Stepper Motors: Types, Design, and Applications
Discover the different types of stepper motors such as Hybrid (HB) motors and disc magnet motors, their unique features, advantages, and applications. Learn about the classification based on size and power, as well as the drive modes used in stepper motor systems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
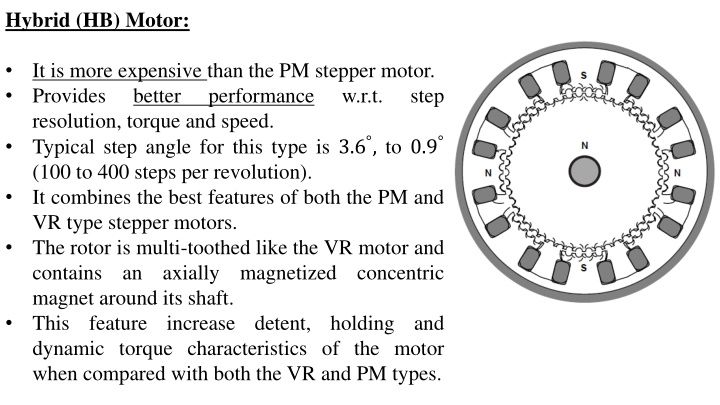
Hybrid (HB) Motor: It is more expensive than the PM stepper motor. Provides better performance resolution, torque and speed. Typical step angle for this type is 3.6 , to 0.9 (100 to 400 steps per revolution). It combines the best features of both the PM and VR type stepper motors. The rotor is multi-toothed like the VR motor and contains an axially magnetized concentric magnet around its shaft. This feature increase detent, holding and dynamic torque characteristics of the motor when compared with both the VR and PM types. w.r.t. step
There also exist some special stepper motor designs. One is the disc magnet motor. Here the rotor is designed as a disc with rare earth magnets. This motor type has some advantages such as very low inertia and an optimized magnetic flow path with no coupling between the two stator windings. These qualities are essential in some applications.
Size and Power Stepper motors are classified according to frame sizes which corresponding to the diameter of the body of the motor. For instance, a size 11 stepper motor has a body diameter of approximately 1.1 inches. Likewise a size 23 stepper motor has a body diameter of 2.3 inches (58mm). The body length may however, vary from motor to motor within the same frame size classification. As a general rule the available torque output from a motor of a particular frame size will increase with increased body length. Power levels for IC-driven stepper motors typically range from below a Watt for very small motor up to 10-20 Watts for larger motors.








