THYROID GLAND
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in the body by producing hormones that regulate various functions. Learn about the location, hormones released, functions, and regulation of thyroid hormones. Explore the evolutionary significance and hormone cascade pathways involved in thyroid regulation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
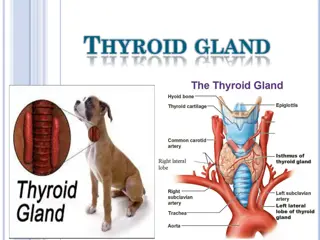
THYROID GLAND By Katie Hall and Grace Ellis A.P. Biology
Location in the Body http://www.organsofthebody.com/thyroid/
Hormones Released The thyroid converts iodine into two thyroid hormones: Thyroxine(T4) 6 times more than T3 minority of cell response amine (peptide) hormone Triiodothyronine (T3) Majority of cellular response converted from T4 in the cell by taking one iodine amine (peptide) hormone Calcitonin peptide hormone
Functions of the Hormones Calcitonin- lowers blood calcium level Thyroid hormone - acts on target cells throughout the body to control bioenergetics; help maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, and muscle tone; and regulate digestive and reproductive functions Evolution During evolution hormones begin to take on different functions between species. Such as thyroxine which usually regulates metabolism, stimulates the reabsorption of a tadpole s tail. http://slideplayer.com/slide/3447952/
Functions of the Hormones Peptide Hormones create a rapid, short lived response. Peptide hormones are made of amino acids. Steroid Hormones create a slow, long lived response. Steroid hormones are made of lipids. http://slideplayer.com/slide/5878079/
Thyroid Hormones are Regulated by... Hormone Cascade Pathways Sets of hormones target the thyroid gland Signals go through pathway to be redirected to affect thyroid Hormones that cause release of hormones from thyroid come from... 1) Hypothalamus 2) Anterior pituitary Hormone cascade pathways related to the thyroid gland often involve Negative Feedback Accumulation of end product of a process slows the beginning Counteract the initial change
Feedback Loops 1 Thyroid hormone levels drop below the normal range. Hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) into the blood. Portal vessels carry TRH to the anterior pituitary. TSH stimulates thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormone (T3and T4) into the circulatory system. 4 Thyroid hormone blocks TRH release. 2 5 TRH causes the anterior pituitary to secrete TSH (thyrotropin; thyroid- stimulating hormone) into the circulatory system. 3 Thyroid hormone levels increase in blood & body tissues (back to normal range). 5 http://slideplayer.com/slide/3447952/
Feedback Loops: Negative Feedback Negative-feedback loop prevents overproduction of thyroid hormone Normal range TRH release is blocked T3& T4 TSH TRH Hormone cascade pathway: T3& T4levels too low TRH released
Thyroid Disease http://slideplayer.com/slide/3447952/ Thyroid disease:any dysfunction of the thyroid gland goiter Hyperthyroidism: occurs when thyroid gland makes more thyroid hormones than the body needs Hypothyroidism: occurs when thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormones Thyroid hormone contains iodine; iodine allows more thyroid hormone to be made. Thyroid cancer: uncontrolled cell division on thyroid Physicians use a radioactive isotope of iodine to detect abnormal iodine uptake. Goiter: enlargement of the thyroid gland due to iodine deficiency This thyroid scan indicates thyroid disease. Thyroid nodules: lumps in the thyroid gland Thyroiditis: swelling of the thyroid
Thyroid Disease Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Excess of thyroid hormones Excess of thyroid hormones - Graves disease (autoimmune disorder) - Excess of iodine - Taking excess of synthetic thyroid hormone Thyroid hormone deficiency Thyroid hormone deficiency - Hashimoto's disease (autoimmune disorder) Causes Women & people over 60 Women & people over 60 Most Commonly Affects - - - - Weight gain Muscle pain Cold intolerance Slowed heartbeat - - - - Weight loss Fatigue or muscle weakness Heat intolerance Rapid heartbeat Symptoms *Metabolic dysfunction! Medicines, radioiodine therapy (used to destroy thyroid tissue not removed by surgery), or thyroid surgery Medicines, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid, radiation treatment of the thyroid Treatment
Citations Thyroid Diseases. MedlinePlus, National Institutes of Health, 31 Jan. 18AD, medlineplus.gov/thyroidcancer.html. The American Cancer Society medical and editorial content team. Radioactive Iodine (Radioiodine) Therapy for Thyroid Cancer. American Cancer Society, American Cancer Society, 15 Apr. 16AD, www.cancer.org/cancer/thyroid-cancer/treating/radioactive- iodine.html.