Sources of Variability in Experiment Design
In research studies, the number of trials conducted can vary based on the sources of variability within and between participants. Social psychology studies focus on variability between individuals, while visual psychophysics studies highlight variability within participants due to attentional factors. Cognitive psychology experiments involve both within and between participant variability. The task discussed in this content requires multiple trials to assess attention across different conditions. The variation in trials and participants helps researchers account for different effects and ensure robust findings in their experiments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
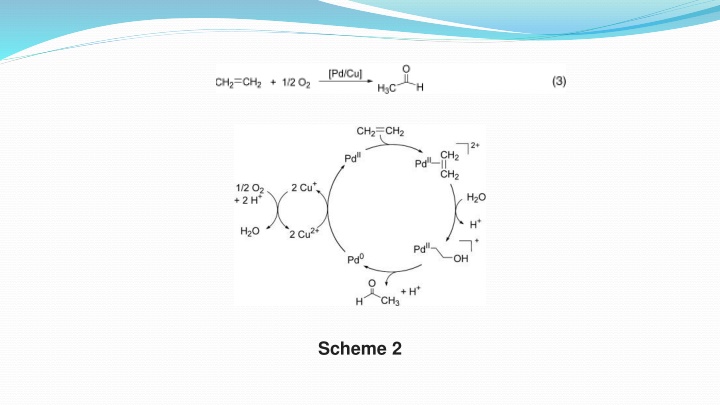
Palladium is perhaps the most active and versatile transition metal employed in organic synthesis, catalyzing both oxidative and ations,Prominent examples include the Wacker process [Eq. (3), oxidative] and numerous cross coupling reactions between nucleophilic and electrophilic partners [Eqs.(4) (7), nonoxidative]. The latter nonoxidative catalytic transformations are among the most efficient carbon carbon and carbon heteroatom bond forming reactions in organic chemistry. The reduced attention to oxidation reactions possibly reflects the added complexity that arises from the need for a stoichiometric oxidant to regenerate the active catalyst. In most palladium catalyzed oxidation reactions, stoichiometric oxidants such as copper (II) salts, benzoquinone, and alkyl hydroperoxides must be used because molecular oxygen is not an effective oxidant. nonoxidative transform-
A persistent problem in both oxidative and nonoxidative palladium catalysis is decomposition of the homogeneous catalysts into inactive bulk metal (Scheme 3). The dramatic success of palladium catalyzedcross coupling reactions reflects, in part, the utility of phosphanes and other soft donor ligands to stabilize palladium(0). These ligands also serve to promote reactions between palladium(0) and substrates, such as the oxidative addition of an aryl halide (Scheme 3 a). Dramatic ligand effects have been observed, and certain palladium/ligand combinations allow more than 1000000 catalytic turnovers. Unfortunately, similar success has not been achieved in oxidation catalysis. Most common ligands decompose rapidly under oxidizing reaction conditions, and therefore palladium oxidation chemistry has been dominated by the use of simple palladium salts and their solvates such as palladium acetate, palladium chloride, and [(CH3CN)2PdCl2].
Simplified cross coupling (a) and oxidation (b) reactions. This Review surveys the development of homogeneous palladium catalyzed oxidation reactions that undergo direct dioxygen coupled catalytic turnover without a redox active cocatalyst. These results promise a significant increase in the scope of aerobic oxidation reactions. In many of these reactions, the identification of oxidatively stable organic ligands plays an important role in the reaction success. Palladium mediated oxidation stoichiometric palladium, palladium(II)/cocatalyst systems, palladium colloids, and heterogeneous catalysts will be cited in certain cases, but numerous excellent monographs and reviews of these topics are available elsewhere. catalytic cycles of palladium catalyzed reactions that use
2. Palladium Oxidase: Reaction and Catalyst System Direct dioxygen coupled turnover significantly enhances the appeal of palladium catalyzed oxidation reactions by lowering cost, increasing net atom efficiency, facilitating product isolation, and, in many cases, improving reaction selectivity. During the past 10 years, the scope of these reactions has expanded considerably. The most prominent reaction classes developed to date consist of alcohol oxidation, that is, dehydrogenation [Eq. (8)], and oxidative couplings between substrates such as alkenes and various carbon and heteroatom nucleophiles [Eq. (9,10)].