Structure and Functions of Proteins
Proteins are essential macromolecules composed of amino acid chains, contributing to various biological roles. Explore the structure, types, and bonds of proteins to understand their significance in biological processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dr. C. Mercy, Assistant professor, PG Department of zoology, Sarah Tucker College, Tirunelveli.
CONTENT INTRODUCTION STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS SHAPE OF PROTEINS CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEINS BIOLOGICALS OF ROLES PROTEINS FUNCTION OF PROTEINS CONCLUSION
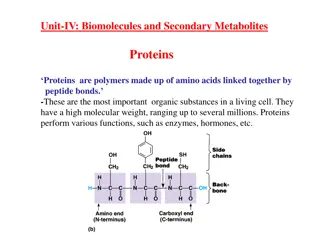
introduction Protein is a macromolecules composed of one or more polypeptide chains possessing a characteristic amino acid sequence. It is a polymer of amino acids. It is the body builder. The term protein was first proposed by Berzelius Haemoglobin,myoglobin,myosin,actin,albumin,gl obulin,are important proteins.
STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Protein are polypeptides with more than 100 amino acid residues. Protein are polymer of amino acid monomers. The amino acid are linked together to form a chain called peptide chain. It is four types; Dipeptide Tripeptide Oligopeptide polypeptide
types Dipeptide; It is 2 amino acid resides. Tripeptide; It is 3 amino acid monomers. Oligopeptide; It is made up less than 10 amino acid. Polypeptide; it is made up more than 10 amino acid.
Chemical bond structure Protein are the polymer of amino acid monomer. Any two amino acid monomer are linked together by chemical bonds. They are 5 types PEPTIDE BONDS DISULFIDE BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS NONPOLAR BONDS IONIC BONDS
CONTINUE Peptide bonds; it is amide bond c-atom of cooH group one amino acid N-atom of NH2 group. Disulfides bonds; it is a covalent bridge two polypeptide chains a cystine residue. Hydrogen bonds; it is single atom two electro negative atom. It is weak bond. It is low energy bond.
Conti. NONPOLAR BONDS; it is nonpoler group with aqueous system is bonds. Ionic bonds; it is formed ionisation.it is transfer one atom to another. -coo mg=ooc- -NH3-OOC-
SHAPES OF PROTEINS Protein are either fibrous or globular. The fibrous protein are in the from of long fibres.The are formed one or more polypeptide chains. The globular protein are spherical in shape. They are made up one or more polypeptide chains.
Classification of proteins On the basis of their solubility and shape On the basis of increasing complexity of structure.
On the basis solubility and shape It is 2 group globular proteins fibrous proteins GLOBULAR PROTEINS; It is spherical shape, soluble in water examble,enzymes,antibodies. FIBROUS PROTEINS; It is insoluble in water the are fibre.the are linear molecules.
On the basis increasing complexity of structure It is 3 groups; simple proteins conjugated proteins derived proteins Simple proteins; it is amino acids. The are 7sub types Albumins; it is insoluble in water. The are coagulated by heat.E.Xserum albumin of blood..
Conti. Globulins; it is insoluble in water ,the are coagulated by heat.ex.serum globulin . Glutelines; it is insoluble in water, the are coagulated by heat.ex glutelin in wheat. Prolamines; it is soluble in 70to80 ethyl alcohol. Ex.zein.
Conti Histones; soluble in water by insoluble in ammonia.ex.salmon sperm Albuminoids; it is insoluble in water.ex keratin in hair Protamines; it is soluble in water.ex.sturine
Conti It is non-proteins substances. it is5 sub types Glycoprotein; it carbohydrates as prosthetic group.ex.egg albumin. Phosphoproteins; it is phosphoric acids.ex.vitellin in egg yolk. Lipoproteins; it is phospholipides.ex.lipoprotein in blood serum.
Conti Nucleoproteins; it is nucleic acid.ex. Nucleohistone etc. Chromoproteins; it is coloured proteins.ex.haemoglobin. Derived proteins; it intermediate produce natural protein. It is 2types Primary derived proteins; it is derivatives of protein the size. It is 3types
Conti. Proteans; it is denatured proteins. They are insoluble in water.ex.fibrin derived fibrinogen. Metaproteins; it s action of acid or alkali on protein. Coagulated protein; it is insoluble produced of heat or alcohol. Derived secondary protein; it is original protein. They are3 sub types
Conti Proteoses; they are soluble in water. It is not coagulated by heat. Peptones; it soluble water they are not coagulated by heat. Polypeptides; it containing many amino acid units.
Biological roles They are intermediates in the formation of protein. They appear as constituents group called alkaloids. Antibacterial present fungi ,bacteria. Penicillin G is common antibiotics. Certain peptide growth factors. Folic acid, soluble vitamin peptide growth factor for microorganisms. Higher animals synthesize peptide as hormones.
Function of proteins All the enzymes are nothing but proteins. All the are catalysed by enzymes. Protein transport ions and small molecules. Certain protein function as storage Ex. Seed store nutrient protein. Certain protein function as nutrients.ex.egg contains ovalbumin Many hormones are protein .ex.insulin,growth hormone, parathyroid hormones
conclusion Protein is a body builder. It is importance of body haemoglobin,myoglobi n,myosin,actin,albumin ,globumin,are important proteins.