The Formation and Characteristics of the Nazi Government in Germany
Explore the rise of the National Socialist regime in Germany under Hitler's leadership, including the consolidation of power, treatment of minority groups, opposition faced, and the structure of governance. Learn about key figures like Josef Goebbels and Heinrich Himmler who played significant roles in implementing the Nazi agenda, shaping propaganda, internal security, and the dreaded secret police. Uncover the myths and image construction surrounding Hitler, and understand the complexities of leadership within the Nazi hierarchy.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Issue 3: Nazis Control of Germany Formation and characteristics of the National Socialist Government; National Socialism in power: intimidation; treatment of Jews and other minority groups; opposition to National Socialism by socialists, communists, and the churches.
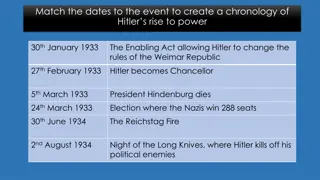
The Formation and Characteristics of the Nazi Government Lesson Starter: Give 4 ways in which the Nazis were able to consolidate their power in 1933-34.
We are learning to Understand how the Nazi regime was structured. I can Describe the structure of power in Nazi Germany.
Copy: Hitler Myth Hitler s image was carefully constructed he was always portrayed in a very positive way. He was considered to: Be committed to serving Germany with no selfish interests. Understand the German people. Be responsible for the improving economy in Germany. Represent justice. Defend Germany against its enemies. Be responsible for all major successes. Be rebuilding Germany s strength internationally.
Leadership Although Hitler was undoubtedly the leader in Germany, there were other groups/people who were responsible for making sure the country ran smoothly. These groups often competed with each other in order to gain favour with Hitler.
Task Over the next few slides you will be given information about some of the most influential members of the Nazi party. You should use the information to create a factfile like the one opposite about each of the leaders. Name: Role: Most known for:
Josef Goebbels When the Nazis came to power Goebbels was made the Minister of Enlightenment and Propaganda. He was in charge of propaganda and ensured the Nazis were always portrayed in a positive light. Responsible for the Nuremburg rallies and all radio/press coverage. If you tell a lie, tell a big one.
Heinrich Himmler Himmler was responsible for Internal Security. He was in charge of the SS and the Gestapo - the Nazi s secret police. He became one of the most feared men in Germany as he could monitor every German s moves. Eventually he was put in charge of organising concentration camps. The best political weapon is the weapon of terror. Cruelty commands respect. Men may hate us. But, we don t ask for their love; only for their fear.
Hermann Goering One of the highest ranking Nazi leaders, Goering was in charge of the Luftwaffe the German airforce. He was highly regarded by Hitler as he was a WWI veteran. Education is dangerous - every educated person is a future enemy.
Copy: Nazi Control Other lower ranking members of the Nazi party also had an important part to play. They ensured that the orders of the leaders were carried out effectively. They were responsible for checking that Nazi rules were being followed in local neighbourhoods. The Reichstag lost all of its authority as all laws were passed through Hitler. Gauleiter: Official who governed a district under Nazi rule.
Source Task Source A Hitler s courage in taking firm action has made him a hero in the eyes of many Germans. He has won approval and sympathy for the steps he took. People think his action is proof that he wants order and decency in Germany. Reports from different parts of the country are all agreed that people are expressing satisfaction that Hitler has acted against the serious threat posed by Rohm and the SA to Germany and her people. Source B On the morning of 30 June 1934, Rohm and other SA leaders were arrested and eventually shot. Hitler s personal popularity soared as a result of the Night of the Long Knives. Most Germans disliked the corruption of the SA and welcomed the strong action against it. President Hindenburg s telegram to Hitler read: By your determined action and brave leadership, you have saved the German nation from serious danger. Compare the views of Sources A and B about the attitude of Germans to the Night of the Long Knives. (Compare the sources overall and/or in detail.) 4 marks