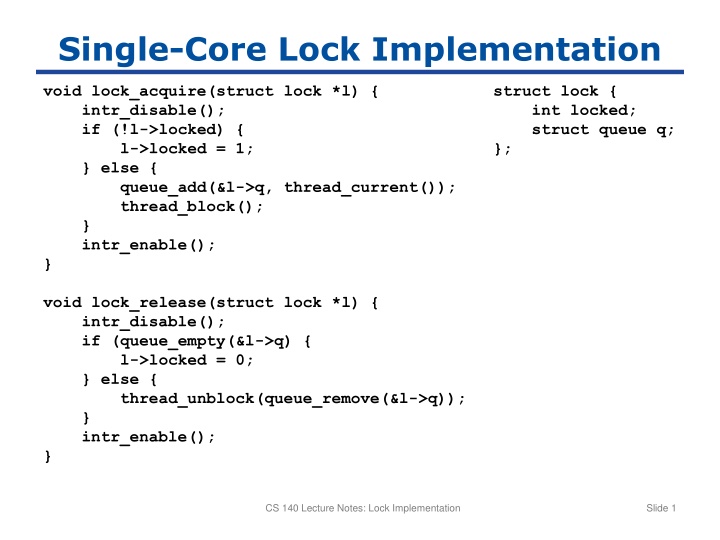
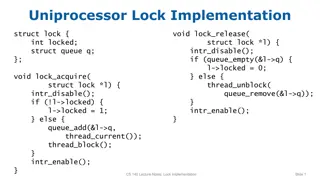
Single-Core Lock Implementation void lock_acquire(struct lock *l) { intr_disable(); if (!l->locked) { l->locked = 1; } else { queue_add(&l->q, thread_current()); thread_block(); } intr_enable(); } struct lock { int locked; struct queue q; }; void lock_release(struct lock *l) { intr_disable(); if (queue_empty(&l->q) { l->locked = 0; } else { thread_unblock(queue_remove(&l->q)); } intr_enable(); } CS 140 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 1
Locks for Multi-Core, v1 struct lock { int locked; }; void lock_release( struct lock *l) { l->locked = 0; } void lock_acquire( struct lock *l) { while (swap(&l->locked, 1)) { /* Do nothing */ } } CS 140 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 2
Locks for Multi-Core, v2 struct lock { int locked; struct queue q; }; void lock_release( struct lock *l) { if (queue_empty(&l->q) { l->locked = 0; } else { thread_unblock( queue_remove(&l->q)); } } void lock_acquire( struct lock *l) { if (swap(&l->locked, 1)) { queue_add(&l->q, thread_current()); thread_block(); } } CS 140 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 3
Locks for Multi-Core, v3 struct lock { int locked; struct queue q; int sync; }; void lock_release( struct lock *l) { while (swap(&l->sync, 1)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (queue_empty(&l->q) { l->locked = 0; } else { thread_unblock( queue_remove(&l->q)); } l->sync = 0; } void lock_acquire( struct lock *l) { while (swap(&l->sync, 1)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (!l->locked) { l->locked = 1; l->sync = 0; } else { queue_add(&l->q, thread_current()); l->sync = 0; thread_block(); } } CS 140 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 4
Locks for Multi-Core, v4 struct lock { int locked; struct queue q; int sync; }; void lock_release( struct lock *l) { while (swap(&l->sync, 1)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (queue_empty(&l->q) { l->locked = 0; } else { thread_unblock( queue_remove(&l->q)); } l->sync = 0; } void lock_acquire( struct lock *l) { while (swap(&l->sync, 1)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (!l->locked) { l->locked = 1; l->sync = 0; } else { queue_add(&l->q, thread_current()); thread_block(&l->sync); } } CS 140 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 5
Locks for Multi-Core, v5 struct lock { int locked; struct queue q; int sync; }; void lock_release( struct lock *l) { intr_disable(); while (swap(&l->sync, 1)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (queue_empty(&l->q) { l->locked = 0; } else { thread_unblock( queue_remove(&l->q)); } l->sync = 0; intr_enable(); } void lock_acquire( struct lock *l) { intr_disable(); while (swap(&l->sync, 1)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (!l->locked) { l->locked = 1; l->sync = 0; } else { queue_add(&l->q, thread_current()); thread_block(&l->sync); } intr_enable(); } CS 140 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 6