Thyroid Disease and Its Effects
The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, regulates important hormones affecting metabolism and calcium levels. Learn about thyroid function, hormone regulation, types of thyroid disease like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, their causes, symptoms, and effects on the body.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Thyroid Disease Thyroid Disease
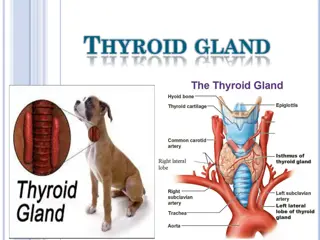
What is the thyroid and what does it do? The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck just below the Adams apple. The two most important thyroid hormones are thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) . Once released from the thyroid gland into the blood, a large amount of T4 is converted to T3 - the active hormone that affects the metabolism of cells throughout our body. Calcitonin is a hormone that contributes to the regulation of calcium and helps to lower calcium levels in the blood.
Thyroid hormone regulation Thyroid hormone regulation Hypothalamus - TRH Pituitary-TSH Thyroid - T4 and T3
thyroid disease is a medical condition impairing the function of the thyroid What types of thyroid disease can occur when the function of the thyroid is affected?? Hypothyroidism If the thyroid itself is under-active, or if the regulators of the thyroid gland are not functioning properly, hypothyroidism can result
causes 1-Hashimotos thyroiditis(autoimmune thyroiditis) 2- Postpartum thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland after pregnancy) 3- Acute thyroiditis 4-Silent thyroiditis 5- Thyroid hormone resistance 6- Medications that affect thyroid function such as amidarone (Cordarone)
signs and symptoms fatigue mental fogginess and forgetfulness feeling excessively cold constipation dry skin fluid retention non specific aches and stiffness in muscles and joints excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia) depression
hyperthyroidism If the thyroid is overactive, or if the regulators of the thyroid gland are pushing the thyroid to produce too much hormone, hyperthyroidism can result. causes Graves disease toxic multinodular goiter Toxic nodule ("hot" nodule) Excessive intake of iodine Medications (ingesting thyroid hormone)
signs and symptoms Excessive sweating Heat intolerance Increased bowel movements Tremor (usually a fine shake) Nervousness; agitation Rapid heart rate weight loss Fatigue Irregular and scant menstrual flow
Diagnosis Diagnosis Blood tests thyroid hormones T4 and T3 Autoantibodies(anti-TG, TSH receptor stimulating antibodies). There are two cancer markers for thyroid derived cancers. Thyroglobulin(TG) for well differentiated papillary or follicular adenocarcinoma, thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH ) Ultrasound Radioiodine scanning and uptake Biopsy
Treatment Treatment Medical treatment 1-hypothyroidism Levothyroxine is a stereoisomer of thyroxine which is degraded much slower and can be administered once daily the thioamide drugs propylthiouracil, carbimazole or methimazole or rarely with Lugol's solution patient with Graves' disease 2-Hyperthyroidism as well as thyroid tumors may be treated with radioactive iodine. Surgery
ROLE OF DENTIST ROLE OF DENTIST First, the dentist may be the first to suspect a serious thyroid disorder and aid in early diagnosis. Thus, as part of a health care team, the dentist plays an important role in detecting thyroid abnormalities second avoid possible dental complications resulting from treating patients with the thyroid disorders. Modifications of dental care must be considered when treating patients who have thyroid disease.
1- hypothyroidism may develop hypothyroidism ( myxedema) coma which is precipitated by : Surgical procedure, trauma., infection. So, to prevent those complications we have to do the following: 2- Identification of the patient by history and clinical examination. 3- If the patient is untreated or poorly controlled: a- Avoid the tranquilizers, barbiturates, and narcotic analgesics, because the patient is sensitive to the effect of those drugs. b- Control the pain non-narcotic analgesics. c- Avoid the precipitation of hypothyroidism, so we should avoid surgical procedure and treat the acute oral infection conservatively and antibiotic. The potential problem of those patients with severe
myxedema coma--- Hypothermia Bradycardia -Hypotension 1-Hydrocortisone I.V 100 -300 mg . 2-Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation is indicated in these cases.
Identification of patient by history and clinical examination. In order to avoid the complication. If the patient is uncontrolled, we have to refer him to physician and take the following points in consideration: a- Avoid surgical procedure. because the Thyrotoxic crisis is precipitated by the surgical procedure, trauma, stress, and infection. b- If the patient has un odontogenic infection, he should be treated conservatively and give the patient an effective antibiotic c- We should avoid local anesthesia with adrenalin. Patient with good medical control a- We can do any indicated dental treatment.
If the patient developed a thyrotoxic crisis which is characterized by: Extreme restlessness, nausea, vomiting, professed sweating, marked tachycardia, congestive heart failure developed then coma hypotension, and finally death may occur. The treatment of thyrotoxic crisis is by: a- Ice packs b- Hydrocortisone I.V 100 300 mg. c- I.V Glucose