Social Identity and Personal Identity in Society
Explore the concept of identity, including social identities such as collective, roles, personal, and how identities are shaped by interactions with others. Learn about influential sociologists like Charles Cooley and Erving Goffman who studied the complexities of identity formation through social relationships.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
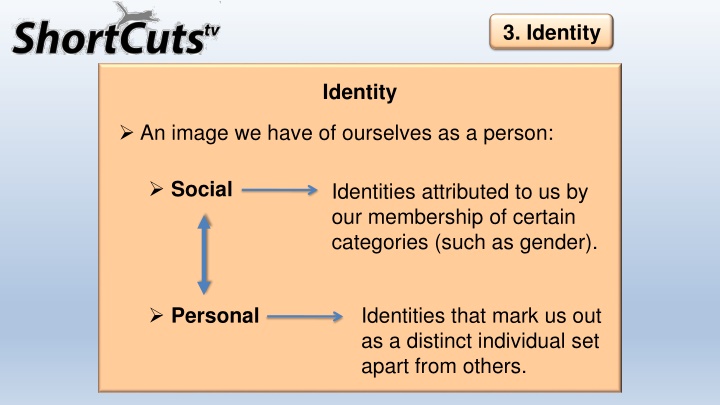
3. Identity Identity An image we have of ourselves as a person: Social Identities attributed to us by our membership of certain categories (such as gender). Identities that mark us out as a distinct individual set apart from others. Personal
3. Identity Social Identity Collective identities those we share with others. Examples: Nation Region Ethnicity Gender Class Age
3. Identity Roles Another important source of social identity. Examples: Mother Father. Student Teacher. Employer Employee. Doctor Patient. Link between the individual and the social world. Locate and position the individual in the social world.
3. Identity Personal Identity Our unique characteristics - what separates us from others. Common sense: sees personal identity as fixed and purely individual. Sociologically: personal identity develops through primary and secondary socialisation: Learning who we are through social interaction.
3. Identity Charles Cooley Looking-glass self: Images of ourselves reflected in the reactions of others Identities created through social interaction and social relationships: I know who I am by understanding how others see me.
3. Identity Erving Goffman Seeing ourselves in relation to how others see us. Focus on how identities are: Presented and managed in everyday life. Masks we put on to negotiate everyday situations. Identities change as social contexts change.
3. Identity Identity or Identities? Do we have: Single or true identity? Multiple identities? In different situations we assume different identities. School? Home? Supermarket? Club?
3. Identity Identities: Key Points Arise from social life and social interaction Need to be sustained through the reactions of others. Can easily be fractured and damaged (spoiled identities).






















