SQL Techniques for Creating and Defining Tables Efficiently
Learn how to create tables in SQL by defining column structures, copying existing tables, and inserting data in one query. Explore different methods, including defining columns manually or copying from another table. Understand ANSI compliance for data types and how to name and define columns appropriately.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
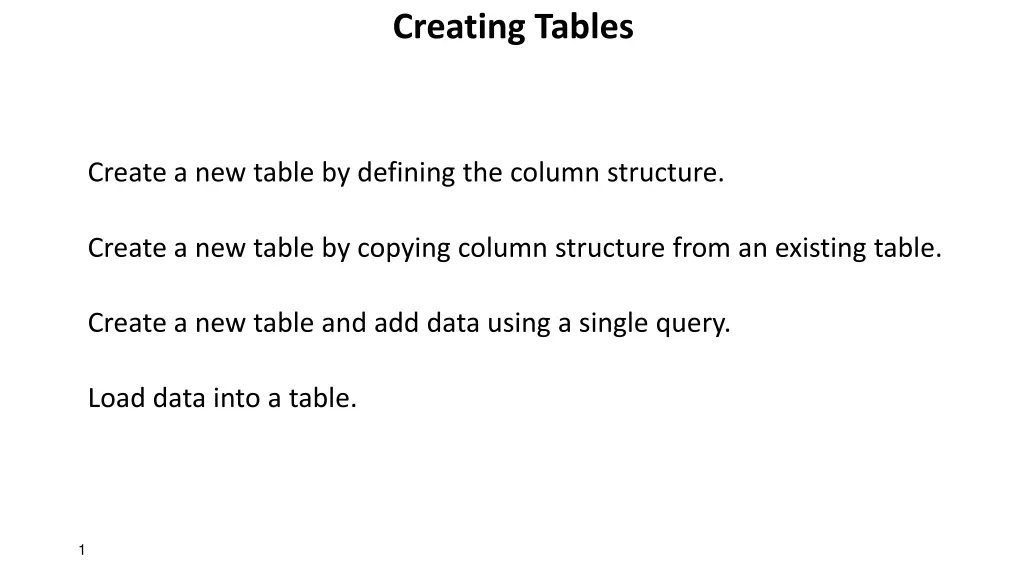
Creating Tables Create a new table by defining the column structure. Create a new table by copying column structure from an existing table. Create a new table and add data using a single query. Load data into a table. 1
Creating Tables with SQL Multiple techniques are used to create tables and insert data into tables with SQL. Method Syntax Result CREATE TABLE table-name (column-name type(length) <, ...column-name type(length)>); Create an empty table by manually specifying all column attributes. 1 CREATE TABLE table-name LIKE old-table-name; Create an empty table by copying column attributes from an existing table using a LIKE clause. 2 CREATE TABLE table-name AS query- expression; Create a table and add data all in one step, using a query. 3 2
Creating Tables Method 1: Define the columns. General form of the CREATE TABLE statement: CREATE TABLE table-name (column-name type(length) <, ...column-name type(length)> ); 3
Method 1: Defining Columns The table definition is enclosed in parentheses. Individual column definitions are separated by commas. proc proc sql create table Discounts (Product_ID num format=z12., Start_Date date, End_Date date, Discount num format=percent.); quit quit; proc proc contents contents data=discounts;run sql; Name the new table. Define the columns. run; 4
Method 1: Defining Columns For ANSI compliance, PROC SQL accepts the following data types in table definitions: ANSI Type Resulting SAS Type Default Length Default Format CHAR(n) Character 8 $w. VARCHAR Character 8 $w. INTEGER Numeric 8 BEST. SMALLINT Numeric 8 BEST. DECIMAL Numeric 8 BEST. NUMERIC Numeric 8 BEST. FLOAT Numeric 8 BEST. REAL Numeric 8 BEST. DOUBLE PRECISION Numeric 8 BEST. DATE Numeric 8 DATE. 5
Method 1: Defining Columns proc proc sql create table Testing_Types (Char_Column char(4 4), Varchar_Column varchar, Int_Column int, SmallInt_Column smallint, Dec_Column dec, Num_Column num, Float_Column float, Real_Column real, Date_Column date, Double_Column double precision); quit quit; proc proc contents contents data=testing_types;run sql; run; 6
Creating Tables Method 2: Copy the table structure. CREATE TABLE table-name-2 LIKE table-name-1; 7
Method 2: Copying Table Structure proc proc sql create table work.New_Sales_Staff like orion.Sales ; quit quit; proc proc contents contents data=new_sales_staff; run run; sql; 8
Creating Tables (Review) Method 3: Create and populate a table with an SQL query. CREATE TABLE table-name AS query-expression; 9
Method 3: Create and Populate a Table with an SQL Query (Review) proc proc sql create table work.Melbourne as select Employee_Name as Name,Salary from orion.Staff as s, orion.Employee_addresses as a where s.Employee_ID=a.Employee_ID and City ="Melbourne"; quit quit; proc proc contents contents data=melbourne;run sql; run; 10
Adding Data to a Table, the INSERT Statement The INSERT statement can be used to add data to an empty table, or to append data to a table that already contains data, using one of three methods. Method Syntax Description INSERT INTO table-name SET column-name=value, column-name=value,...; One clause per row using column-value pairs A INSERT INTO table-name <(column list)> VALUES (value,value,...); One clause per row using positional values B INSERT INTO table-name <(column list)> SELECT columns FROM table-name; A query returning multiple rows, and based on positional values C 11
Create the example table, discounts proc proc sql create table Discounts (Product_ID num format=z12., Start_Date date, End_Date date, Discount num format=percent.); quit quit; proc proc contents contents data=discounts;run sql; run;
Method A: Adding Data with a SET Clause The SET clause requires that you add data using column name value pairs: proc proc sql insert into Discounts set Product_ID=230100300006 Start_Date='01MAR2007'd End_Date='15MAR2007'd set Product_ID=230100600018 Start_Date='16MAR2007'd End_Date='31MAR2007'd ; quit quit; proc proc print print data=discounts;run sql; 230100300006, '01MAR2007'd, '15MAR2007'd,Discount=.33 230100600018, '16MAR2007'd, '31MAR2007'd, Discount=.15 .33 .15 run; 13
Method B: Adding Data with a VALUES Clause proc proc sql create table Discounts (Product_ID num format=z12., Start_Date date, End_Date date, Discount num format=percent.) ; insert into Discounts values (230100300006 230100300006,'01MAR2007'd '15MAR2007'd '15MAR2007'd,.33 values (230100600018 230100600018,'16MAR2007'd '31MAR2007'd '31MAR2007'd,.15 ; select * from discounts; quit quit; sql; '01MAR2007'd, .33) '16MAR2007'd, .15) The VALUES clause adds data to the columns in a single row of data. The VALUES clause must produce values in the same order as the INSERT INTO statement column list. 14
Method B: Adding Data with a VALUES Clause proc proc sql sql; create table Discounts (Product_ID num format=z12., Start_Date date, End_Date date, Discount num format=percent.) ; insert into Discounts (Start_Date,End_Date, Product_ID, Discount) values ('01MAR2007'd '01MAR2007'd,'15MAR2007'd '15MAR2007'd,230100300006 values ('16MAR2007'd '16MAR2007'd,'31MAR2007'd '31MAR2007'd,230100600018 ; 230100300006,.33 230100600018,.15 .33) .15) select * from discounts; quit quit; Optionally, the INSERT statement can list the columns into which data is to be inserted, in the order in which the VALUES clause will provide the data. 15
Method C: Adding Data with a Query proc proc sql sql; create table Discounts (Product_ID num format=z12., Start_Date date, End_Date date, Discount num format=percent.) ; insert into Discounts (Product_ID,Discount,Start_Date,End_Date) select distinct Product_ID,.35 '01MAR2007'd '01MAR2007'd,'31mar2007'd '31mar2007'd from orion.Product_Dim where Supplier_Name contains 'Pro Sportswear Inc' ; select * from discounts; quit quit; .35, Query results are inserted positionally. The query must produce values in the same order as the INSERT statement column list. 16
