TECOS
TECOS trial aimed to assess the cardiovascular safety of sitagliptin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease. The baseline characteristics, including age, gender, diabetes duration, race, BMI, lipid levels, blood pressure, and kidney function, were examined in the placebo and sitagliptin groups. Additionally, the presence of cardiovascular disease at baseline and medication usage for glucose-lowering and cardiovascular conditions were outlined. The study design, patient criteria, and primary/secondary endpoints were detailed.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
TECOS EDUCATIONAL SLIDE MODULE Date of preparation: August 2018 Version 2.0 Date of preparation: February 2016 SC-CRP-02186
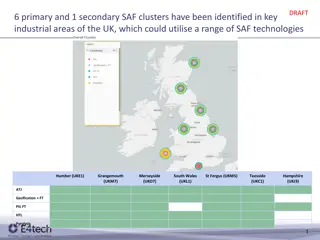
TECOS: trial design Aim: to assess the CV safety of sitagliptin versus placebo in patients with T2D and established CV disease Sitagliptin 100 mg daily* + standard of care Pre-treatment period Placebo + standard of care Median duration: 3 years 1390 primary events Screening Randomisation (1:1) N=14,671 double-blind End of treatment Main inclusion criteria Age 50 years with T2D HbA1c 6.5 8.0% receiving stable oral glucose-lowering therapy or insulin with or without metformin Established CV disease Main exclusion criteria DPP-4 inhibitor, GLP-1 receptor agonist or TZD (other than pioglitazone) within the last 3 months 2 episodes of severe hypoglycaemia in the preceding 12 months eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2 4P-MACE (3P-MACE or hospitalisation for unstable angina) Primary endpoint Non-fatal stroke Hospitalisation for unstable angina 3P-MACE (CV death, non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke) Key secondary endpoints *50 mg daily if baseline eGFR 30 and <50 ml/min/1.73 m2 TZD, thiazolidinedione Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232 2
TECOS: baseline characteristics Placebo (n=7339) Sitagliptin (n=7332) Age, years (mean SD) Male, n (%) Diabetes duration, years (median, IQR) Race, n (%) White Asian Black Other BMI, kg/m2 (mean SD) HDL-C, mg/dl (mean SD) LDL-C, mg/dl (mean SD) HbA1c, % (mean SD) Systolic blood pressure, mmHg (mean SD) Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg (mean SD) 65.5 8.0 5176 (70.5) 11.6 8.1 65.4 7.9 5198 (70.9) 11.6 8.1 5002 (68.2) 1611 (22.0) 241 (3.3) 485 (6.6) 30.2 5.7 43.4 13.0 90.7 51.2 7.2 0.5 135 17.1 77.2 10.6 4955 (67.6) 1654 (22.6) 206 (2.8) 517 (7.1) 30.2 5.6 43.5 12.0 91.2 63.8 7.2 0.5 135 16.9 77.1 10.3 3 Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232
TECOS: CV disease at baseline Placebo (n=7339) Sitagliptin (n=7332) Established atherosclerotic disease 5466 (74.5) 5397 (73.6) Coronary artery bypass graft 1819 (24.8) 1845 (25.2) Myocardial infarction 3122 (42.5) 3133 (42.7) Heart failure 1340 (18.3) 1303 (17.8) Current smoker 813 (11.1) 865 (11.8) Data are n (%) Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232 4
TECOS: kidney function at baseline Placebo (n=7339) Sitagliptin (n=7332) eGFR, ml/min/1.73 m2 (mean SD) 74.9 20.9 74.9 21.3 <50 ml/min/1.73 m2, n (%) 683 (9.3) 686 (9.4) 5 Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232
TECOS: glucose-lowering medication and CV medication at baseline Placebo (n=7339) Sitagliptin (n=7332) Glucose-lowering medication Insulin 1684 (22.9) 1724 (23.5) Metformin 6030 (82.2) 5936 (81.0) Sulphonylurea 3299 (45.0) 3346 (45.6) Thiazolidinedione 200 (2.7) 196 (2.7) CV medication Statin 5851 (79.8) 5868 (80.0) Aspirin 5754 (78.4) 5764 (78.6) ACE/ARB 5743 (78.3) 5812 (79.2) Beta-blocker 4675 (63.7) 4647 (63.4) Data are n (%) ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232 6
TECOS: 4P-MACE primary outcome Sitagliptin was non-inferior to placebo for the primary composite outcome of CV death, non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke or hospitalisation for unstable angina 15 Placebo Sitagliptin HR 0.98 (95% CI 0.89, 1.08) p<0.001 (non-inferiority) p=0.65 (superiority) Patients with event (%) 10 5 0 0 4 8 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 Months No. at risk Placebo Sitagliptin 7339 7332 7146 7131 6902 6937 6751 6777 6512 6579 6292 6386 4411 4525 3272 3346 2034 2058 1234 1248 7 Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232
TECOS: other CV and mortality outcomes There was no difference between sitagliptin and placebo across other CV and mortality outcomes Patients with event (%) Sitagliptin (n=7332) Placebo (n=7339) p-value HR (95% CI) CV death 380 (5.2) 366 (5.0) 1.03 (0.89, 1.19) 0.71 Fatal or non-fatal MI 300 (4.1) 316 (4.3) 0.95 (0.81, 1.11) 0.49 Fatal or non-fatal stroke 178 (2.4) 183 (2.5) 0.97 (0.79, 1.19) 0.76 Hospitalisation for unstable angina 116 (1.6) 129 (1.8) 0.90 (0.70, 1.16) 0.42 Hospitalisation for HF 228 (3.1) 229 (3.1) 1.00 (0.83, 1.20) 0.98 Hospitalisation for HF or CV death 538 (7.3) 525 (7.2) 1.02 (0.90, 1.15) 0.74 All-cause mortality 547 (7.5) 537 (7.3) 1.01 (0.90, 1.14) 0.88 0.5 1 2 Intention-to-treat analysis Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232 8 Favours sitagliptin Favours placebo
TECOS: changes in eGFR over 4 years The mean eGFR was marginally lower in the sitagliptin group at the first post-randomisation visit and remained consistently lower thereafter eGFR over 4 years (N=13,604) Placebo Sitagliptin 90 (ml/min/1.73 m2) Mean eGFR 80 70 60 50 0 4 8 12 24 36 48 Months 5482 Patients, n Placebo 6795 4169 3772 5197 3165 1335 1360 Sitagliptin 6809 4135 3809 5263 5553 3291 Mean eGFR reduction from baseline, ml/min/1.73 m2 (SD) Mean treatment difference (95% CI) p-value Placebo Sitagliptin -2.8 18.3 -4.0 18.4 -1.34 (-1.76, -0.91) <0.0001 9 Cornel JH et al. Diabetes Care 2016;39:2304
TECOS: safety overview Overall, reports of AEs were similar between sitagliptin and placebo Placebo (n=7339) Sitagliptin (n=7332) p-value Severe hypoglycaemia 125 (1.7) 144 (2.0) 0.31 Acute pancreatitis 11 (0.2) 20 (0.3) 0.12 Pancreatic cancer 10 (0.1) 9 (0.1) 0.85 Benign, malignant or unspecified neoplasm 371 (5.1) 341 (4.7) Injury, poisoning or procedural complication 133 (1.8) 146 (2.0) Gastrointestinal disorder 102 (1.4) 130 (1.8) Musculoskeletal or connective tissue disorder 93 (1.3) 118 (1.6) Respiratory, thoracic or mediastinal disorder 77 (1.0) 66 (0.9) Data are n (%) Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232 10
TECOS: summary Non-inferiority for 4P-MACE was achieved versus placebo (p<0.001)1 Superiority was not achieved (p=0.65)1 Primary outcomes There was no difference between sitagliptin and placebo across components of 4P-MACE, heart failure or mortality outcomes1 Other CV endpoints The mean eGFR was marginally lower in the sitagliptin group at the start of the trial and remained consistently lower thereafter2 Microvascular outcomes Overall, reports of AEs were similar between sitagliptin and placebo1 Safety 11 1. Green JB et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232; 2. Cornel JH et al. Diabetes Care 2016;39:2304