Superposition Theorem in Electrical Engineering
Explore the Superposition Theorem in electrical engineering, which states that in a network with linear resistances and multiple sources of e.m.f., the current in any branch is the algebraic sum of currents resulting from analyzing each source separately. Dive into examples and applications in Mechatronics and Industrial Robotics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SUPERPOSITION THEOREM COURSE: ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING COURSE CODE: ELE 115 LECTURE NO: #1 PROGRAM: MECHATRONICS AND INDUSTRIAL ROBOTICS SUPERVISOR: PROF.DR. ABOU-HASHEMA MUSTAFA EL-SAYED
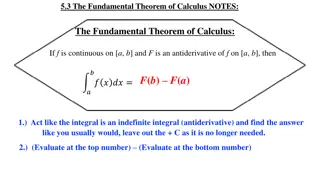
THE SUPERPOSITION THEOREM STATES: In any network made up of linear resistances and containing more than one source of e.m.f., the resultant current flowing in any branch is the algebraic sum of the currents that would flow in that branch if each source was considered separately, all other sources being replaced at that time by their respective internal resistances.