Skeletal System Structure & Function
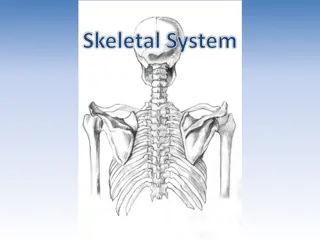
The skeletal system in the human body consists of 206 bones divided into axial and appendicular skeletons. These bones have various functions and meet at joints, supporting movement and protecting vital organs like the brain, ribs, and pelvis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
P1 Describe the Structure & Function of the Skeletal System Unit 1 Principles of Anatomy & Physiology in Sport
The Skeletal System Consists of 206 bones Bones = living tissue, constantly adapting to stresses placed on them Split into Axial & Appendicular skeleton Has different types of bones Has a number of functions Bones meet together at joints
Cranium Mandible Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Vertebral Column Humerus Ulna Pelvis Sacrum Radius Carpals Coccyx Ischium Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Patella Tibia Tarsals Fibula Metatarsals Phalanges
Cranium box like structure brain sits inside protects the brain made up of a number of different bones bones fuse together between 1-3 yrs old Mandible jaw bone Sternum breast bone long, flat bone centre of chest
Ribs long, flat bones 12 pairs 1st 7 pairs attached to sternum other 5 pairs called false ribs Pelvis made up of 2 sets of 3 bones Ilium upper wing like bones, provides the sockets for the hip bones, upper edge = iliac crest Pubis pubic bone, front of the pelvis Ischium lower, posterior bones, sitting bones
Clavicle collar bone long, thin bone makes up the anterior (front) of the shoulder girdle is a strong, mobile attachment for arms Scapula large, triangle shape back (posterior) part of shoulder girdle Humerus long bone, upper arm proximal head = shoulder joint distal end = elbow joint
Ulna Forearm little finger side Radius forearm thumb side moves around ulna when turning hand Carpals 8 short bones wrist 2 rows of 4 Metacarpals 5 long bones palm of the hand run from the carpals to each finger & thumb
Phalanges small long bones fingers & toes 3 in each finger & toes 2 in each thumb & big toe Femur thigh bone longest & strongest top (proximal end) sits in socket of pelvis bottom (distal end) forms the knee joint Patella kneecap large, triangle shaped sesamoid bone sits inside the quadriceps tendon protects knee joint
Tibia shin bone medial, thicker bone proximal end = knee joint with femur distal end = ankle joint Fibula lateral, thinner bone non weight bearing distal end = ankle joint Tarsals 7 bones (ankle) Metatarsals 5 foot bones
Skeletal System Information Appendicular System 220px-Appendicular_skeleton_diagram 126 bones Axial System 240px-Axial_skeleton_diagram 80 bones
220px-Appendicular_skeleton_diagram Appendicular System 126 bones Upper body Lower body Clavicle = collar bone Pelvis = 2 x 3 bones Scapula = Shoulder blade Femur = Thigh Humerus = upper arm Patella = Kneecap Radius = to the thumb Tibia = Shin Ulna = to the little finger Fibular = Outside/ankle Carpals = wrist Tarsals = under ankle Metacarpals = hand Metatarsals = Foot Phalanges = fingers Phalanges = Toes 240px-Axial_skeleton_diagram Axial System 80 bones Skull = 28 bones Hyoid Sternum Ribs = 12 pairs Vertebral Column = 33 vertebrae
Vertebral Column 33 Bones 5 Sections C 1 - 7 T 1 - 12 L 1 - 5 S 1 - 5 Coccyx 1 - 4
Vertebral Column Spine 33 irregular bones Approx 40% of your height Very small movement between each vertebrae Lots of movement of spine altogether
Bones Living tissue = grow during childhood Bleed & hurt if damaged Able to repair if broken Ossification a hardening process that takes place when bones mature. Makes bones solid structures that can withstand a lot of pressure/stresses. Collagen = resilience Calcium = strength
Types of Bones F.L.I.S.S. F L I S S lat Protection Scapula, sternum, ribs, pelvis ongMovement Femur, humorus, tibia rregularShape Vertebrae, facial bones hortCube shaped Carpals, tarsals esamoidInside a tendon Patella