SWOT Analysis in Strategic Planning
SWOT Analysis is a valuable planning technique used to identify internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats in an institution. Learn about its components, how to conduct it, and its significance in strategic decision making.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SWOT Analysis | WP1 Dr. Charalambos Vrasidas pambos@cardet.org Stockholm 8 - 9 May 2017 1
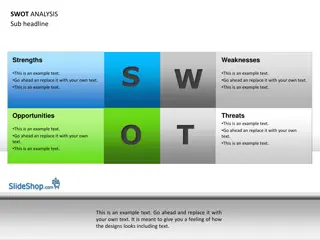
What is SWOT Analysis? SWOT stands for: Strengths (S) Weaknesses (W) Opportunities (O) Threats (T) SWOT is a planning technique used to identify and analyze associated with a strategic institutional situation. issues SWOT values are categorized into internal and external factors or known as positive and negative. SWOT involves an in-depth examination of the four categories faced by an institution completed by a group or team of people with broad input and discussion. Sources: (Pickton & Wright, 1998, Zhu & Justice Mugenyi, 2015) 2
What is SWOT Analysis? 2/2 Table 1. SWOT Analysis Grid of values POSITIVE (+) NEGATIVE (-) INTERNAL Strengths Weaknesses EXTERNAL Opportunities Threats Internal factors An institution s internal environment (strengths and weaknesses) External factors Come out of the university s borders to control the internal process of an institution (opportunities and threats) 3
Definition of SWOT Components 1/2 Strengths : Tangible assets that capture the positive aspects internal to each institution. i.e. Quality programs, positive reputation., dedicated and highly-skilled faculty and staff, technological infrastructure Weaknesses : Factors that are within the institution s control and capture the negative aspects that detract from the value it offers. i.e. aging facilities, lack of financial resources, slow adaptation to market demands, poor Internet connectivity and speed, low levels of industry connectivity, career-specific advising 4
Definition of SWOT Components 2/2 Opportunities : External attractive factors that represent the reason for each institution to exist and prosper. i.e. Interactive learning experiences, new student halls, privileged location, growth potential, scientific and technological advances Threats : Factors beyond humans control that could place the institution s strategy, or the sustainability of the institution itself, at risk. i.e. Environmental effects ,IT developments, economic downturns, lack of a strategy Sources: (Kenan, Pislaru, & Elzawi, 2014; Khaing, Win & Aung, 2016; Martinho et al., 2016) 5
How to conduct a SWOT Analysis? 1/2 Establish a planning and implementation team Identify the mission, vision and strategic objectives Examine the ICT Infrastructure of the institution Prepare and present a SWOT report Refine, finalise and share with consortium Conduct a SWOT analysis Figure 1. The six steps process for conducting a SWOT analysis for MIELES 6
Checklist Guide for SWOT Analysis 1/2 The Checklist Guide : Checklist Guide articulates a set of steps for the development of the strategy ...describes the interval sub steps of the six steps process of SWOT analysis as presented in Figure 1) provides guidance for the practical direction of the analysis results 7
Checklist Guide for SWOT Analysis 2/2 Establish a planning and implementation team and assign roles and responsibilities Identify the present mission, vision and strategic objectives of the institution Examine the current state of the institutional infrastructure Analyse the current state of e-learning at the institution Review all four categories in detail to gain a clear understanding of SWOT Conduct SWOT analysis by capturing SWOT factors Complete the SWOT worksheet Prioritize 2 - 4 most important items per SWOT category Report key points from SWOT analysis Develop a visual element report Prepare a SWOT report Present the report internally to get feedback Refine and finalize report Share with consortium 8
E-Learning Strategy| (WP2) Prepared by CARDET Dr. Charalambos Vrasidas pambos@cardet.org Stockholm 8 - 9 May 2017 9
Higher Education at a Glance The overall higher education environment is changing... 21 million enrolments grow between 2011 and 2020 250+ million enrolments by 2025 China and India fastest growth in tertiary enrolments 60% of young people have a higher education qualification As overall distance learning has grown, on-campus enrolments have dropped 10
Addressing HEI Challenges Emerging technologies have the potential : to address and alleviate several of the challenges facing today s higher education E-learning : Refers to technology enhanced learning, blended learning, open and distance learning, Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) Powerful tool that can support and enhance the learning experience of higher education students Enables HEI to develop their mission and vision and fulfil their strategic objectives (Divjak & Redep, 2015; Veletsianos & Vrasidas, 2015; Urh, Vukovic, & Jereb, 2015; Brali , 2016) 11
Addressing HEI Challenges E-learning strategies need to be integrated within a strategically developed framework; clearly linked to the mission and vision of an institution. Source: Moser, 2007 Institutions need to formulate clear vision, mission, goals and actions in order to set a positive environment that will foster e- learning development. Source: Arabasz, Pirani, and Fawcett, 2003 12
Developing a Strategy for e-learning in Higher Education 1 Analyse Needs 2 4 Develop Vision Evaluation Monitoring Action Plan and Mission Develop E- Learning Strategy Prepare Define SMART Objectives 3 Implementation 13
Definition of Mission and Vision The mission statement is about the here and now, whereas, the vision statement describes the future . Mission statement reflects the realities of an institution s environment, while vision statements drive these realities. Mission and vision statements establish an institution s identity and place in the higher education sector. Sources: (Lewis, 2005, p. 5; Abelman, 2014; Hartley, 2014) 14
Developing Mission and Vision of HEI See Table 1 and Table 2 which comprise a set of tips and questions to consider for developing a vision and mission statement respectively. 15
Table 1 16
Table 2 17
Defining SMART objectives and Action Plan SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Time-bound. SMART method is defined as the process for developing effective, measurable goals and objectives. Objectives are specific statements that indicate what is expected to be completed as for the vision and mission to be achieved. See Table 3 for issues and questions to consider while determining SMART Objectives Source: Hofman and Hofman, 2011 18
Table 3 19
To D List Complete the below templates included in the Practical Guide - Toolkit : for SWOT Analysis for e-learning strategy Checklist Guide SMART Objectives Objectives and Actions Mission and Vision ICT Infrastructure Action Plan Status of e-learning Checklist for e-learning strategic plan Planning and Implementation Team SWOT Analysis Worksheet 20
References 1/2 Abelman, R. (2014). Reviewing and Revising the Institutional Vision of U.S. Higher Education. Review of Communication Research, 2(1), 30-67. Bralic, A. (2016, January). ICT and e-learning in higher education in Croatia: strategies and current state. In Central European Conference on Information and Intelligent Systems (p. 91). Faculty of Organization and Informatics Varazdin. Divjak, B., & Redep, N. B. (2015). Strategic Decision Making Cycle in Higher Education: Case Study of E- learning. International Association for Development of the Information Society. Hartley, M. (2014). Call to purpose: Mission-centered change at three liberal arts colleges. London: Routledge. Hofman, W. A., & Hofman, R. H. (2011). Smart management in effective schools: Effective management configurations in general and vocational education in the Netherlands. Educational Administration Quarterly, 47(4), 620-645. Khaing, S. S., Win, A., & Aung, T. N. (2016). SWOT Analysis of E-Learning Course Operation in Higher Education (Case Study: University of Technology, Yatanarpon Cyber City). Genetic and Evolutionary Computing, 413. 21
References 2/2 Kenan, T., Pislaru, C., & Elzawi, A. (2014). Trends and policy issues for the e-learning implementation in Libyan universities. International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, 5(1), 105. Lewis, C. (2005, November 24). Mission and vision statements. The Times (London), p. 5. Martinho, A. P., Vaz-Fernandes, P., de Oliveira, C. P., Bacelar-Nicolau, P., Azeiteiro, U. M., & Caeiro, S. (2016). Strengths and Weaknesses of an E-learning Program in Environmental Sciences at Universidade Aberta, Portugal. In Teaching Education for Sustainable Development at University Level (pp. 49-66). Springer International Publishing. Urh, M., Vukovic, G., & Jereb, E. (2015). The model for introduction of gamification into e-learning in higher education. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 197, 388-397. Veletsianos, G. & Vrasidas, C. (2015). Contributions to the mosaic describing learners experiences with open online learning. Educational Media International, 52(2), 69-51. 22
Thank you for your attention! Dr. Charalambos Vrasidas pambos@cardet.org Stockholm 8 - 9 May 2017 23