The Nervous System: Functions, Divisions, and Injuries
The nervous system plays a crucial role in receiving and responding to information, maintaining homeostasis, and coordinating various bodily functions. Explore the functions, divisions, and regions of the brain, along with common nervous system injuries such as concussions and spinal cord injuries. Learn about how neurons transmit impulses, reflex actions, and the importance of sensory input. Enhance your understanding of this intricate system that controls our every move and response.
Uploaded on Apr 16, 2025 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
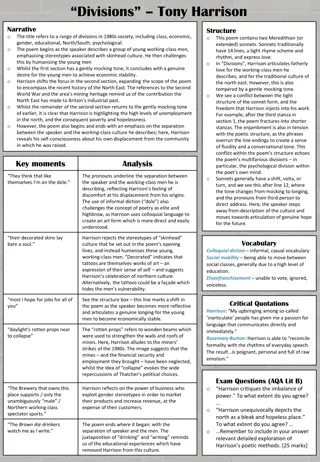
The Nervous System Chapter 6
Functions Receives information Responds to information Maintains homeostasis
Divisions of the Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System Network of nerves that branch out from central nervous system Somatic-voluntary actions Autonomic-involuntary actions
Regions of the Brain Cerebellum- balance and coordination Cerebrum-learning, memory Brain Stem- involuntary actions (breathing, heart beat)
Nervous System Injuries Concussions Spinal Cord Injuries Occur when spinal cord is bruised or cut Impulses can no longer travel along axons Can result in paralysis Bruise-like injury of brain Occurs when soft tissue collides against skull Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage
Receiving Information Your senses are used to receive information from the environment Include taste, touch, smell, sight, hearing
Responding to Information Stimulus- change in environment Response-reaction to change
Kinds of Neurons Sensory neuron Interneuron Motor neuron
How nerve impulses travel Travel up to 120 meters per second Axons release chemicals to help nerve impulse travel across synapse
Reflexes Automatic response that occurs rapidly and without conscious control Helps protect your body