The Impact of Brain Development and Emotion on Learning
Explore the intricate relationship between brain development, emotion, and learning in students. Discover how teachers can leverage storytelling, curiosity, and emotional engagement to foster skillful learners equipped for the modern world. Gain insights into the effects of stress on memory and the adolescent brain.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
If the brain is the organ for learning, then why arent teachers brain experts? Learning is constructed in the mind based on a student s experiences The brains of students today are completely different than the brains of our students even 10, 20 or 100 years ago
Emotion and Learning Appeal to a student s emotion through Storytelling- Story Chunking Piquing curiosity Questioning Novelty Prior knowledge Movement Too many public schools focus on the measurable to the exclusion of the possible. We are preparing for tests, but are we preparing for skillful learners in the world beyond school?
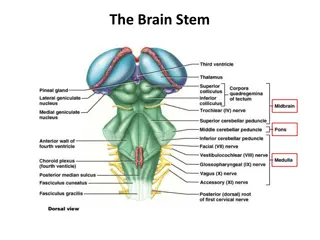
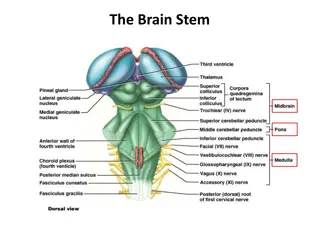
Brain Development and Adolescence What we have to remember when teaching subject matter and content standards Prefrontal lobe- looks like Swiss cheese- seat of logical reasoning, problem solving, decision making Amygdala- clusters of neurons that are intimately tied to our emotional responses and memory functions
Adolescent Development and Learning Hormones surging Peers Sexual exploration Identity and Role Confusion Development of abstract thinking and metacognition Reactionary or thalamic responses come from the amygdala which is usually stimulated and over functioning
Stress and its effects on Learning and Memory High stress levels- affect immune system, clarity of thought, and memory function Causes of Stress Over packed curriculum Fear of being wrong Test-taking Frustration with difficult material Boredom from lack of stimulation! Embarrassment ( to read aloud)
What is the worst thing a parent or teacher could do in the eyes of an adolescent? A. Pile on added chores or assignments B. Scream and yell engaging in power struggles over every issue that is irritating C. Embarrass the adolescent
Stress- The Diagnosis of the 21st century Anytime there is perceived fear, there is stress and a decrease in flow of information to the PFC. Boredom makes you do crazy things- it may create its own fun or novelty Most often, it is not the child s choice- misbehavior is when the lower brain is in control Flight-withdrawal, look like ADD or ADHD Fight- ODD Freeze-Social Anxiety and Seizures or OCD Dr. Judy Willis
Why do students drop out of school? 75%- material wasn t interesting 39% material wasn t relevant 37%no interactions with teachers Boredom is stressful! So what do we do? Create a community and classroom culture that feels safe and accepting. Teach students ways to control their own responses MODEL!!! Visualizations and activities that are physical and tactile- movement engages 100% of the brain which no cognitive skill or strategy can do this!
How May I Serve You? We ask the questions: what do you need? How can I help? What can I do? Brain processes questions long after they have been asked Self-reflection time Story-telling in content areas Choices
Strategies Allow students to design quizzes and test questions There is a 95% or higher retention rate over a 24 hour period when students are allowed to teach what they need to learn Hand Exercise- when we are holding onto power or control , there is no room for growth, novelty or leadership from students
Strategies continued Writing with non-dominant hand Why do you need to know this? What professions or jobs would ask for these skills? Self-reflection Feedback- informative, frequent and displayed with variety
Environment is Key Genius is much more than genes! When you enrich the environment and exercise the muscles of the brain and power of the mind, you are literally creating neurons, neural connections and stimulating IQ and brain development Frequent informal assessment strengthens learning Self-assessment
Strategies that enhance Learning Prediction Multi-sensory Memory- manipulation of information and focused attention Hooks at the beginning and end!
Memory Facts If you yelled for 8 years, 7 months and 6 days you would have produced enough sound energy to heat one cup of coffee. (Hardly seems worth it.) If you farted consistently for 6 years and 9 months, enough gas is produced to create the energy of an atomic bomb. (Now that s more like it!) The human heart creates enough pressure when it pumps out to the body to squirt blood 30 feet. (O.M.G.!) A pig s orgasm lasts 30 minutes. (In my next life, I want to be a pig.) A cockroach will live nine days without its head before it starves to death. (Creepy.) (I m still not over the pig.) Banging your head against a wall uses 150 calories an hour. (Do not try this at home. Maybe at work.) The male pray mantis cannot copulate while its head is attached to its body. The female initiates sex by ripping the male s head off. ( Honey, I m home. What the .?! )