Stress Ulcers: Lesions in Gastric Mucosa Due to Ischemia
Stress ulcers are acute lesions in the gastric mucosa caused by ischemia, typically affecting ICU patients. Learn about risk factors, epidemiology, and pathophysiology of stress ulcers, along with initial management of gastric bleeding.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dr. SaptoPriatmo, Sp.PD SMF Penyakit Dalam RS BETHESDA STRESS ULCER
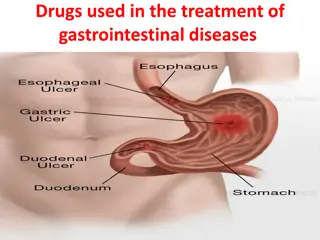
Definition of Stress Ulcers Adanya lesi/ perlukaan pada mukosa gaster yang bersifat akutdan disebabkan oleh iskemik pada mukosa gaster
Stress Ulcers UlserasiGastrointestinal bagian atas lambung Duodenum Perdarahan makroskopis ASHP Therapeutic Guidelines on Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis, AJHP 1999;56(4) 347-379
Epidemiologi Stress ulcer masih sering didapatkan pada pasien ICU (>30% of ICU patients) Pasien < 5% pasien ICU dg perdarahan makroskopik 1. 2. ASHP Therapeutic Guidelines on Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis, AJHP 1999;56(4) 347-379 Del Valle, J. Chapter 287 - Peptic Ulcer Disease and Related Disorders , Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine - 17th Ed. (2008).
Pathophysiologi Stress Ulcers Etiologi complek Berkurangnya pH Gastric Iskemik Produksi mukus gaster berkurang Biasanya terjadi 24 48 jam setelah taruma/stres Del Valle, J. Chapter 287 - Peptic Ulcer Disease and Related Disorders , Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine - 17th Ed. (2008).
FAKTOR RISIKO STRESS ULCER Gagal nafas dan memerlukan ventilator Syok Sepsis berat Gangguan pembukuan darah (DIC) Trauma kepala berat Luka bakar yang luas Gagal multi organ
Morbiditas/Mortalitas Mortalitas pasien : 48.5% dg perdarahan yg bermakn 9.1% tanpa perdarahan yg bermakna Cook DJ, et al. Risk factors for gastrointestinal bleeding in critically ill patients. NEJM 1994;330(6):377-81
Penatalaksanaan awal perdarahan lambung Pengobatan perdarahan ulkus peptikum bertujuan untuk menstabilkan sirkulasi, menghentikan perdarahan yang sedang terjadi dan mencegah perdarahan ulang. Adapun pengobatannya termasuk: Penggantian cairan (tranfusi darah bila diperlukan) Endoskopi dengan endoscopic haemostasis bila dibutuhkan Tindakan bedah, bila perdarahan tidak bisa dikontrol dengan metode diatas Leontiadis GI, et al. Health Technol Assess 2007;11:1 164
ASAM LAMBUNG MENGHAMBAT HEMOSTASIS PADA PERDARAHAN ULKUS PEPTIKUM
pH > 6 diperlukan untuk kestabilan agregasi platelet Agregasi (%) 0 ADP pH=6,0 Disagregasi=77% 20 40 Buffer 60 pH=6,4 Disagregasi =16% 80 pH=7,3 Disagregasi =0% 100 0 1 2 3 4 5 Waktu (menit) ADP,adenosine diphosphate Green FW, et al. Gastroenterology 1978;74:38 43
Antagonis reseptor H2tidak dapat meningkatkan pH sampai 6 Tidak ada data pendukung mengenai penggunaan antagonis reseptor H2 (pada perdarahan non variseal), dan obat ini tidak dapat meningkatkan pH > 6 secara konsisten. Non-variceal upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage: guidelines British Society of Gastroenterology Palmer KR, et al. Gut 2002;51(Suppl IV):iv1 iv6
Guidelines merekomendasikan pemberian PPI iv dosis tinggi untuk pengobatan perdarahan ulkus peptikum PPI iv bolus dilanjutkan dengan PPI infus efektif dalam menurunkan perdarahan ulang pada pasien yang sudah menjalani terapi endoskopi Evidence-based management guidelines developed by the multidisciplinary Non-variceal Upper GI Bleeding Consensus Conference Group Barkun AN, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152:101-113.
Guidelines merekomendasikan pemberian PPI oral setelah pemberian sediaan PPI iv Setelah keluar dari rumah sakit, pasien harus diberi PPI oral 1 kali sehari dengan durasi sesuai dengan penyakit penyebabnya Evidence-based management guidelines developed by the multidisciplinary Non-variceal Upper GI Bleeding Consensus Conference Group Barkun AN, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152:101-113.
PENATALAKSANAAN Pasang infus dg cairan kristaloid untuk mempertahankan hemodinamik Bila diperlukan dapat diberi cairan koloid Pasang NGT dan spool air es atau NaCl Puasakan dan segera diberi diit cair setelah NGT jernih Transfusi darah dengan PRC atau WB bila perdarahan banyak Beri PPI (omeprazol, pantantoprazol) iv Sucralfat
PENCEGAHAN Profilaksi dengan PPI, H2RA dan sukralfat pada pasien sakit kritis dapat menurunkan insidensi Stress nulcer 50% Direkomendasikan pemberian profilaksis pada semua pasien dg sakit kritis
KOMPLIKASI Perdarahan saluran cerna Syok Pneumonia Kematian