Switching from TDF to TAF in GS-US-292-0109 Study
Explore the GS-US-292-0109 Study which involves switching from TDF to TAF, focusing on virologic outcomes, patient characteristics, and treatment efficacy in HIV-positive individuals over 96 weeks. The study investigates the maintenance of HIV RNA levels, bone mineral density changes, renal function, and adverse events associated with the regimen switch.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Switch from TDF to TAF GS-US-292-0109 Study
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Design Randomisation 2 : 1 Open-label W48 W96 N = 959 Switch to E/C/F/TAF HIV+ 18 years On E/C/F/TDF or EFV/FTC/TDF or boosted ATV + FTC/TDF > 96 weeks HIV RNA < 50 c/mL eGFR (Cockroft-Gault) > 50 mL/min Continue TDF-based regimen N = 477 *Randomisation was stratified by previous treatment regimen Endpoints Primary: proportion of patients maintaining HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48 (ITT, snapshot) ; non-inferiority if lower margin of a two-sided 95% CI for the difference = -12%, 99% power Secondary: percentage change in hip and spine bone mineral density, change in serum creatinine, and change in EFV-related symptom score at W48 GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Baseline characteristics and patient disposition E/C/F/TAF N = 959 41 11% 68% / 18% / 6% 98% 675 TDF-based regimens N = 477 40 10% 66% / 21% / 7% 98% 662 Median age, years Female Race: white / black / asian HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL CD4 cell count (/mm3), median eGFR, mL/min, median Cockroft-Gault CKD-EPI Dipstick proteinuria: grade 1 / grade 2 Discontinuation by W48, N (%) For adverse event For lack of efficacy Investigator discretion Consent withdrawal Loss to follow-up Non-compliance Death 105.7 92.8 9% / < 1% 32 (3.3%) 9 1 2 8 6 2 4 107.7 93.9 9% / < 1% 40 (8.4%) 12 0 3 16 7 2 0 GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Virologic outcome at W48 and W96 (ITT, snapshot) TDF-based regimens (N = 477) E/C/F/TAF (N = 959) HIV RNA < 50 c/mL 97.2 93.1 Virologic failure No virologic data % 93 89 100 80 60 40 9 20 5.7 5 2 2 1.8 1* 1.3 0 Week 48 Week 96 (95% CI) = 3.7% (0.4 to 7.0) Week 48 Week 96 Week 48 Week 96 Difference (95% CI) = 4.1% (1.6 to 6.7) Superiority of E/C/F/TAF N=10 N=6 * One patient in the TAF group with virologic failure (W8) had genotypic resistance : M184I/M. The patient resuppressed 4 weeks later without a change of regimen GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52 ; DeJesus E. ASM Microbe 2016, Abs. LB-087
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL at W48 by prior treatment regimen, % E/C/F/TAF TDF-based regimens Primary Endpoint p < 0.001 p = 0.02 p = 0.02 p = NS 98 97 97 96 97 100 93 92 90 80 60 40 20 959 477 251 125 402 Prior boosted ATV + FTC/TDF 199 306 153 0 All prior regimens Prior Prior EFV/FTC/TDF E/C/F/TDF 1.6 to 6.7 95% CI = 0.5 to 12.3 0.9 to 9.2 -1.9 to 3.9 GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Differences in patients with HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL at W96 by subgroup, % (95% CI) TDF-based regimens E/C/F/TAF Overall < 50 > 50 Age, years Male Female Sex Black Nonblack Race < 95% > 95% Adherence -12 -6 0 -6 12 GS-US-292-0109 DeJesus E. ASM Microbe 2016, Abs. LB-087
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Changes in bone mineral density from baseline to W48 TDF-based regimens Difference in least square means (95% CI) E/C/F/TAF Hip BMD change (N) 869 428 0.13 (0.10 0.15) ; p < 0.0001 1.81 (1.49 2.13) ; p < 0.0001 T-score mean change from baseline 0.11 - 0.02 Percent change from baseline 1.47% - 0.34% 0 to 3% increase in BMD > 3% increase 56% 21% 38% 8% p < 0.0001 Spine BMD change (N) 881 436 0.19 (0.16 0.23) ; p < 0.0001 2.00 (1.55 2.45) ; p < 0.0001 T-score mean change from baseline 0.17 - 0.02 Percent change from baseline 1.56% - 0.44% 0 to 3% increase in BMD > 3% increase 41% 33% 34% 13% p < 0.0001 GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Changes in bone mineral density from baseline to W48 in patients previously on ATV + r + FTC/TDF E/C/F/TAF ATV + r + FTC/TDF Hip BMD mean change (N) 41 13 During 144 weeks of prior ATV + r + FTC/TDF - 4.58% Percent change from baseline to W48 + 1.35% - 0.77% Spine BMD mean change (N) 42 16 During 144 weeks of prior ATV + r + FTC/TDF - 3.1% Percent change from baseline to W48 + 2.83% - 0.74% GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
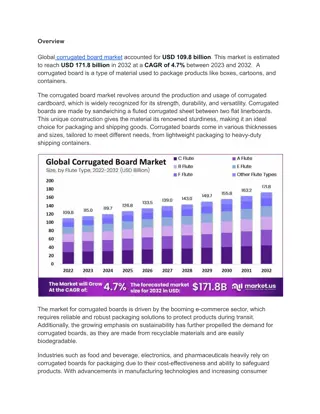
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Median % change in BMD (Q1, Q3) on DXA E/C/F/TAF TDF-based regimens 4.5 Spine BMD All Patients (N=1369) 3.5 2.5 2.0 1.5 p < 0,001 0.5 -0.3 -0.5 -1.5 -2.5 Baseline Week 24 Week 48 Week 96 4.5 Hip BMD All Patients (N=1354) 3.5 2.5 2.1 1.5 p < 0,001 0.5 -0.5 -0.6 -1.5 -2.5 Baseline Week 24 Week 48 Week 96 Regardless of prior treatment regimen, differences between arms were statistically significant for spine and hip BMD GS-US-292-0109 DeJesus E. ASM Microbes 2016, Abs. LB-087
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Change in Osteopenia/Osteoporosis Diagnosis (defined by T-Score) Normal Osteopenia Osteoporosis Spine 4.8 Hip % % 1.3 5.8 7.6 0.7 2.1 7.2 0.7 100 100 36 32 35 37 31 26 32 32 80 80 60 60 59 64 57 56 69 73 67 66 40 40 20 20 0 0 Baseline Week 48 Baseline TDF-Based Regimen N = 457 Week 48 Baseline Week 48 Baseline TDF-Based Regimen N = 452 Week 48 E/C/F/TAF N = 912 E/C/F/TAF N = 902 Differences between E/C/F/TAF and TDF-based regimens were statistically significant (p < 0.001) GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. IAS 2015, Abs. TUAB0102; Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Serum creatinine and eGFR changes from baseline to W48 EFV/FTC/TDF (unboosted regimen) - + 1.77 - Other TDF-based regimens E/C/F/TAF - 0.4 + 9.2 + 1.2 + 2.9 - - 3.7 Mean serum creatinine change, mol/L Median eGFR (Cockroft-Gault), mL/min Median changes in markers of renal function from baseline to W48 TDF-Based regimens + 0.7 + 0.3 - 0.1 E/C/F/TAF p Fractional excretion of phosphate Fractional excretion of uric acid TmP/GFR *, mg/dL + 0.2 - 0.8 - 0.1 0.054 < 0.001 0.63 * TmP/GFR: ratio of tubular maximum reabsorption of phosphate (TmP) to GFR GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Renal Safety Results (Median % change in proteinuria at W48) E/C/F/TAF TDF-based regimens Tubular Proteinuria 30 UPCR UACR RBP:Cr -2-m:Cr 20 18.1 18.7 10 8.5 9.6 0 -10 -17.9 -20.9 -20 -33.4 -30 -40 -52.3 -50 Each difference between treatment arms was statistically significant (p < 0.001) -60 UPCR: urine protein:creatinine ratio ; UACR: urine albumin:creatinine ratio ; RBP, retinol-binding protein ; -2-m: beta-2 microglobulin GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Adverse events, N (%) (W48) E/C/F/TAF N = 959 21% 9% 65 (7%) 0 9 (0.94%) * 2 0 TDF-based regimens N = 477 16% 11% 35 (7%) 2 (< 1%) 12 (2.52%) ** 5 (1 Fanconi) 3 (all on boosted ATV) Study-drug related adverse event Grade 3 or 4 adverse event Serious adverse event Study drug-related serious adverse event Premature study drug discontinuation for kidney-related adverse event for jaundice * Panic attack; apathy, amnesia, speech disorder; Reiter s syndrome; nausea, vomiting, and headache; suicide attempt; leg swelling and impaired concentration; depression; acute renal failure (after cancer chemotherapy: sepsis and multisystem organ failure); tubulo-interstitial nephritis (recurrent hematuria with subsequent diagnosis of Hodgkin lymphoma) ** Abnormal dreams; depression, insomnia, and irritability; depression, insomnia, and nightmares; elevated bilirubin; jaundice (N = 2); memory impairment; chronic kidney disease; elevated serum creatinine (N = 2); Fanconi s syndrome and mild jaundice; renal colic No discontinuation for adverse event in both groups between W48 and W96 GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Most-common drug-related adverse event, % (W48) E/C/F/TAF N = 959 TDF-based regimens N = 477 Upper respiratory tract infection 16 11 Diarrhea 10 9 Nasopharyngitis 9 8 Headache 7 4 Cough 7 5 Syphilis 5 6 Insomnia 5 6 Arthralgia 6 5 Bronchitis 6 5 Depression 4 6 Osteopenia 6 5 Back pain 5 5 Nausea 5 3 Sinusitis 5 5 GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Grade 2-4 laboratory abnormalities (W48) E/C/F/TAF N = 959 TDF-based regimens N = 477 Any abnormality 25% 31% Creatine kinase 10% 10% AST 5% 7% ALT 5% 5% Neutropenia 4% 3% Hypophosphatemia 2% 3% Hyperuricemia 2% 1% Alkaline phosphatase < 1% < 1% Leukopenia < 1% < 1% Platelets < 1% < 1% Total bilirubin < 1% 24% Hemoglobin 0 < 1% Creatinine 0 < 1% GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Fasting Lipids (mg/dL, median), baseline and W48 250 5 E/C/F/TAF Baseline Week 48 TDF-Based Regimens Baseline Week 48 202 200 4 3.8 3.6 183 181 181 3.6 3.6 150 3 131 125 116 114 120 100 2 116 114 112 52 50 50 1 49 52 0 0 Total Cholesterol p < 0.001 p < 0.001 p = 0.003 p < 0.001 p = 0.004 LDL HDL Triglycerides TC:HDL Ratio Participants initiating lipid-modifying medications: E/C/F/TAF: 8% ; TDF-based regimens: 6% GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52
GS-US-292-0109 Study: Switch TDF to TAF Conclusion Switching virologically suppressed patients to TAF regimen (EVG 150 mg, cobicistat 150 mg, emtricitabine 200 mg, and TAF 10 mg) was non inferior to the to 3 TDF-containing regimens at week 48 and week 96 It was also superior to continuing with the TDF-containing regimens. Switching to the TAF group showed several important safety advantages of TAF over any of the TDF-containing regimens : Improvements in hip and spine bone mineral density Improvements in renal function Decreases in serum creatinine in patients switched from a boosted regimen Decreases in dipstick proteinuria, in quantitative tests of total urine protein, and total urine albumin, in specific proximal tubular proteins Improvements in proximal renal tubular function (fractional excretion of uric acid, fractional excretion of phosphate, and renal tubular maximum reabsorption rate of phosphate to the glomerular filtration rate Slightly higher lipid concentrations with TAF than with TDF-based regimens GS-US-292-0109 Mills A. Lancet Infec Dis 2016;16:43-52