Systems Engineering in Healthcare: Enhancing Efficiency and Quality
Industrial and Systems Engineers play a crucial role in healthcare by designing, implementing, and improving integrated systems to enhance efficiency, safety, and value of patient care delivery. Components include methods like Six Sigma, Lean, and clinical informatics, aiming to optimize operations and clinical decision-making.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Update on the UT System Initiative - Systems Engineering in Healthcare Victoria Jordan, PhD Director, Quality Measurement and Engineering MDACC UT Health Services Fellow for Systems Engineering October 27, 2011
Industrial and Systems Engineering Industrial and Systems Engineers deal with systems. They design, implement, or improve integrated systems comprised of people, material, information, and/or energy. Industrial and Systems Engineering focuses on developing a better way of doing just about anything. Industrial and Systems Engineering makes things better, faster, safer, cheaper
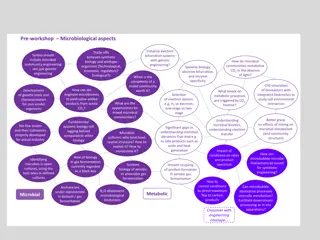
Components of Systems Engineering Frontline Improvement Methods Six Sigma Lean Standardization Human Factors Error Proofing Safety Ergonomics Quality Engineering Methods Statistical Quality Control Reliability Engineering Economics Logistics Facility Design Layout Supply Chain / Inventory Management Data Mining and Analytics Clinical Informatics Clinical Decision Making Reporting Process Optimization Methods Operations Research Scheduling Simulation Staffing Models
Systems Engineering in Healthcare Clinical Operations (Efficiency, Safety, Value of Patient Care Delivery) Business Operations (Efficiency, Value of business systems such as administrative requests, research approvals systems, inventory management) Therapeutic Optimization
Systems Engineering in Healthcare Make health care safe, timely, effective, efficient, equitable, and patient centered Design / layout new facilities Reduce patient wait times Increase efficiency so we can deliver the same quality of care without increasing staff Eliminate non-value-added steps to improve efficiency, reduce cost Simulation to try new processes Make care safer for patients Identify when we need to add resources (staff or equipment or rooms)
Example: Virginia Mason In two years (2002-2004) Va Mason showed the following improvements: Inventory down 53% ($1.35 million) Productivity up 36% (158 FTE s deployed to other, value-added, jobs) Floor space required down 41% (22,200 sf) Lead time down 65% (23,082 hours) People Distance traveled down 44% Product Distance traveled down 72% Set up time down 82% 6
UT Example Nurse Scheduling Problem in OR Develop two integer programming nurse scheduling models Nurse Assignment Model (NAM) Nurse Lunch Model (NLM) Consider nurse scheduling attributes in an operating suite Case specialties Procedure complexities Nurse skill levels Consider different aspects of goals Minimizing nurse over times and idle times Maximizing surgery case demand satisfactions Provide efficient schedule for each nurse
Link Between Systems Engineering and Clinical Safety and Effectiveness Course Optimization Heuristics Mathematical Programming Queuing Systems Thinking Forecasting Constraint Base Scheduling Data Mining Operations Research Human Factors Analysis Scheduling Decision Analysis System Dynamics Facility Design Layout Network Analysis Discrete Event Simulation Complexity Inventory Modeling Human Factors Analysis Classification System Statistical Analysis Ethnography Decision Trees Evidenced Based Medicine Six Sigma Fault Tree Analysis Failure Mode Effect Analysis Lean Quality Function Deployment Statistical Process Control Patient Safety Current CS&E Content QI Leadership Root Cause Analysis Plan-Do-Study-Act Usability Process Mapping Basic Quality Tools Decision Making Clinical Variation Time/Motion Study Project Management Qualitative Quantitative Created by: Office of Performance Improvement, UT MDAnderson Cancer Center
What Others Are Doing Johns Hopkins ($30 million Systems Institute) Brigham and Women s ($30 million for Systems View of Primary Care) Mayo Clinic (Systems Engineering Group) Geisinger (Operations Research) VA Engineering Resources Centers Virginia Mason (Lean) Charleston Area Medical Center, WV (Six Sigma) Banner (Relationship with Academia) Academic Centers (CHOT - Center for Healthcare Operations Transformation, others) Institute for Industrial Engineers (IIE) Society for Healthcare Systems (SHS)
UT Systems Engineering Mission Apply industrial and systems engineering tools and methods to further advance clinical effectiveness and safety and improve operations across the health institutions of The University of Texas System. 10
UT System - Systems Engineering Steering Committee Steering Committee includes members from across the UT System: UT Southwestern, UTMB, UT MD Anderson, UT Tyler, UTHSC San Antonio, UTHSC Houston UT Austin McCombs School of Business, Cockrell School of Engineering; UTSA Ind Engr, UT-Arlington Ind Engr; UT-Dallas-Ind Engr; UT Medical School UT Physicians UT Health Services Vice Chancellor s Office 11
Our Expected Deliverables Develop a whitepaper to serve as a recommendation for Dr. Shine to the UT System and Board of Regents (presented Aug, 2011) Provide educational sessions for academic, business, and clinical leaders on the role of Systems Engineering in healthcare (increase awareness) and courses in frontline methodology Coordinate grants for transformational efforts using Systems Engineering Explore the possibility of a Systems Engineering internship program among the UT health institutions Initiate an annual conference to share success stories 12
Board of Regents August 2011 Approved $4 million to fund the initiative for three years Approx $1 million for infrastructure support Approx $3 million for grants for transformational change using Systems Engineering tools and techniques 13
Next Steps Communication across UT System - Present plan to Presidents, Deans, CMO s, and CQO s Develop plan for embedding frontline training and application of Lean tools - Target Feb start for Lean and Systems Engr Overview courses Launch RFP process for grants and initiate projects; Grant solicitation and approval Mar- May; approvals in June First (to be annual) conference in Galveston, April 13, 2012 Plan for internships and sabbaticals to begin Summer and Fall 2012
We need your help Support the effort learn more about it Spread the word at your institution Attend the April 13 conference and invite others Look for opportunities to apply for grants talk with UT Ind Engrs in your area Identify opportunities for system transformation at your institution 15