The Trisynaptic Neuronal Network of the Hippocampus
The hippocampus, a vital part of the limbic system, is responsible for memory and spatial navigation. Learn about its structure, including the dentate gyrus and subicular complex, and explore the trisynaptic circuit that defines its neuronal pathways. Delve into the intricacies of the hippocampal anatomy and understand the significance of the trisynaptic loop in cognitive functions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Trisynaptic Neuronal Network Of The Hippocampus. Created By: Alex Szendrei
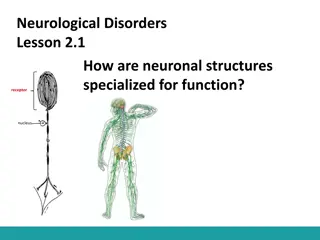
The Hippocampus Part of the limbic system Memory and spatial navigation Located in the medial temporal lobe, underneath the cortical surface Two halves: left and right sides of the brain Resembles a seahorse, "hippo- kampos"
Parts Of Hippocampus Dentate gyrus (DG) Hippocampus proper: CA1 3 (cornu ammonis) Subicular complex: Subiculum (sb) Presubiculum (prs) Parasubiculum (pas) Entorhinal cortex (EC): Medial (MEC) Lateral (LEC)
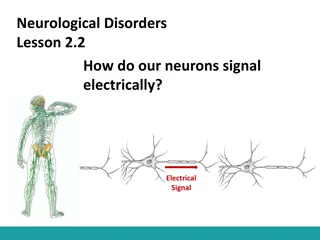
Trisynaptic Circuit In transverse plane, three interconnected afferent pathways Three major cell groups: granule cells, CA3 pyramidal neurons, and CA1 pyramidal cells. Trisynaptic pathway Entorhinal cortex -> the dentate gyrus Dentate gyrus -> CA3 via mossy cell fibers. Ca3 -> ca1 via schaffer collaterals Ca1 -> sbiculum, carried out through the fornix. Collectively the dentate gyrus, ca1 and ca3 of the hippocampus compose the trisynaptic loop.
Thank you for your attention. Sources: Http://www.News-medical.Net/health/hippocampus-what-is-the-hippocampus.Aspx Http://neuralnetoff.Umn.Edu/mediawiki/index.Php/hippocampal_anatomy Http://www.Nature.Com/nrn/journal/v9/n1/fig_tab/nrn2303_f1.Html Https://en.Wikipedia.Org/wiki/trisynaptic_circuit Http://www.Scholarpedia.Org/article/entorhinal_cortex Https://www.Ncbi.Nlm.Nih.Gov/pmc/articles/PMC2492885/ Http://neuroscience.Uth.Tmc.Edu/s4/chapter05.Html Https://www.Cs.Cmu.Edu/afs/cs/academic/class/15883-f13/slides/hc-anatomy.Pdf