The urinary system
The urinary system functions to filter blood, create urine, and eliminate waste products. It includes organs like the kidneys, bladder, and ureters. Learn about the roles of these organs in maintaining overall health.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The urinary system Preparation assistant teacher Fatima kareem
Lesson Lesson objectives objectives After After the the end end of of the the lecture, lecture, the the student student will will be be able able to to: :- - ** **It is known as The urinary system .
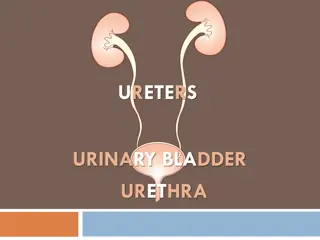
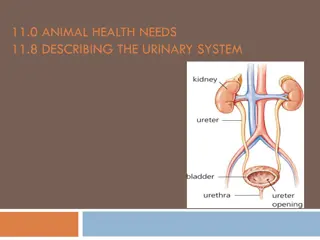
The urinary system The urinary system The urinary system's function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra. The body takes nutrients from food and converts them to energy. After the body has taken the food components that it needs, waste products are left behind in the intestine and in the blood.
Parts of Parts of The urinary system The urinary system 1-The kidney help the body to eliminate liquid waste called urea, and to keep chemicals, such as potassium and sodium, and water in balance. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and certain vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it is removed along with water and other wastes in the form of urine.
Two kidneys. This pair of purplish-brown organs is located below the ribs toward the middle of the back. Their function is to: Remove waste products and drugs from the body. Balance the body's fluids. Release hormones to regulate blood pressure. Control production of red blood cells.
2-Two ureters These narrow tubes carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls continually tighten and relax forcing urine downward, away from the kidneys. About every 10 to 15 seconds, small amounts of urine are emptied into the bladder from the ureters
3-Bladder This triangle-shaped, hollow organ is located in the lower abdomen. It is held in place by ligaments that are attached to other organs and the pelvic bones. The bladder's walls relax and expand to store urine, and contract and flatten to empty urine through the urethra. The typical healthy adult bladder can store up to two cups of urine for two to five hours.
4-Urethra This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
The urethra is a tube that drains urine from the bladder out of the body. In men, the urethra is about 8 inches (20 centimeters) long, ending at the tip of the penis. In women, the urethra is about 1 inches (4 centimeters) long, ending at the vulva (the area of the external female genital organs).
Male Reproductive Organs
In the anatomy typically called male, there are three parts to the urethra: The prostatic urethra: The part of the urethra that carries seminal fluid through the prostate gland to produce the semen that will be ejaculated. The membranous urethra: The short part of the urethra that transports fluids through the pelvic floor. The penile urethra (also called the spongy urethra or the cavernous urethra): The longest piece of the urethra. This section extends the entire length of the penis and ends at the urethral meatus or the opening outside the body.
Facts about urine Normal, healthy urine is a pale straw or transparent yellow color. Darker yellow or honey colored urine means you need more water. A darker, brownish color may indicate a liver problem or severe dehydration. Pinkish or red urine may mean blood in the urine.
Diseases Of The Urinary System? Examples of urinary disorders include cancers of the urinary tract, incontinence (inability to control urine flow), interstitial cystitis, kidney stones, kidney failure, and urinary.
Thank you for listening