Thermochemistry and Heat of Vaporization
Explore the concepts of endothermic and exothermic reactions, enthalpies of fusion and vaporization, and the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Learn about molar heat of vaporization and fusion to understand the energy changes in physical and chemical processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
General Chemistry General Chemistry CHEM 101 (3+1+0)
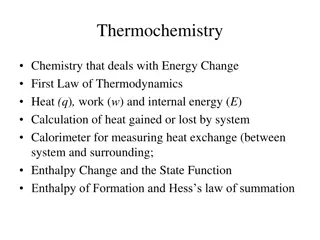
Chapter 6 - 6 Thermochemistry
Some types of Endothermic and exothermic physical changes and chemical reactions (Enthalpy of fusion, vaporization) 3
Molar heat of vaporization (Hvap) is the energy required to vaporize 1 mole of a liquid at its boiling point. Clausius-Clapeyron Equation Hvap RT P = (equilibrium) vapor pressure ln P = - + C T = temperature (K) R = gas constant (8.314 J/K mol) Vapor Pressure Versus Temperature 4
Molar heat of fusion (Hfus) is the energy required to melt 1 mole of a solid substance at its freezing point. 5