The Role of N1-Methylpseudouridine in COVID-19 Vaccines
The use of N1-methylpseudouridine (m1) in COVID-19 mRNA vaccines enhances their effectiveness. This article explores the development and function of m1 in synthetic mRNAs, shedding light on its impact on vaccine efficacy and future innovations in chemical biology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
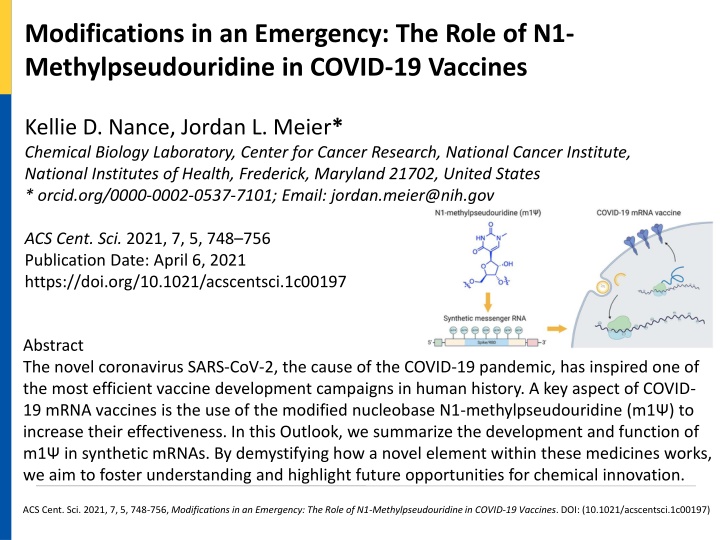
Modifications in an Emergency: The Role of N1- Methylpseudouridine in COVID-19 Vaccines Kellie D. Nance, Jordan L. Meier* Chemical Biology Laboratory, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Frederick, Maryland 21702, United States * orcid.org/0000-0002-0537-7101; Email: jordan.meier@nih.gov ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 5, 748 756 Publication Date: April 6, 2021 https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.1c00197 Abstract The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic, has inspired one of the most efficient vaccine development campaigns in human history. A key aspect of COVID- 19 mRNA vaccines is the use of the modified nucleobase N1-methylpseudouridine (m1 ) to increase their effectiveness. In this Outlook, we summarize the development and function of m1 in synthetic mRNAs. By demystifying how a novel element within these medicines works, we aim to foster understanding and highlight future opportunities for chemical innovation. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 5, 748-756, Modifications in an Emergency: The Role of N1-Methylpseudouridine in COVID-19 Vaccines. DOI: (10.1021/acscentsci.1c00197)
(a) mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine strategy. (b) Structural features of uridine and m1. TCR = T-cell receptor. MHC = major histocompatibility complex. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 5, 748-756, Modifications in an Emergency: The Role of N1-Methylpseudouridine in COVID-19 Vaccines. DOI: (10.1021/acscentsci.1c00197)
Top: Design elements found in synthetic mRNA therapeutics. Bottom: Sequence of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine tozinameran (BNT162b2) DOI: (10.1021/acscentsci.1c00197)
Production of m1 mRNAs by in vitro transcription. Left: Components of in vitrotranscription reaction. Right: Incorporation of m1-triphosphate into RNA is guided by m1s ability to form a canonical base p DOI: (10.1021/acscentsci.1c00197)
(a) Activation of innate immune response by mRNA secondary structures (b) Structure of the single-stranded RNA sensor TLR7 in complex with a polyuridine (poly(U)) ligand (PDB ID: 5GMF). Replacing uridine with m1 demonstrates the steric incompatibility DOI: (10.1021/acscentsci.1c00197)
m1 exerts context-dependent effects on translation. Left: m1-dependent enforcement of secondary structure in the 5-UTR of synthetic mRNAs can inhibit translation initiation. Right: m1 DOI: (10.1021/acscentsci.1c00197)