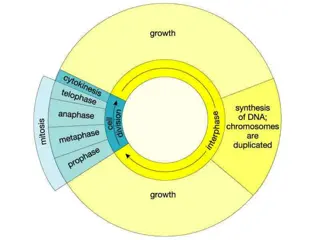
The Cell in Its Environment
This lab report was prepared by Ibrahim Mohammed and supervised by Dr. Trefa Salih Mohamad for the academic year 2023-2034. It likely contains research findings, experimental data, analysis, and conclusions related to a specific topic in the scientific field. The report signifies the collaborative effort between the student and the supervisor to produce valuable insights and contribute to the field's knowledge. It showcases the dedication and commitment of the individuals involved in conducting research and presenting their findings.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Cell in Its Environment pg. 28 How Do Materials Move Into and Out of Cells?
Lab Activity (with your pod): 1. Fill beaker way with cold water. Place the beaker on the desk and allow it to sit until there is no movement in the water. 1. 2. 2. Add one drop of food coloring to the water. 3. you notice on p. 28 in the margin. 3. Observe for a few minutes and write down write down changes 4 4. Bring materials back & wait to discuss with class
Words you may have used to describe: Starts as a glob of color in the middle Color spreads out slowly After a while, the color became more equal throughout
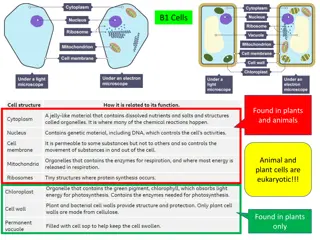
Oxygen Water Food Particles (salts & sugars) Carbon dioxide Waste materials **Highlight/underline those!
Structure: Double layer of lipid lined up side by side lipid molecules Selectively permeable cross the membrane while others cannot Selectively permeable: some substance can Substances passive transport or active transport Substances can move in & out of a cell by passive transport or active transport can move in & out of a cell by
Check out 3 of the 5 molecules that all living things have!!! Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
In what way is the cell membrane like a gatekeeper? In what way is the cell membrane like a gatekeeper? Answer: controlling or Answer: It is in charge of controlling who comes in or out of the cell! It is in charge of who comes in out of the cell!
Passive Transport of dissolved materials across a cell membrane without using the cell s energy Passive Transport: : the movement Fun example: riding a bike down a hill
Molecules are always moving! They bump into each other Over time, as molecules continue colliding and moving apart, they become less concentrated (crowded) Eventually, the molecules spread evenly throughout the space Ouch! That kinda hurt!
The process where area of lower The process where molecules move area of higher lower concentration. molecules move from an higher concentration to an area of concentration. from an concentration to an area of
Figure 2take a look at this Figure 2 take a look at this Diffusion A drop of food coloring in a plate of gelatin gradually spreads as molecules of the dye diffuse. How would the third plate look if diffusion continues?
Figure 2take a look at this Figure 2 take a look at this Diffusion A drop of food coloring in a plate of gelatin gradually spreads as molecules of the dye diffuse. How would the third plate look if diffusion continues? You should have a picture of dye spread in a wider circle
Link to eyeball science: http://kitchenpantryscientist.com/edible-eyeballs-a-diffusion- experiment-for-halloween/
T Think about this hink about this Here is a little water critter a Paramecium (found in pond water) nucleus Contractile vacuole
T Think about this hink about this All living things need oxygen a Parameciumdoesn t have lungs to breathe in oxygen so it gets it from the water.
T Think about this hink about this What is water made of? Hydrogen and Oxygen!!!
T Think about this hink about this So, how does the oxygen get INTO the Paramecium s body? DIFFUSION
T Think about this hink about this Diffusion is one form of passive transport because the concentration of oxygen is higher outside the paramecium than it is inside of it. So oxygen moves easily into the cell
Make a quick sketch of this in the margin on page 30. Make a quick sketch of this in the margin on page 30.
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable The diffusion of water molecules selectively permeable membrane Cells cannot function properly without water water Form of passive passive transport Read 2nd paragraph & Figure 3, Effects of Osmosis let s do that
The top picture shows a healthy plant cell water moving in and out through the cell membrane. The 2nd picture shows how the cell membrane has pulled away from the cell because too much water is lost.
Can this happen to us too? YEP think about being stranded on a desert island no fresh water.
Leech or Slug murder Salt on a leech or slug will kill it because their skin has no protective barrier to it. Water leaves their cells to balance out the salt.
Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion molecules going from crowded to less crowded places Energy not needed Does not involve water Osmosis Diffusion of water Water molecules going from crowded to less crowded places What does passive transport mean again? Movement of molecules across a membrane without needing energy
Movement of materials across a cell membrane using Movement of materials across a cell membrane using cellular energy cellular energy Molecules move from areas of higher Molecules move from areas of lower higher concentration lower concentration to concentration to concentration Proteins membrane Proteins move these molecules across the cell membrane (see figure 4) move these molecules across the cell (see figure 4) Substances that do this include and Substances that do this include calcium and sodium calcium, potassium, , potassium, sodium
Crossing the Cell Membrane - figure 4 (pg. 32) Crossing the Cell Membrane Molecules move into and out of a cell by means of passive or active transport. Complete the boxes, and describe where the concentration of each substance is high or low.
Crossing the Cell Membrane - figure 4 (pg. 32) Passive Active Crossing the Cell Membrane Molecules move into and out of a cell by means of passive or active transport. Complete the boxes, and describe where the concentration of each substance is high or low. Osmosis Diffusion
Use diffusion to tell what happens when you drop a sugar cube into water. Sugar dissolves; molecules collide moving from high concentration to low concentration
Draw an arrow to show the overall direction water will travel as a result of osmosis. (The yellow line is the cell membrane)
Active transport depends on to move molecules across the cell membrane. Proteins
How does active transport differ from passive transport? Active transport uses cell energy in moving materials into or out of cells; passive transport does not.
Now I know that the key function of the cell membrane is to Regulate the materials that move into and out of cells