The Aorta and Its Function in the Human Body
Explore the anatomy of the aorta, the largest artery in the body, and learn about its divisions, branches, and the vital role it plays in supplying oxygenated blood throughout the systemic circulation. Discover the sonographic appearance of the aorta and enhance your knowledge of cardiovascular health.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Aorta The Aorta
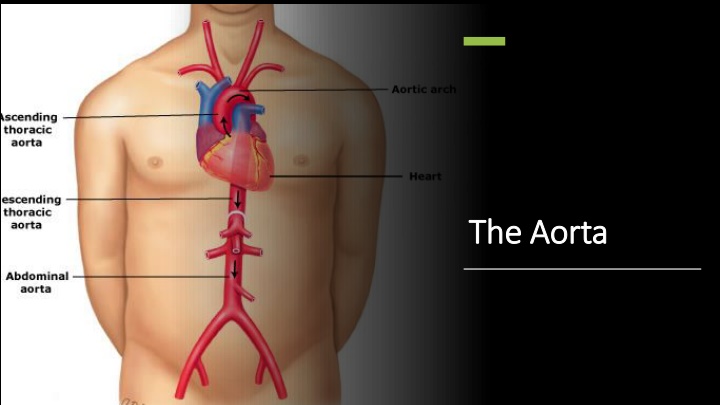
The Aorta is the largest artery of the body, which carries the oxygenated blood from the left ventricle and supplies it to all the parts of the body. The Aorta initially is one inch wide in diameter. The aorta is classified as a large elastic artery. The Aorta
Division of the Division of the Aorta by Aorta by anatomical anatomical compartment compartment The Aorta is divided into two compartments The Thoracic aorta or thoracic portion of the aorta runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The Abdominal aorta or abdominal portion of the aorta from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation
Division of the Division of the Aorta by Aorta by course and course and direction of direction of blood flow blood flow The ascending Aorta, which travels superiorly from the heart and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch, the aorta then travels inferiorly as the descending aorta and ends by dividing into two major blood vessels, which are the common iliac arteries and a smaller midline vessel, the median sacral artery
The first branch of the abdominal aorta is the Celiac trunk/ Axis Branches of Branches of abdominal abdominal Aorta Aorta It branches off into splenic artery and common hepatic artery The splenic artery is the largest branch of the celiac trunk, it feeds the spleen, the body and tail of the pancreas The common hepatic artery branches into the gastroduodenal artery and proper hepatic artery. The second main branch of the abdominal aorta is the Superior Mesenteric Artery (SMA). It is located posterior to the splenic vein and pancreas, the left renal vein is posterior to SMA and anterior to aorta. The third branch of the abdominal aorta is the right and left real arteries, the RRA is longer than the LRA The fourth branch of the abdominal aorta is the Inferior Mesenteric Artery
The aorta supplies all of the systemic circulation, except for the respiratory zone of the lung. Branches from the ascending aorta supply the heart. Branches from the aortic arch supply the head, neck and arms. The pelvis and legs get their blood from the common iliac arteries. Function of Function of the the Aorta Aorta
Sonographic appearance Sonographic appearance of of abdominal Aorta in transverse abdominal Aorta in transverse and sagittal and sagittal plane) plane) The diameter of the normal abdominal aorta is approximately 2.0 cm( range from 1.4 to 3.0cm)